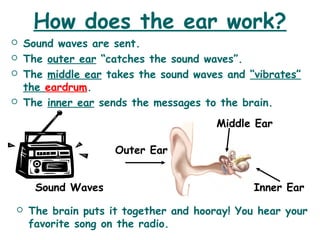
The document discusses how sound works. It explains that sound is a form of energy created by vibrations that travels in waves through gases, liquids, and solids. It describes how sound waves enter the ear and are transmitted to the brain, allowing us to hear. It also discusses volume, pitch, and how covering your ears can block out loud sounds.