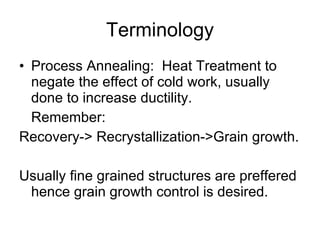
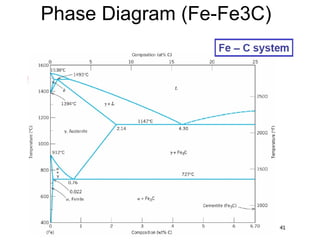
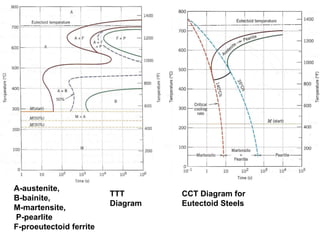
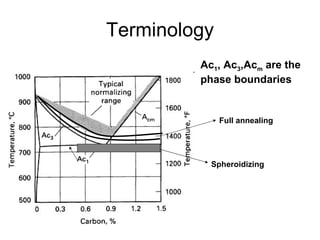
This document provides an overview of heat treatment processes and their effects on material microstructure and properties. It discusses how annealing is used to relieve stresses and modify microstructure by exposing materials to elevated temperatures over time. Process annealing and stress relief annealing are described. Phase diagrams, TTT diagrams, and CCT diagrams are introduced as essential tools for understanding heat treatment of ferrous alloys like steel. Key terms related to heat treatment processes and phase transformations are defined.