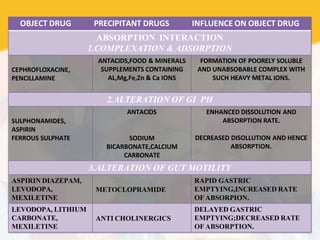
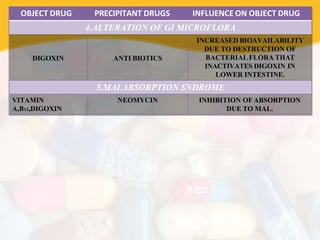
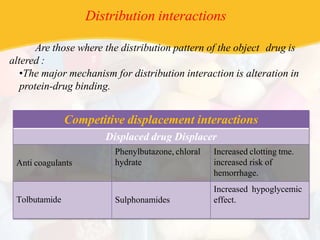
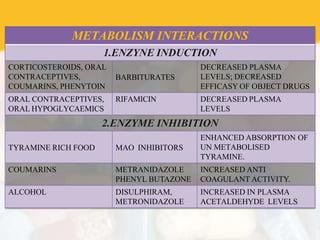
Drug interaction occurs when the pharmacological activity of one drug is altered by another concomitantly administered drug or substance. The object drug whose activity is affected is called the object drug, while the interacting agent is the precipitant. There are several types of interactions including drug-drug, drug-food, and drug-disease. Interactions can be undesirable or beneficial. They are caused by multiple factors and occur via pharmaceutical, pharmacokinetic, and pharmacodynamic mechanisms that alter absorption, distribution, metabolism, or excretion of the object drug. Consequences can range from minor to life-threatening.