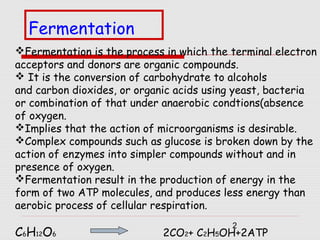
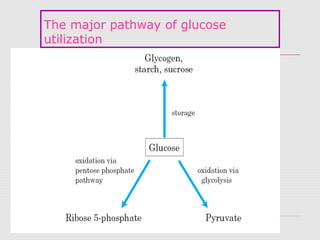
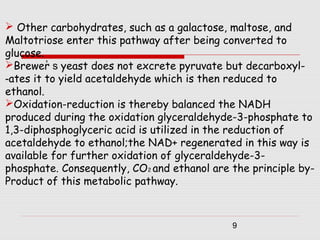
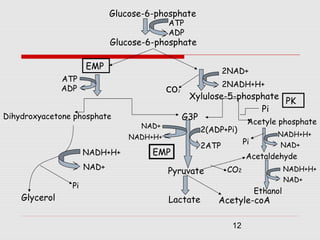
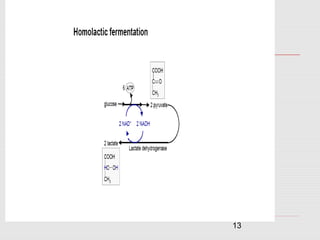
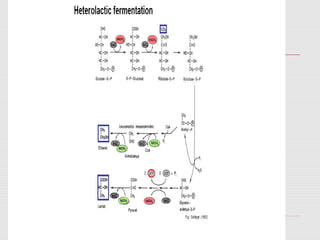
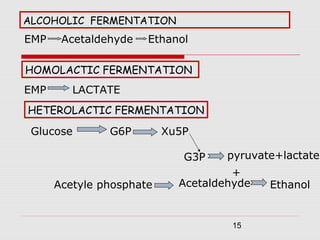
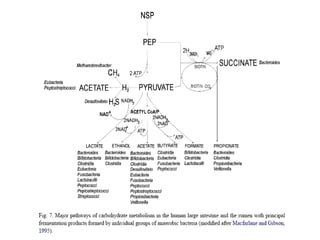
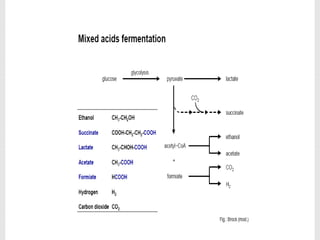
1. The document discusses the fermentation of carbohydrates, which is the conversion of carbohydrates like glucose into alcohols and carbon dioxide by yeast, bacteria, or a combination under anaerobic conditions.
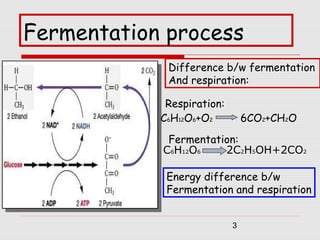
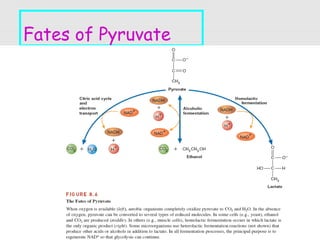
2. Key differences between fermentation and cellular respiration are that fermentation produces less energy in the form of ATP and results in ethanol and carbon dioxide rather than just carbon dioxide.
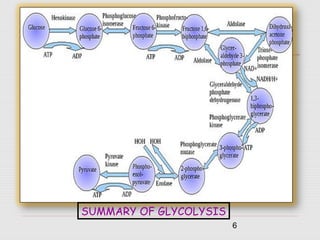
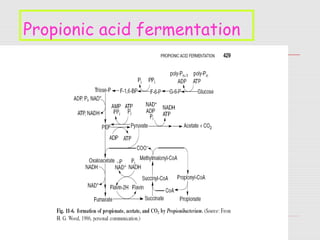
3. Major historic figures in the study of fermentation included Louis Pasteur and Hans and Eduard Buchner; the major pathways involved in carbohydrate fermentation by yeast include glycolysis and production of ethanol.