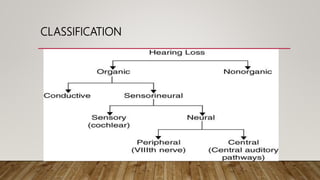
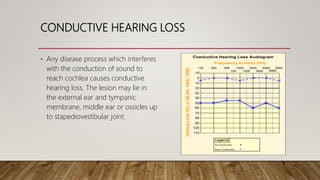
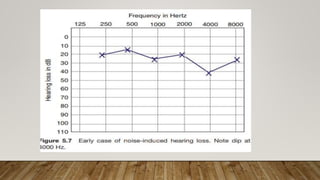
1) Conductive hearing loss results from any disease that interferes with sound conduction to the cochlea, with lesions potentially in the external ear, tympanic membrane, middle ear, or ossicles.
2) Characteristics include a negative Rinne test, Weber lateralized to the poorer ear, and normal bone conduction with an air-bone gap on audiometry.
3) Causes include congenital abnormalities, external ear obstructions, middle ear fluid/mass/fixation, and Eustachian tube blockage.
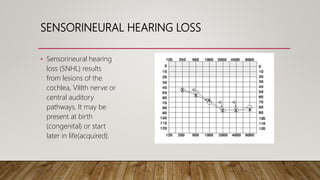
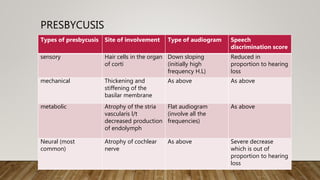
4) Sensorineural hearing loss results from cochlear, nerve, or brain lesions present at birth or later in life. Characteristics include