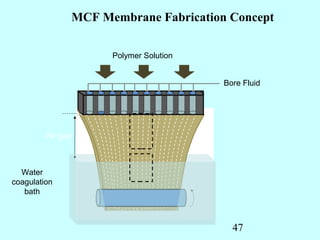
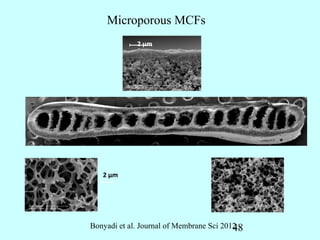
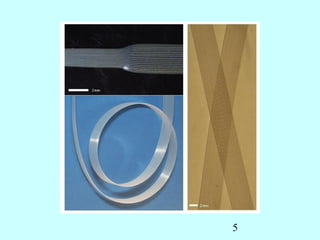
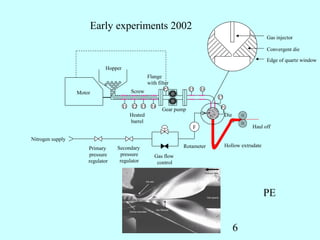
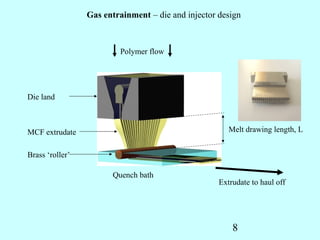
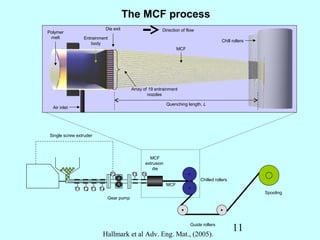
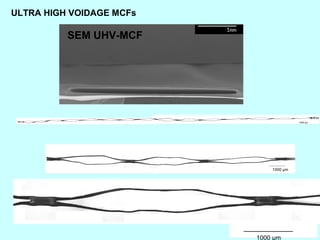
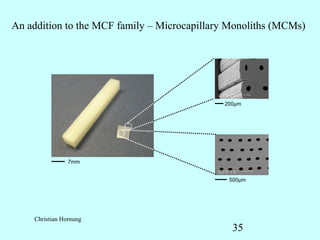
This document summarizes research on inventing plastic microcapillary films (MCFs) conducted by Malcolm Mackley and others at the University of Cambridge. The researchers developed a novel process to continuously extrude plastic MCFs with controlled voidage levels below 10% using a single-screw extruder, die design, and gas injection. They characterized the MCF structures and capillary sizes. Further mechanical drawing of the MCFs after extrusion was shown to orient the structure while limiting drawability due to necking in the capillaries. This research advanced engineering of plastic MCFs with tailored properties.































![MCF Development RTD
PE, EVOH and FEP
50
45 length = 20 m inlet
flow rate = 0.5 ml/min outlet
40
35
30
c [mg/l]
25
20
15
10
5
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
t [min]
38](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mcf-korea-2012-130127113042-phpapp01/85/MCF-Korea-2012-38-320.jpg)