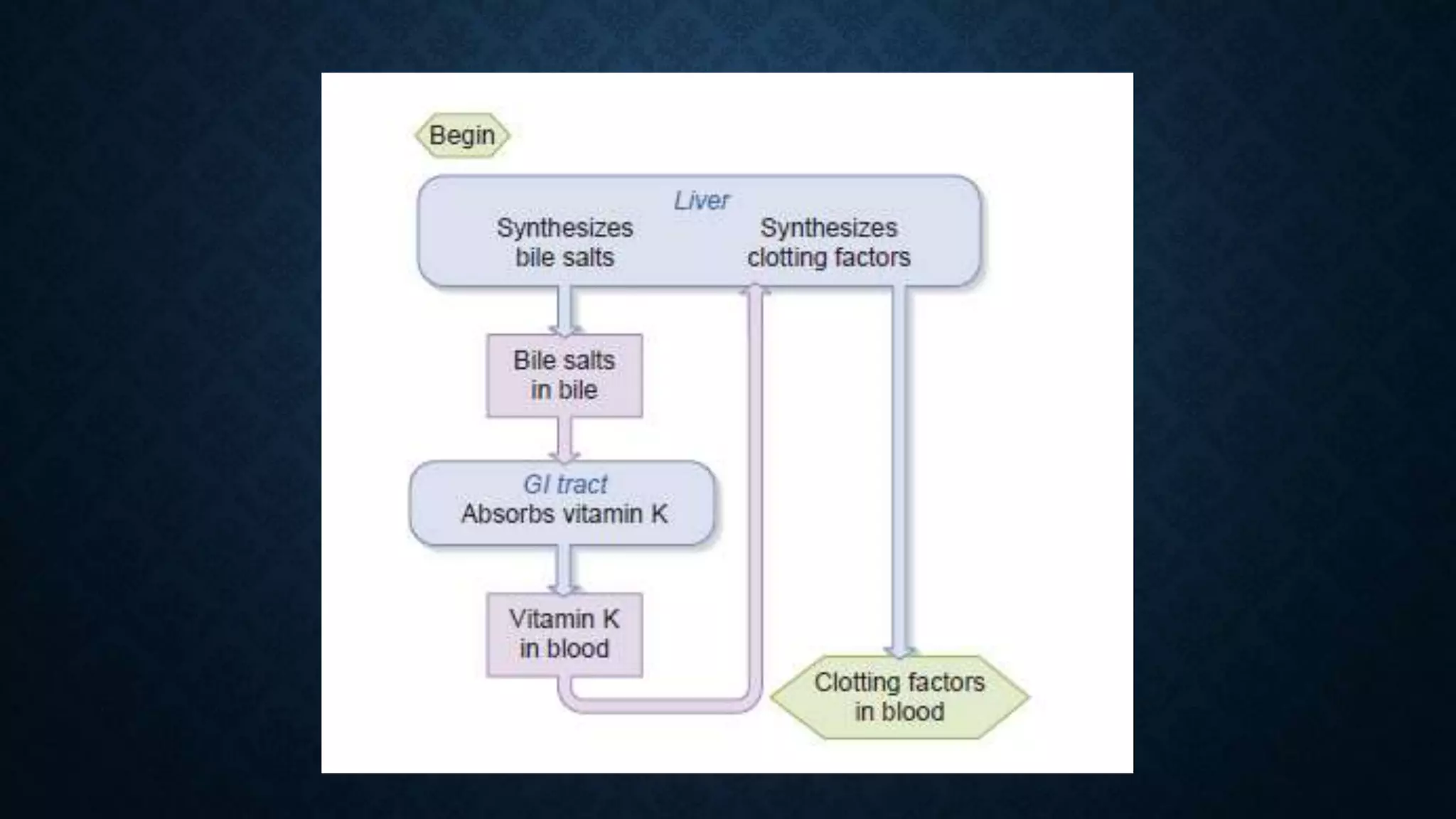
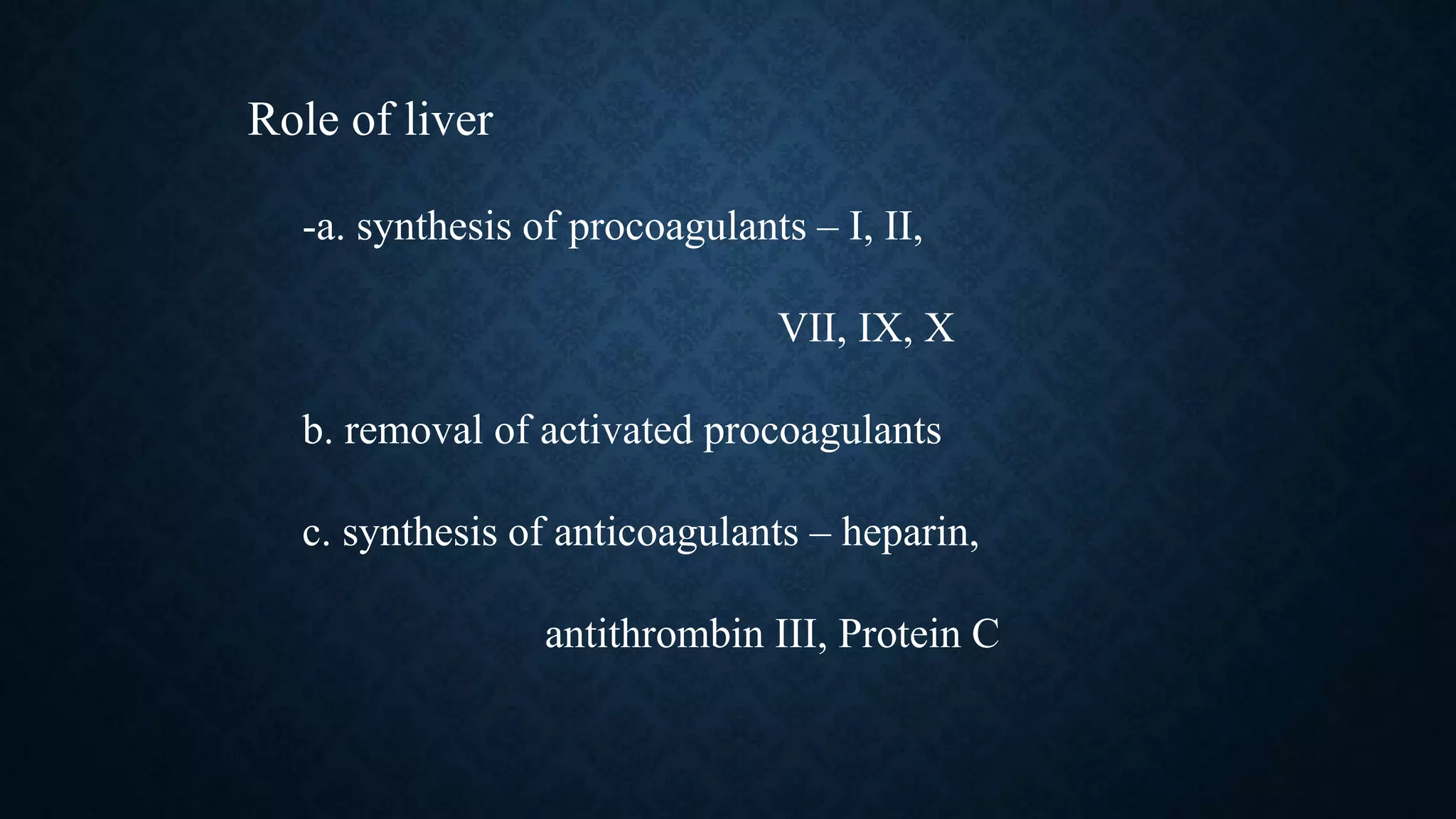
The document provides an in-depth explanation of hemostasis and blood coagulation, detailing the mechanisms and stages involved in blood clotting, including the formation of prothrombin activator, thrombin, and fibrin. It outlines the physiological and pathological aspects of coagulation, including bleeding disorders like hemophilia and purpura, as well as factors affecting clotting and the body’s anticlotting mechanisms. The document also discusses diagnostic tests related to coagulation and specific treatments for bleeding disorders.