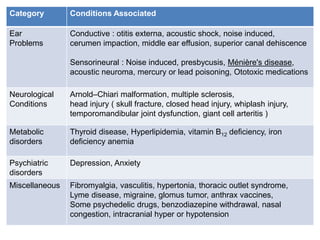
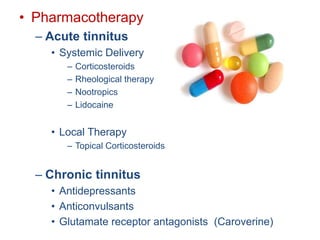
Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. It can result from various underlying causes like ear problems, neurological disorders, psychiatric disorders, and metabolic disorders. Tinnitus is evaluated based on diagnosis, severity, and auditory evoked responses. Management includes psychotherapy, relaxation techniques, sound therapy devices, pharmacotherapy like antidepressants, and other modalities. Recent advances include acoustic coordinated reset neuromodulation and magnetic/electrical brain stimulation.