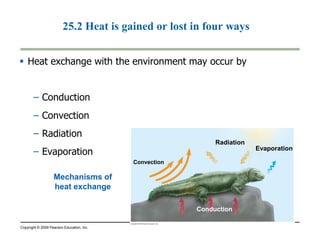
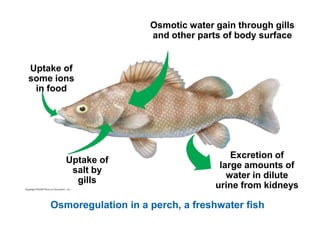
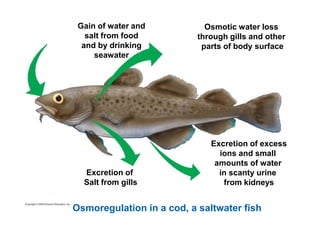
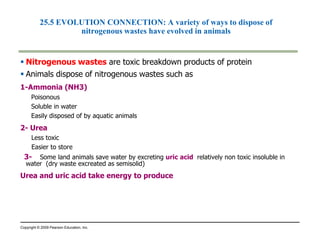
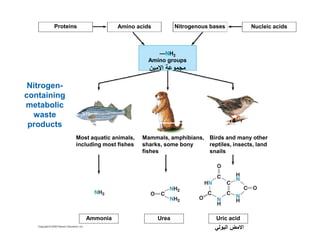
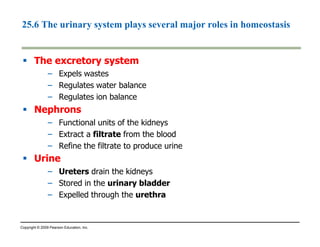
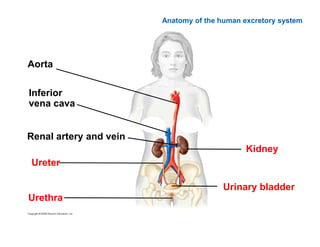
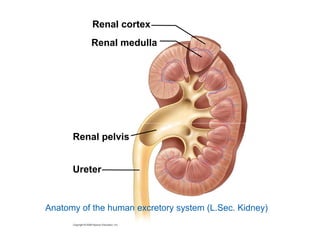
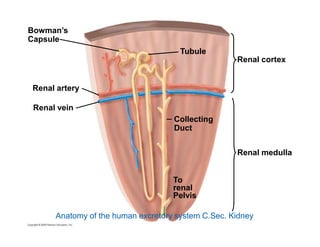
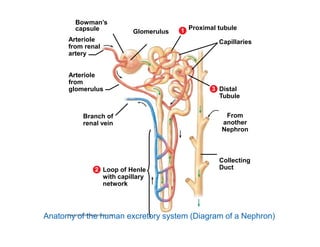
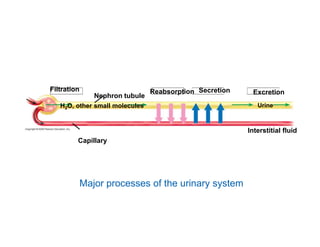
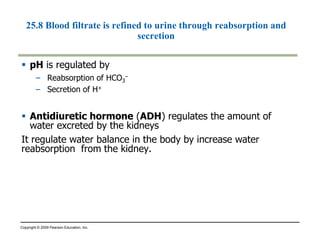
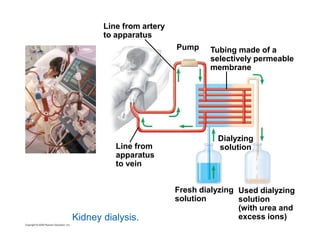
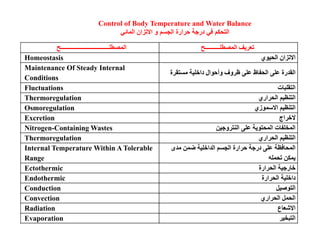
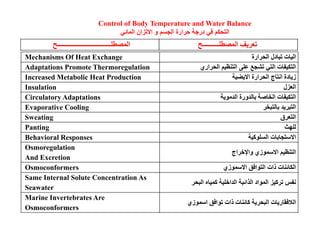
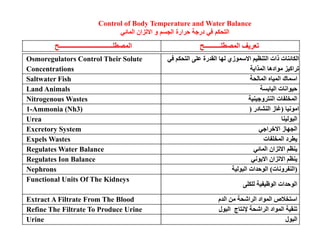
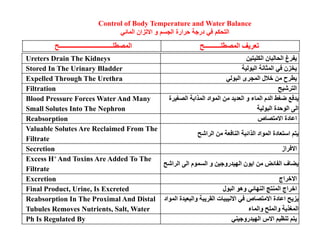
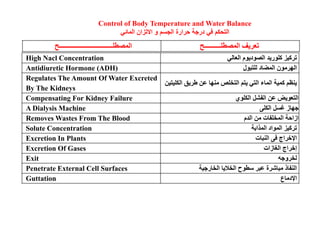
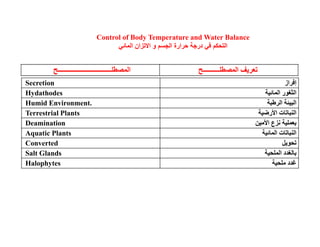
This document summarizes key points from a chapter on thermoregulation and osmoregulation. It discusses how animals regulate their internal temperature and water balance through various physiological adaptations and mechanisms. Specifically, it covers how endothermic and ectothermic animals gain and lose heat, the categories of adaptations that help thermoregulation, and the challenges of osmoregulation for freshwater fish, saltwater fish and terrestrial animals. It also briefly outlines the processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion involved in urine production by the kidneys.