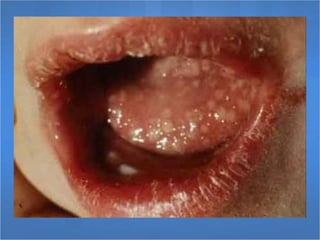
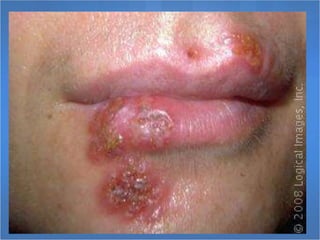
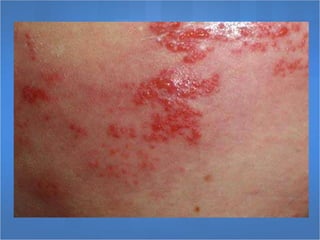
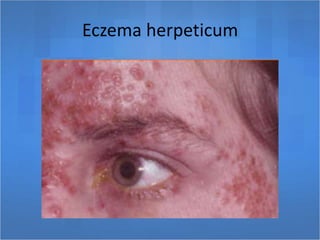
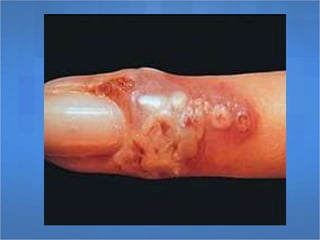
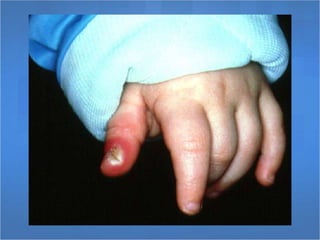
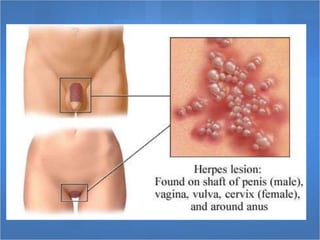
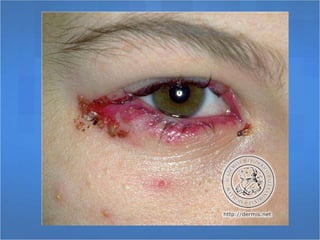
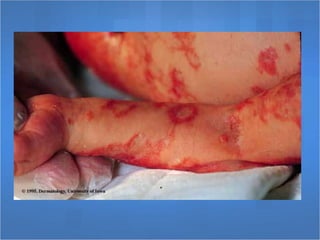
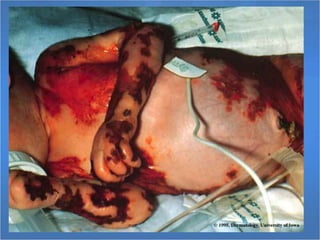
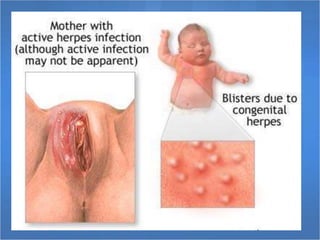
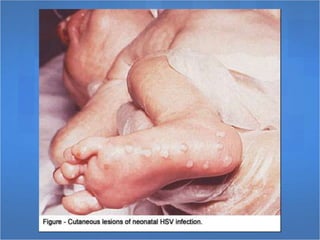
Herpes simplex virus (HSV), categorized as type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2), can cause various infections affecting skin, mucosal surfaces, and neurological tissue, often with mild or asymptomatic presentations in healthy individuals, but potentially severe in immunocompromised populations and newborns. Transmission primarily occurs through direct mucocutaneous contact, with a significant percentage of individuals being unaware of their infection status, especially in cases of genital herpes. Effective antiviral treatments exist, including acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir, which provide significant therapeutic benefits when initiated early.