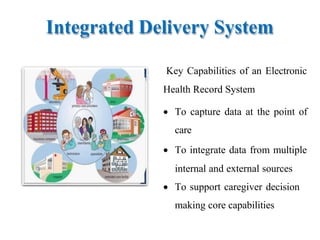
The document discusses nursing informatics, defining it as the integration of nursing science, computer science, and information science to enhance patient care and optimize information management. It emphasizes the role of technology in improving nursing documentation, workflow, and collaboration among healthcare teams, while also addressing challenges such as confidentiality and technology overload. The goal of nursing informatics is to leverage technology to improve healthcare delivery, education, and research for better patient outcomes.































![ Provision of knowledgeand decision-
support systems [that enhance the
quality,safety, and efficiency of
patient care] and
Support for efficient processes for health
care delivery.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nursing-informaticsppt1-240620061851-028f7408/85/nursing-informatics-PPT-1-pptxftfut7r66-39-320.jpg)