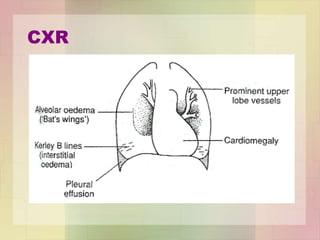
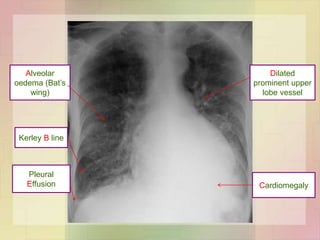
This document discusses the investigation and management of heart failure. It covers the Framingham criteria for diagnosing heart failure which requires simultaneous presence of at least 2 major criteria or 1 major criterion plus 2 minor criteria. It also outlines tools that can be used in diagnosis such as plasma BNP levels, ECG, chest x-ray and echocardiogram. Management of acute heart failure involves treatments to relieve symptoms like nitrates and diuretics. Chronic management focuses on lifestyle changes, treating the underlying cause, avoiding exacerbating factors and using heart failure drugs.