Embed presentation
Downloaded 73 times










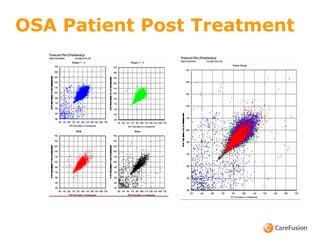
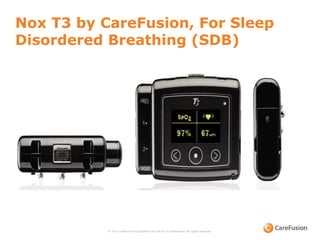




The document discusses heart rate variability (HRV) and its physiological significance, particularly in relation to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). It explains the Poincaré plot as a tool for visualizing HRV, illustrating changes in heart rate during bradycardia and tachycardia, and describes the typical HR patterns in OSA patients. Additionally, it highlights advancements in home sleep testing technology developed by Nox Medical for sleep-disordered breathing.














