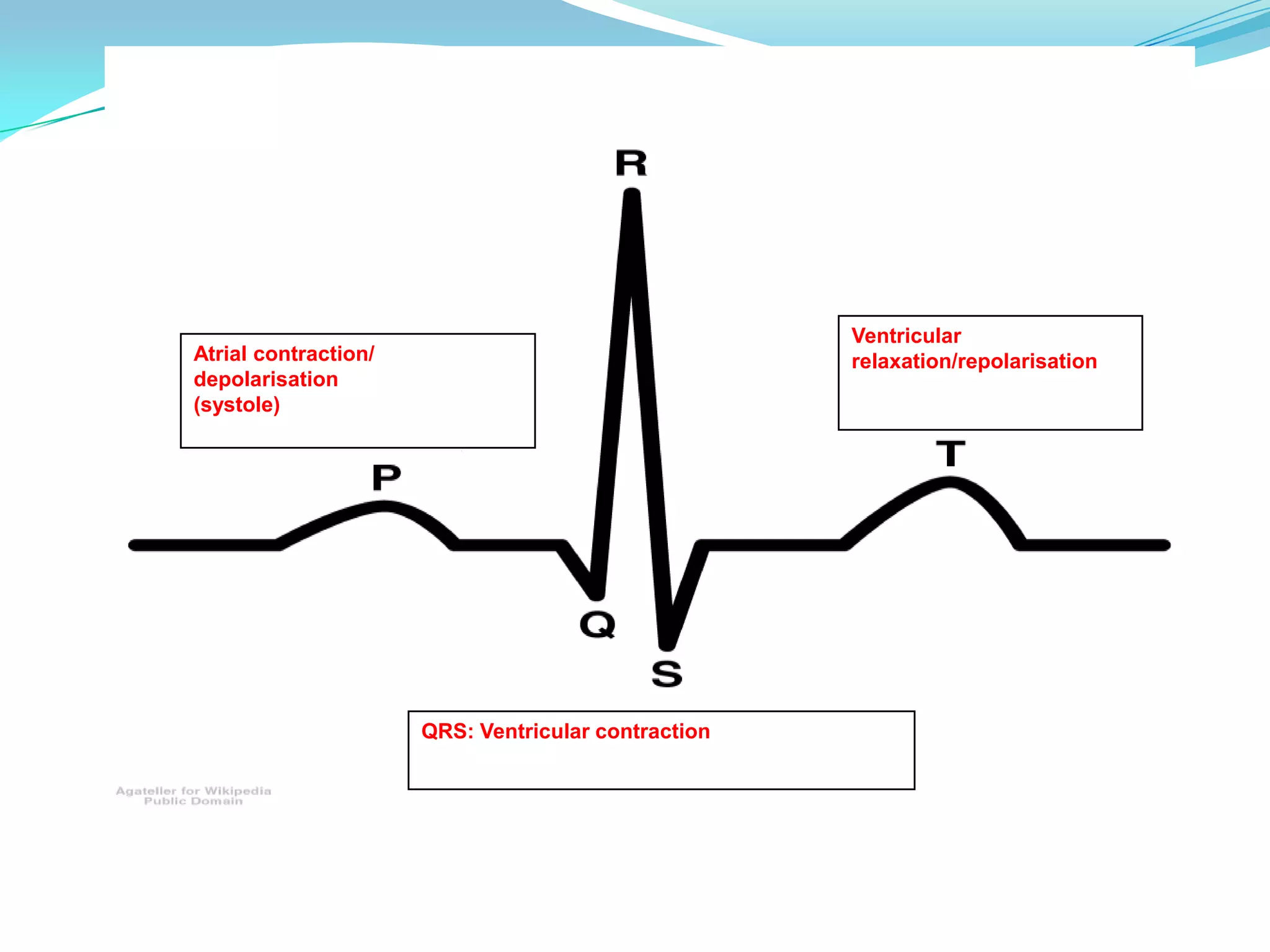
Pulse oximetry, ECG, and blood pressure monitoring are common ways to assess patients. A pulse oximeter uses light absorption to estimate oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin levels non-invasively. An ECG attaches electrodes to record the heart's electrical activity and indicates rate, rhythm, and signs of ischemia. Blood pressure results from cardiac contraction and vascular resistance, and can be measured manually or via an arterial line that displays beat-to-beat variations to assess contractility, tone, and response to interventions.