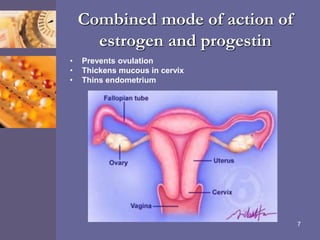
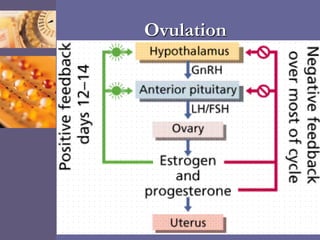
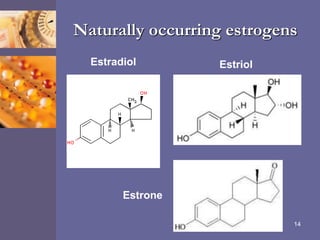
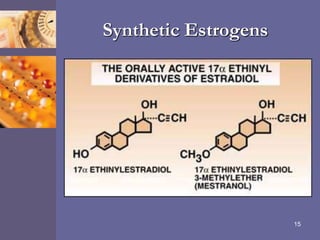
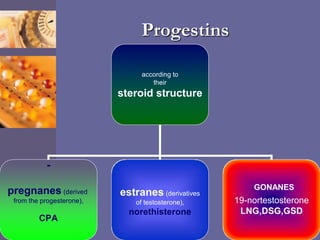
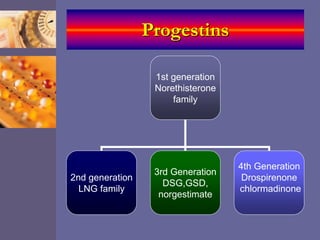
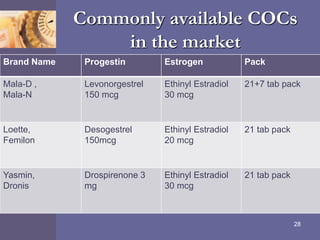
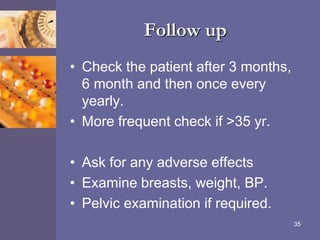
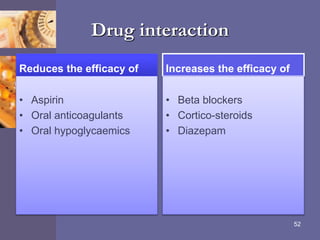
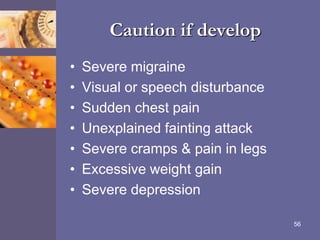
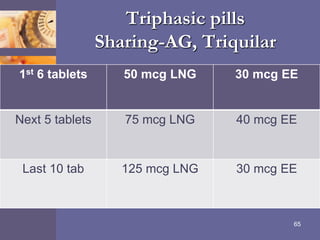
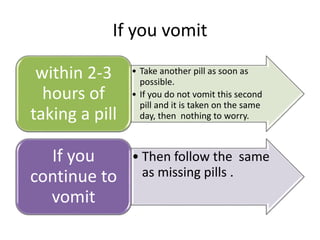
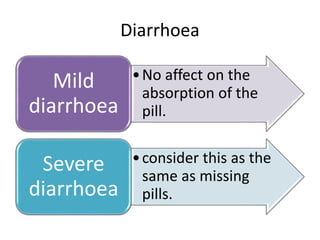
Oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) contain synthetic hormones, usually a combination of estrogen and progestin, that prevent pregnancy through multiple mechanisms. They work by inhibiting ovulation, thickening cervical mucus, and thinning the uterine lining. Common estrogen and progestin components include ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel. OCPs are generally safe and effective when used correctly, with failure rates around 0.1% per year. They also provide non-contraceptive benefits like reducing menstrual cramps and risk of certain cancers. Doctors should screen for contraindications before prescribing OCPs.