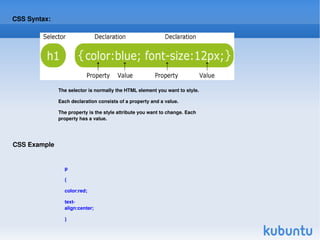
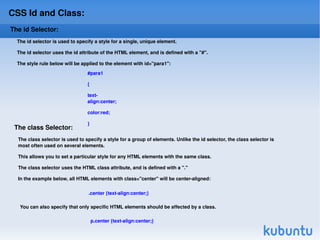
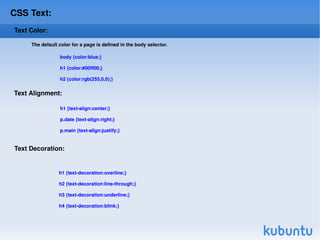
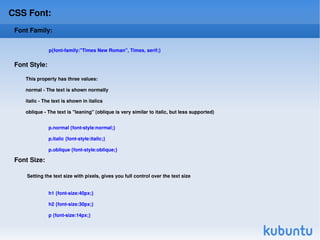
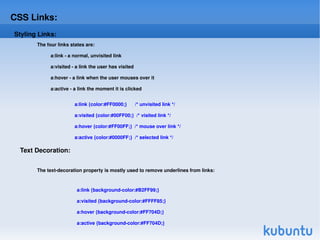
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is used to style and lay out HTML elements. CSS allows you to define styles that specify things like color, font, size, and layout of HTML elements. Styles can be applied to HTML elements using CSS selectors like id and class selectors. CSS properties specify values for attributes like color, background, text, and more. External CSS stylesheets can be linked to HTML documents to style multiple pages consistently.