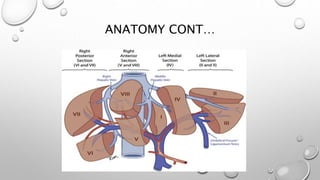
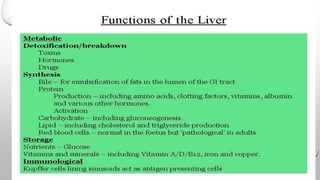
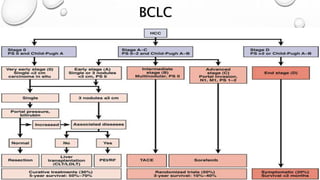
This document provides information on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) including its anatomy, etiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnosis, staging, and management. HCC most commonly develops in cirrhotic livers as a result of risk factors like hepatitis or alcohol abuse. Imaging like ultrasound and CT are used to diagnose and stage HCC lesions. Treatment depends on the extent of disease and liver function, and may include resection, ablation, transplantation, or sorafenib for advanced disease. Managing HCC requires a multidisciplinary approach due to the risk of recurrence from residual disease in the liver.