Embed presentation
Download to read offline





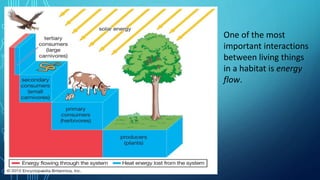



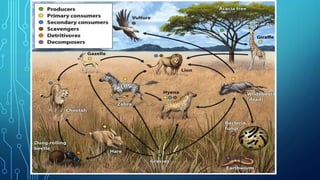
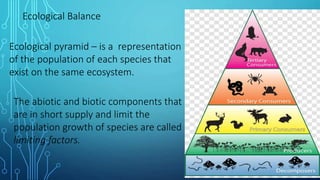

An ecosystem is characterized by the interactions between organisms and their nonliving environment. It contains biotic components like living organisms and abiotic components like energy, water, and soil conditions. Within an ecosystem, a community of interacting populations from different species occupies a habitat, which is an area that provides the necessary abiotic components for that community. One of the most important interactions is the flow of energy from producers like plants through food chains and webs to consumers at different trophic levels and ultimately decomposers, which also play an important role in the ecosystem. The abiotic and biotic factors limiting population growth are called limiting factors, and ecological collapse can occur if the balance is greatly disturbed through mass extinction of species in a community.











