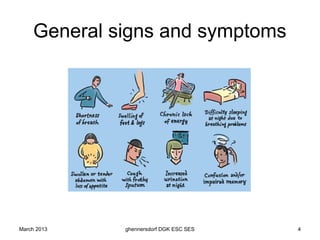
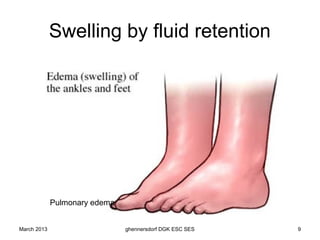
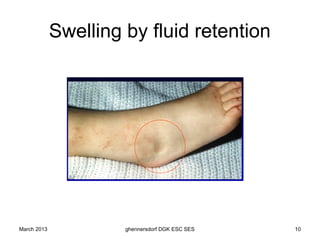
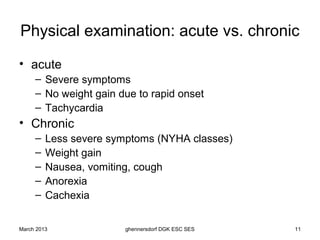
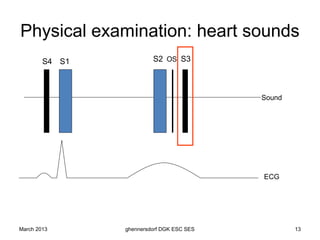
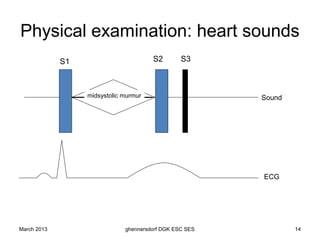
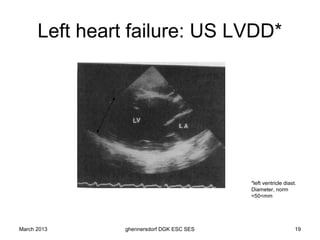
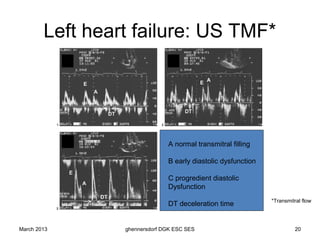
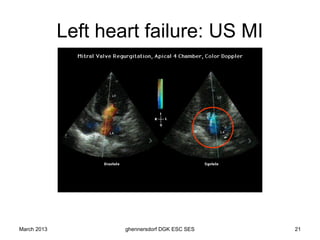
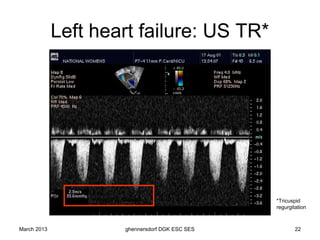
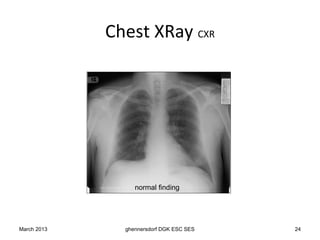
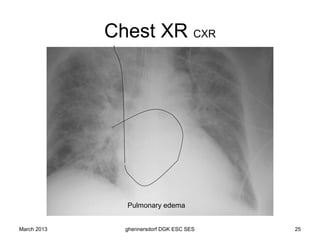
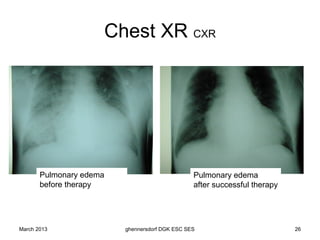
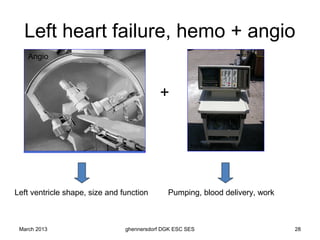
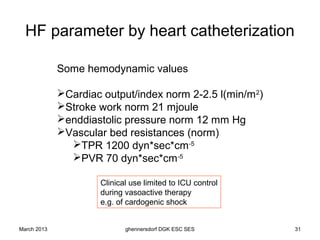
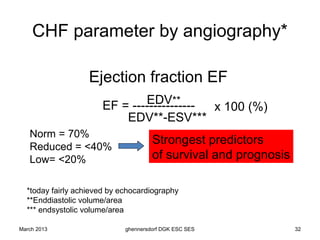
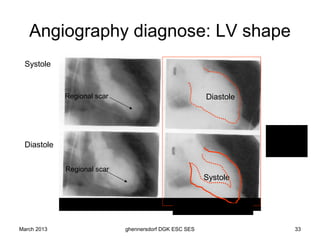
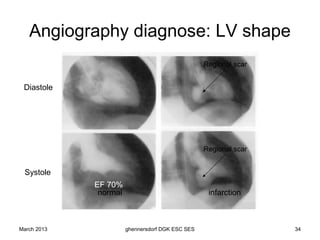
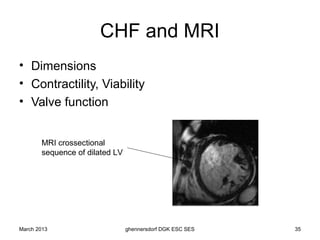
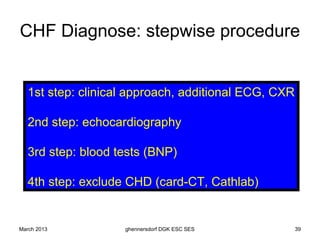
The document discusses diagnostic procedures for congestive heart failure, including clinical exams, echocardiography, blood tests, cardiac imaging like angiography and MRI, and hemodynamic monitoring. Key diagnostic tests are clinical exams, echocardiography to assess heart structure and function, blood tests like BNP to support diagnosis, and additional cardiac imaging tests like angiography to evaluate underlying heart conditions. Hemodynamic monitoring provides cardiac functional parameters but has limited clinical use due to its invasiveness.