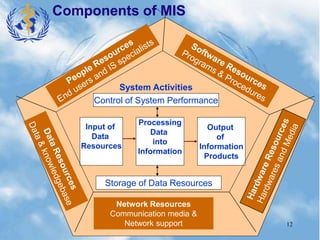
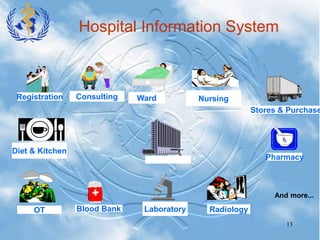
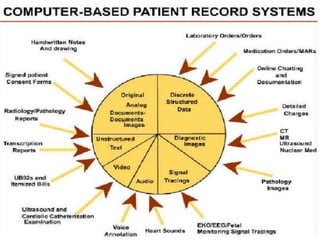
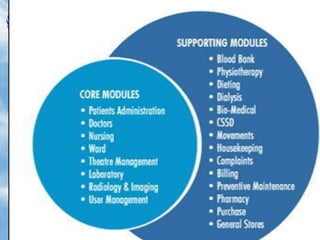
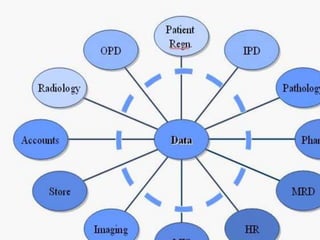
Nursing informatics integrates nursing, computer science, and information science to manage and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice. Nursing informatics enhances the information available to nurses for clinical practice, management, education, and research and facilitates nurses' role as communicators. An effective hospital information system collects, stores, and distributes patient data from various departments to support clinical decision making, administration, and other hospital functions. Key components of a hospital information system include laboratory, radiology, clinical, financial, pharmacy, and nursing information systems.