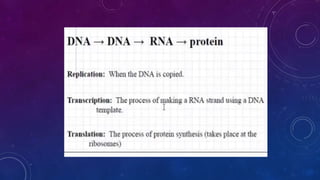
Gregor Mendel conducted early experiments on heredity using pea plants that proved traits are passed from parents to offspring. John Friedrich Miescher discovered DNA in the nuclei of cells in 1869 and called it "nuclein", which later became known as deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA. DNA serves as a blueprint for organisms, containing information that instructs development and function. It is composed of sugars, phosphates, and nucleobases that provide diversity when sequenced in different orders. DNA replicates through a process that begins at specific sites and uses enzymes to copy the long DNA chains quickly. Chromosomes are long DNA molecules that contain genetic material, and the number of chromosomes varies between species. DNA is packaged into chromosomes and