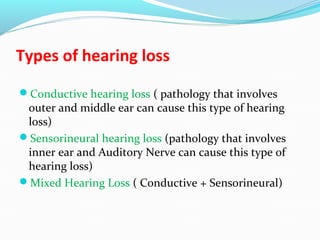
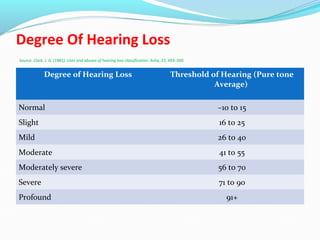
Hearing loss, or hearing impairment, is categorized into conductive, sensorineural, and mixed types, each with distinct causes and rehabilitation needs. Conductive hearing loss can often be treated with medicine or surgery, while sensorineural hearing loss usually requires ongoing rehabilitation and amplification devices. An audiologist is essential for selecting and fitting hearing aids, which are tailored based on the individual's degree of hearing loss and personal circumstances.