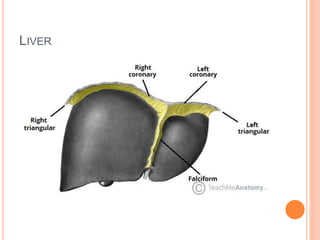
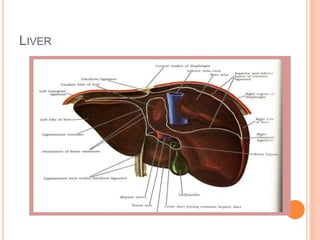
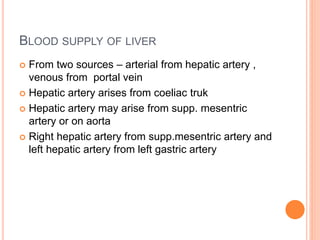
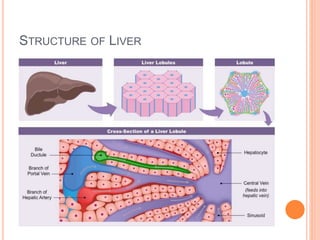
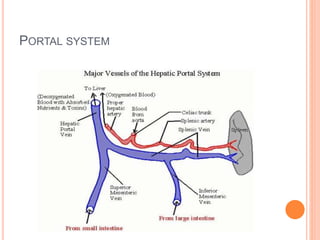
The document provides an overview of the hepatobiliary system, focusing on the anatomy, blood supply, and function of the liver, gall bladder, and biliary tree. It details the liver's structure, functional divisions, and segments, explaining its vital role in drug metabolism and the significance of its blood and lymphatic supply. Additionally, it outlines the portal venous system and its relevance to conditions like portal hypertension.