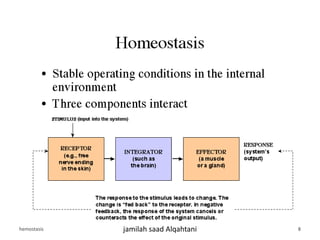
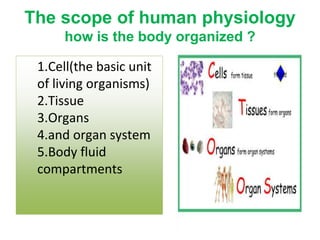
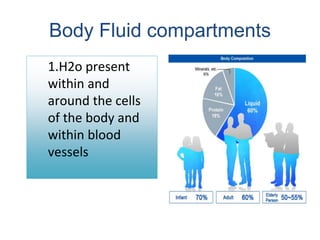
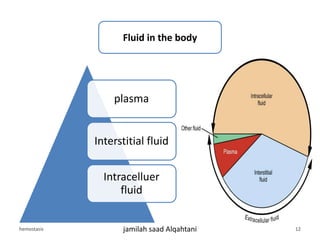
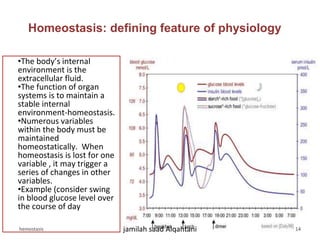
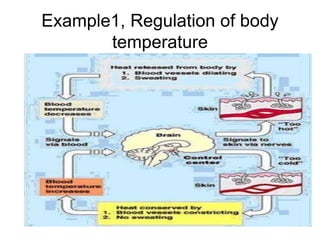
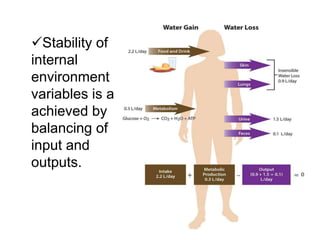
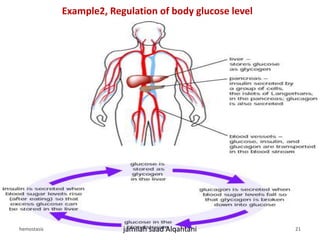
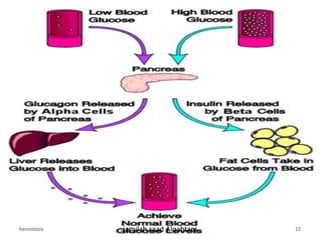
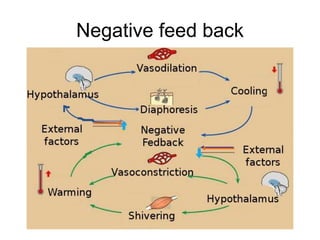
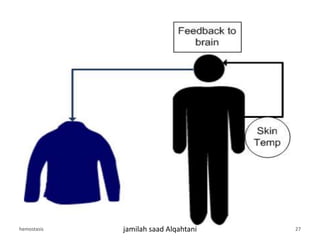
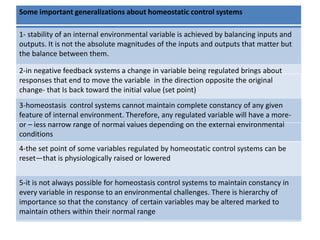
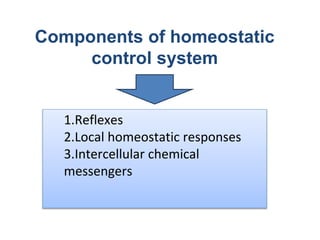
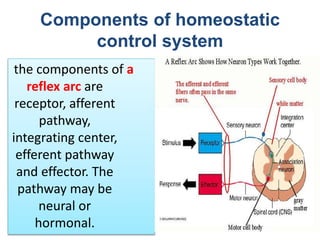
The document discusses homeostasis as a fundamental aspect of human physiology, defining it as the maintenance of the body's internal environment within a narrow range of normal values. It covers the characteristics, components, and feedback systems involved in homeostatic control, emphasizing the importance of these mechanisms in health and illness. Additionally, it highlights the role of nursing in monitoring and maintaining homeostasis to ensure proper body function.