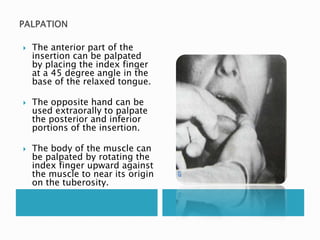
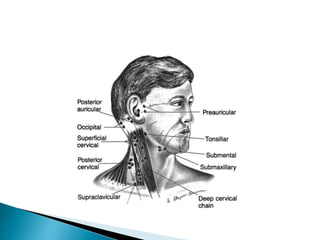
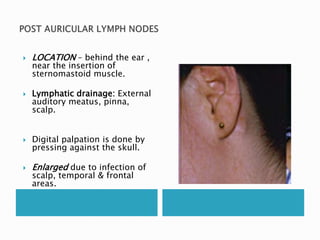
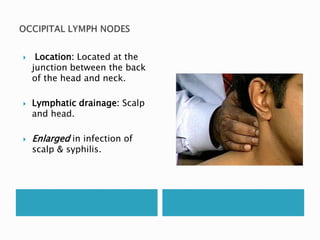
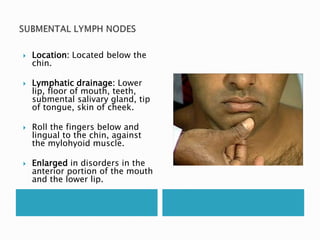
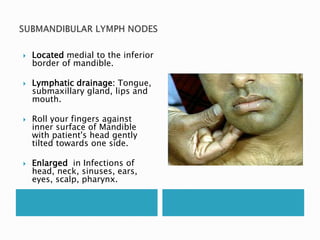
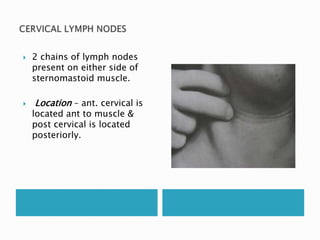
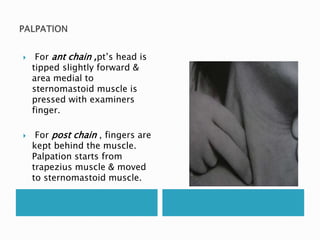
This document provides information on taking a case history for dental patients. It discusses the importance of the case history, outlines the key components that should be covered, and explains the purpose and importance of each component. These include gathering information on the chief complaint, medical history, dental history, social history, and performing an extraoral and intraoral examination. Taking a thorough case history is important for diagnosis, treatment planning, and managing the patient properly.