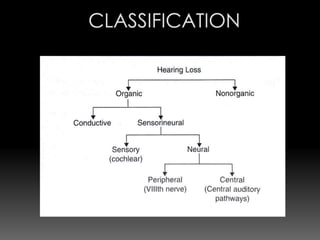
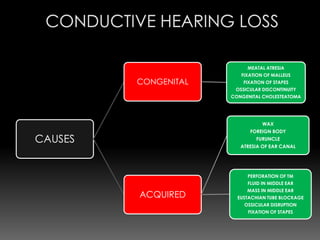
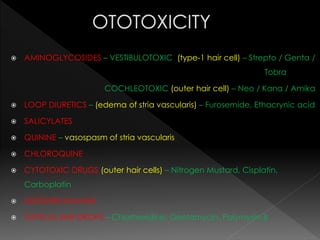
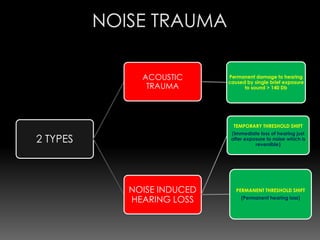
This document discusses various causes and characteristics of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Conductive hearing loss can be acquired from wax, foreign bodies, ear canal atresia, tympanic membrane perforations, or middle ear problems. Sensorineural hearing loss can be acquired from noise exposure, medications, infections, genetic syndromes, or presbycusis. Characteristics of conductive hearing loss include better bone conduction, negative Rinne test, and gap between air and bone conduction thresholds. Characteristics of sensorineural hearing loss include poorer bone conduction, positive Rinne test, and greater than 60 dB loss with poor speech discrimination. Treatment options are discussed depending on the cause.