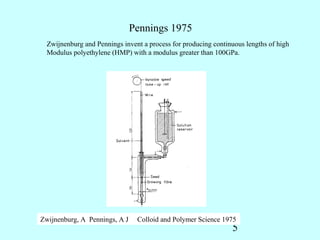
1) In 1969, Prof. Albert Pennings discovered that Taylor vortices in Couette flow could induce elongated "shish kebab" crystal fibers of polyethylene from solution.
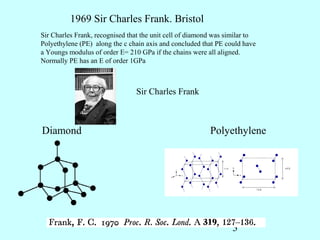
2) Also in 1969, Sir Charles Frank concluded that polyethylene could have a Young's modulus of 210 GPa if the chains were all aligned based on its similarity to diamond's unit cell structure.
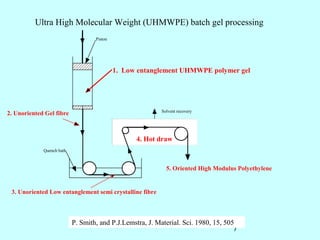
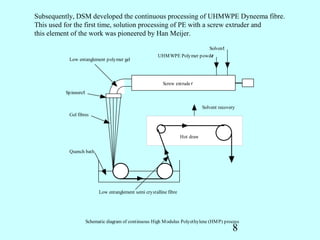
3) In the 1970s, Frank and Mackley's experiments using opposed jets showed localized chain extension and "shish kebab" crystal formation, but with low overall modulus.