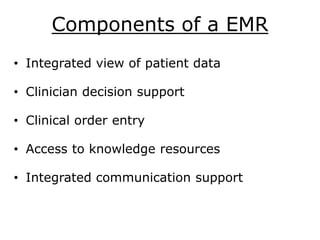
This document discusses electronic medical records (EMRs), including their objectives, components, history of development, advantages, and disadvantages compared to paper records. EMRs digitize patient medical charts and allow for easier storage, retrieval, and sharing of patient data. While EMRs improve efficiency and reduce errors, their implementation requires significant costs and changes to workflow. Legal and security issues also need consideration with the transition to digital health records.