1. A 60-year-old female presents with chest pain below her sternum that radiates to her left shoulder. The pain is worsened after eating spicy foods and is relieved with omeprazole.
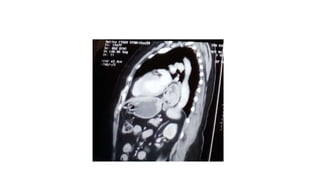
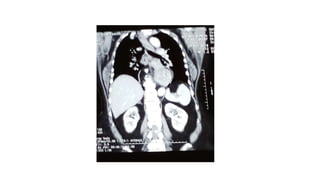
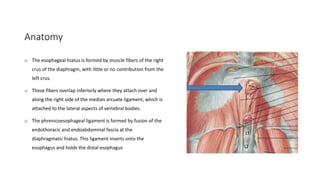
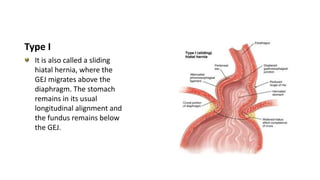
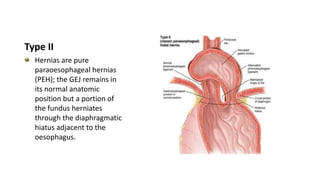
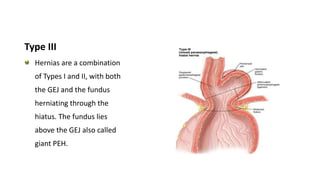
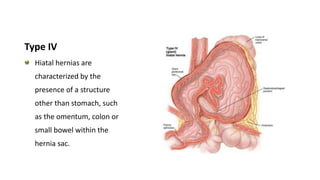
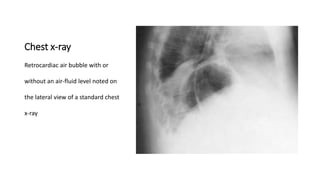
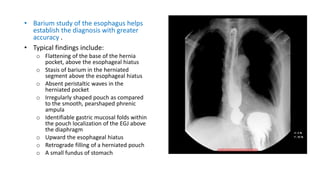
2. She likely has gastroesophageal reflux disease exacerbated by a hiatal hernia, allowing stomach contents to enter her esophagus.
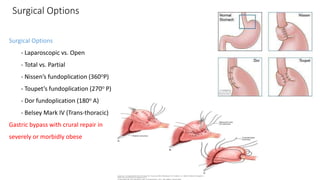
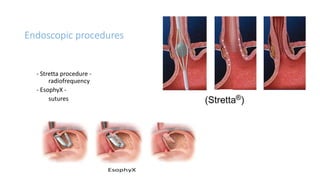
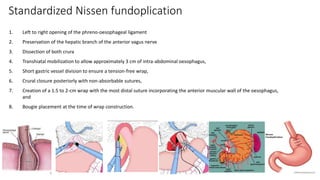
3. Surgical repair of symptomatic hiatal hernias can effectively address her symptoms through approaches like fundoplication to reduce reflux.