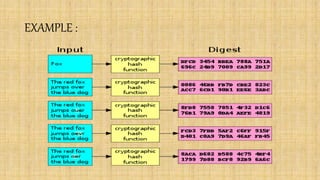
A hash function maps data of arbitrary size to a fixed size value called a hash. Common hash functions include MD5 and SHA, with MD5 producing a 128-bit hash. While hashes were once used to securely store passwords, MD5 is now considered cryptographically broken due to collisions being found in its compression function. One-way signatures allow multiple users to generate linked signatures on the same message in a verifiable chain.