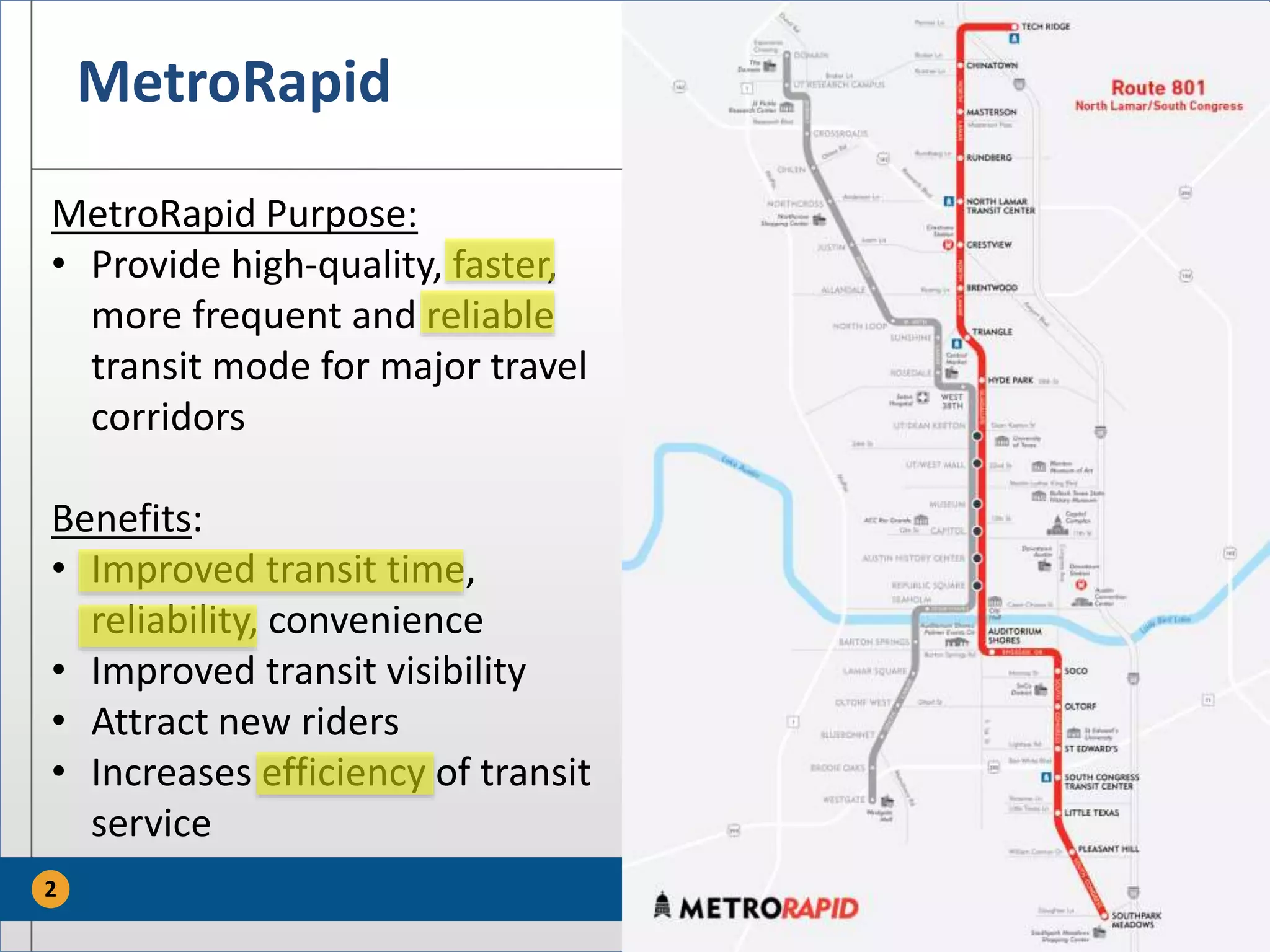
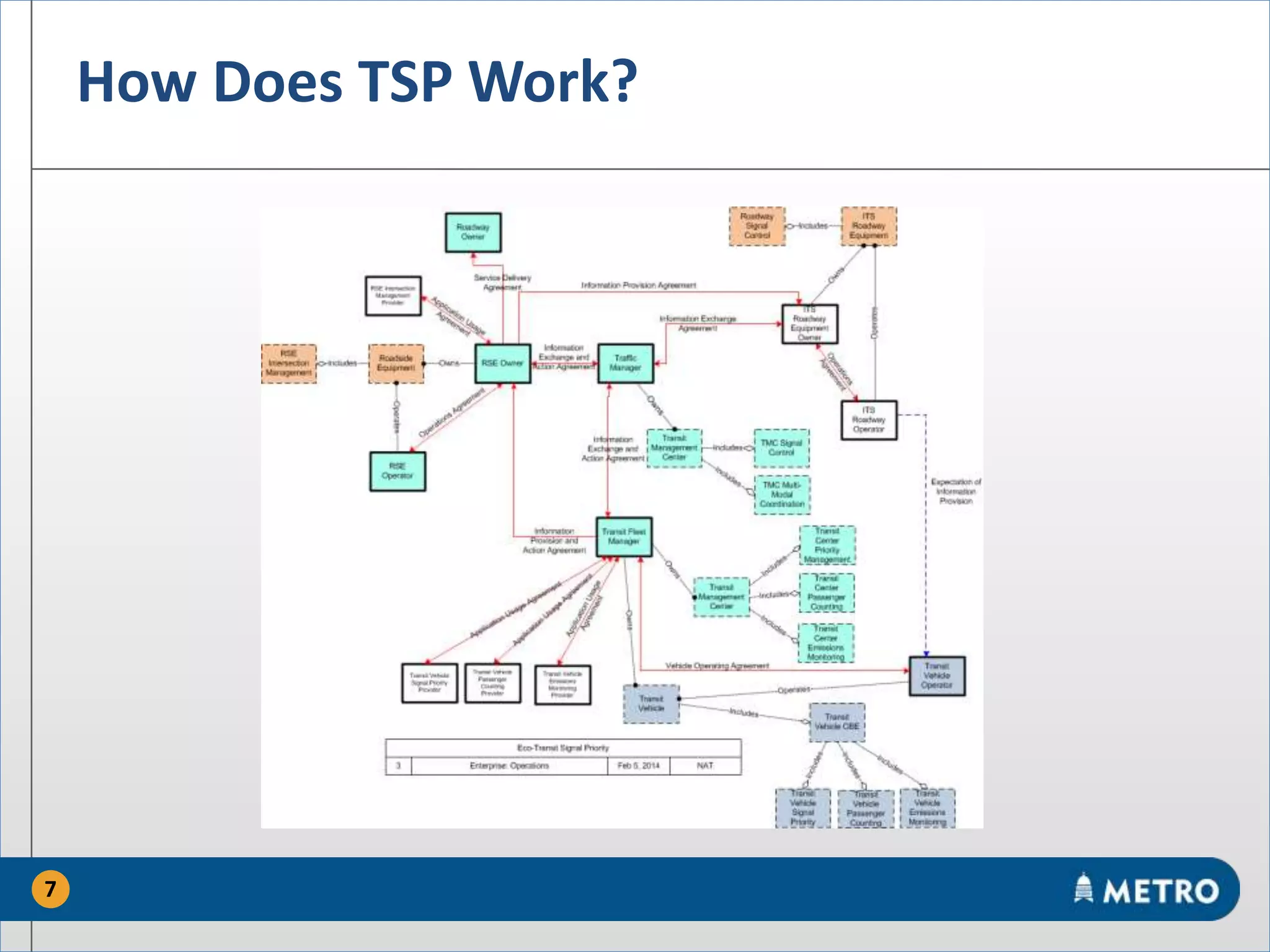
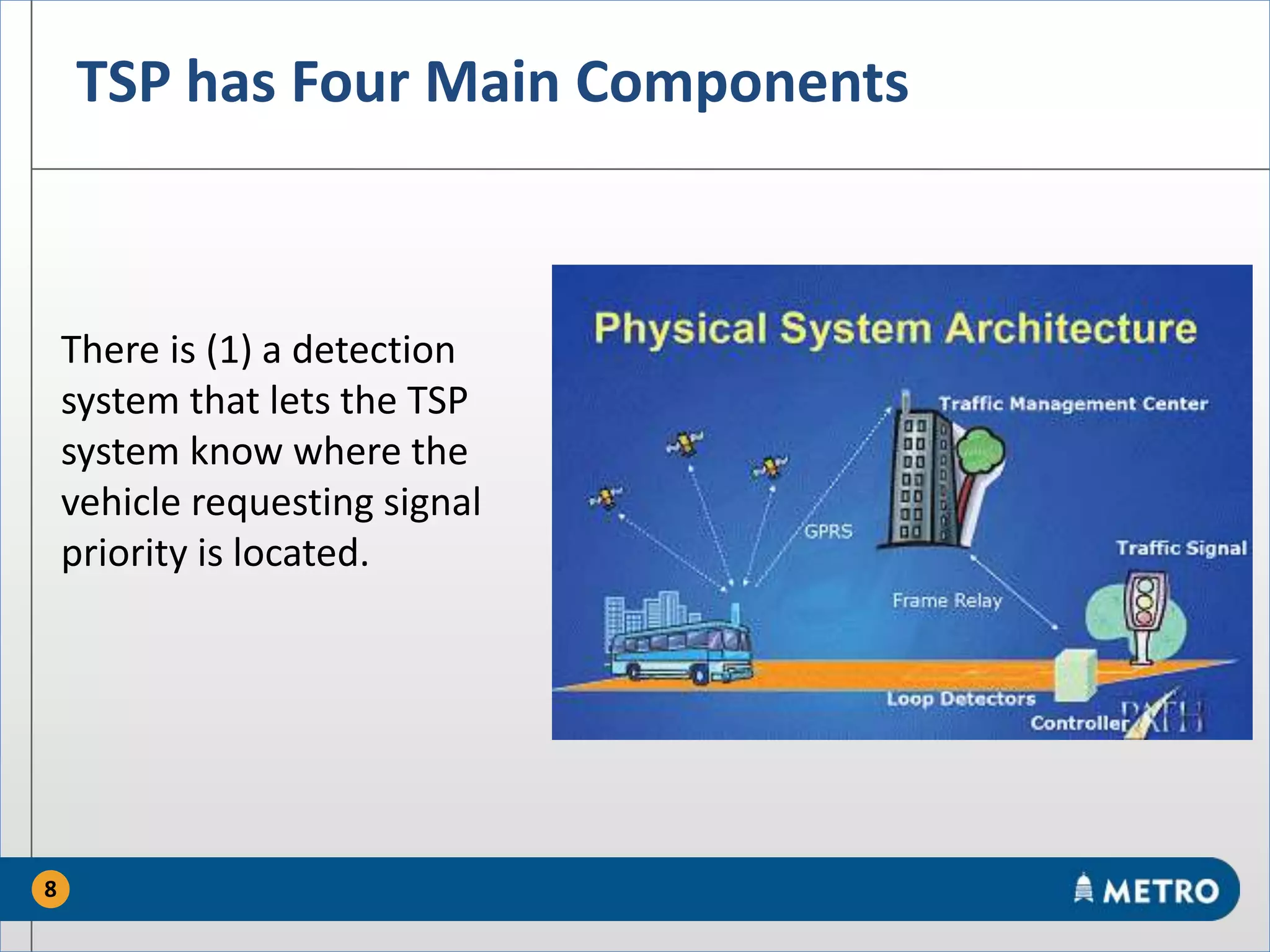
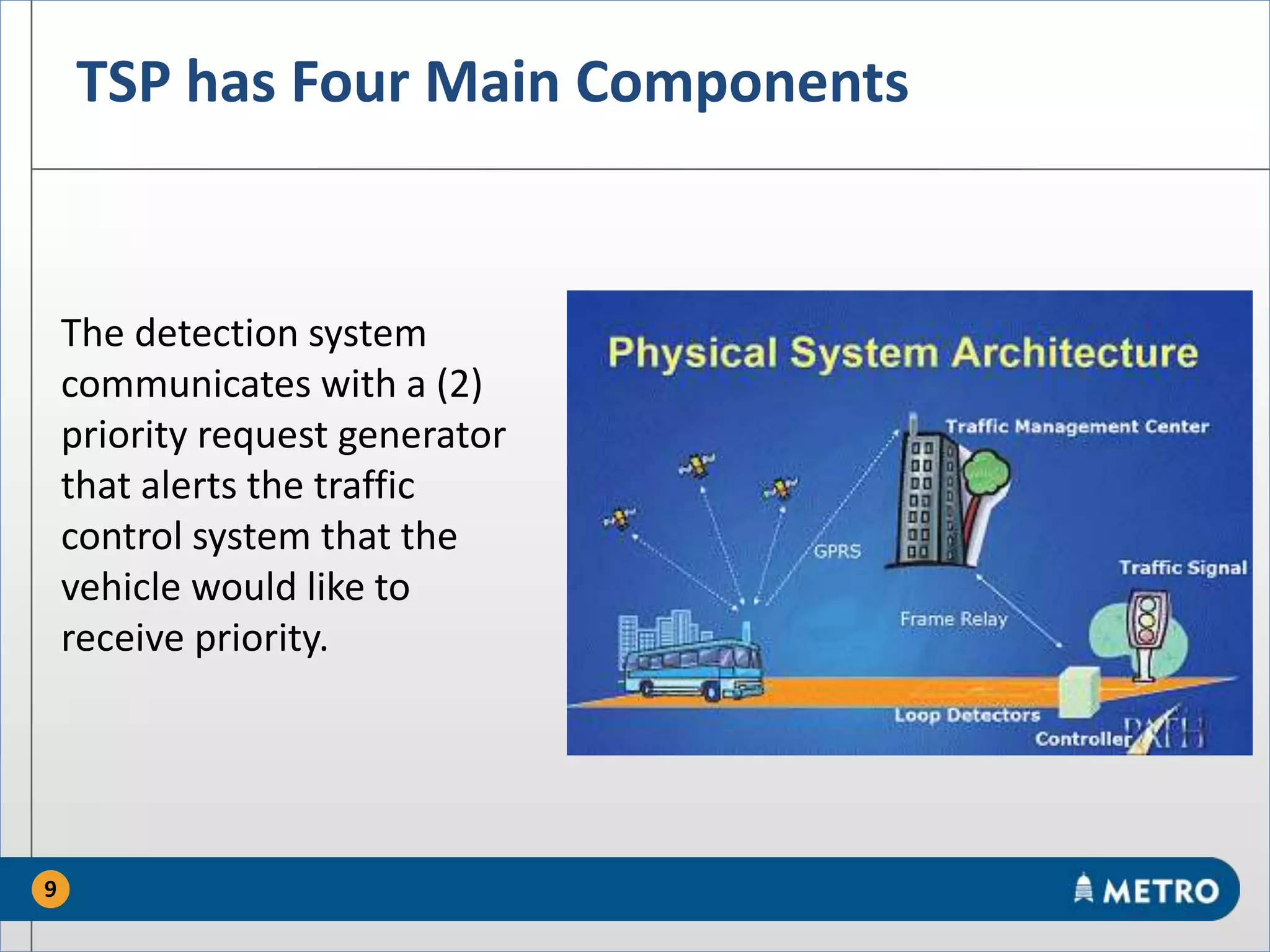
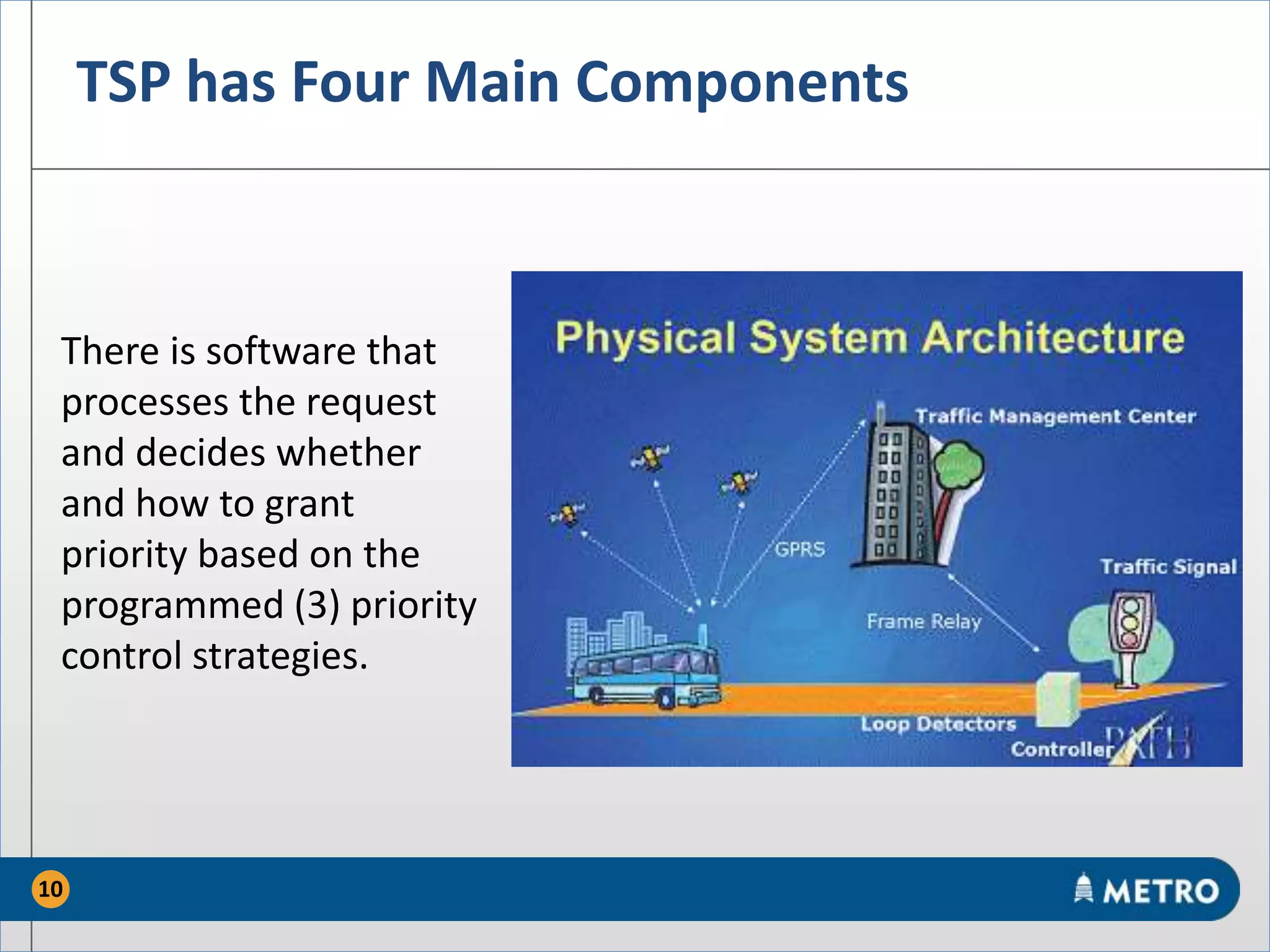
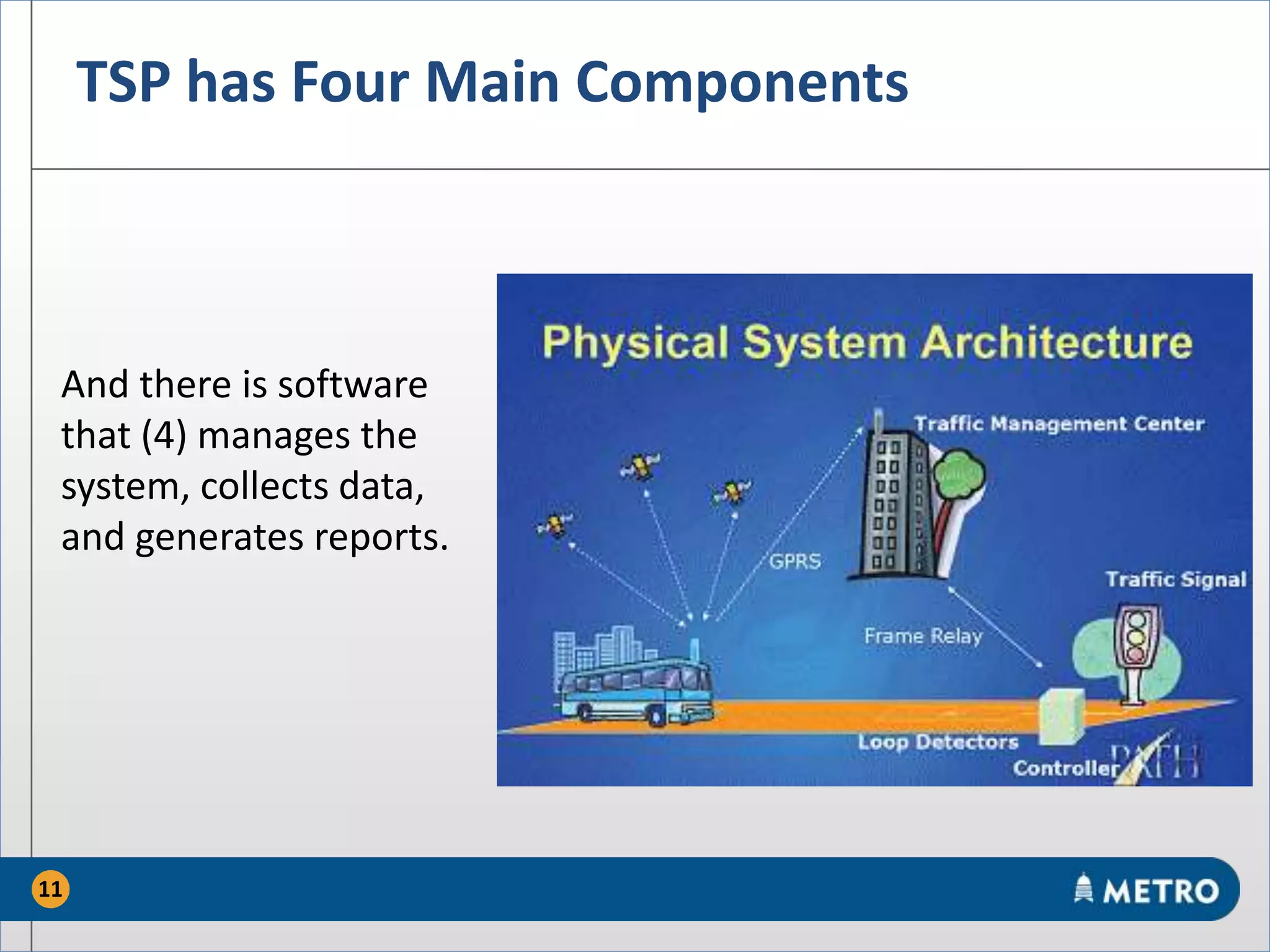
The document discusses the MetroRapid transit signal priority (TSP) system implemented by Capital Metro to enhance bus service quality in Austin, Texas. It outlines the benefits of TSP such as improved travel times and reliability, as well as the system's operational details and current performance challenges. Future efforts will focus on data analysis to optimize TSP operations and improve overall transit efficiency.