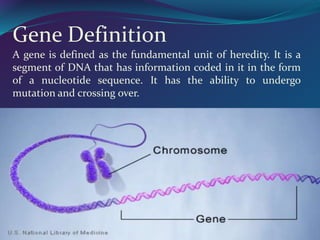
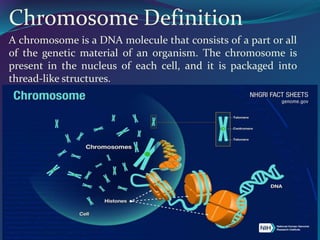
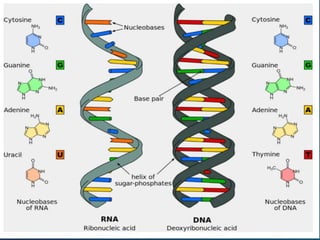
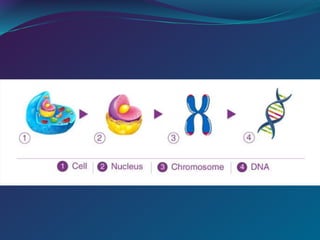
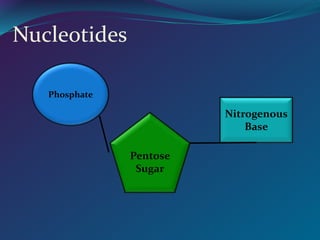
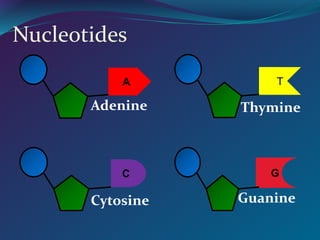
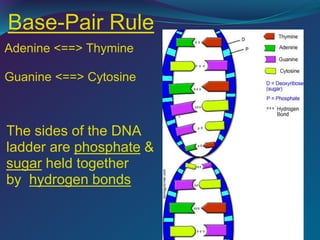
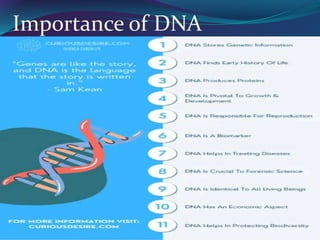
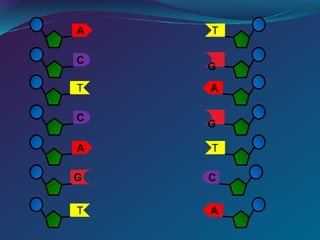
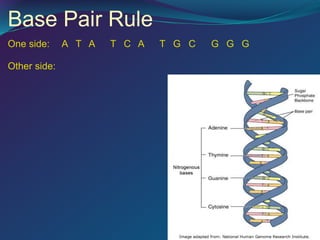
The document discusses key concepts in genetics and DNA structure. It defines genes as segments of DNA that carry hereditary information coded in nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes are DNA molecules packaged into structures in cell nuclei that contain genetic material. DNA has a double helix structure formed by pairing of nucleotides containing nitrogenous bases. The base pairing rule dictates that adenine pairs with thymine and guanine pairs with cytosine. Gene sequences on DNA encode unique proteins that determine an organism's traits.