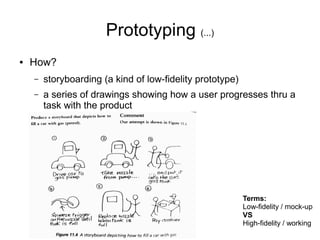
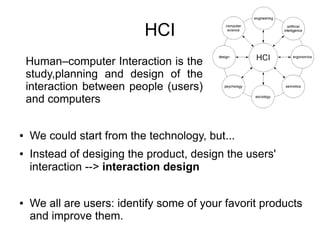
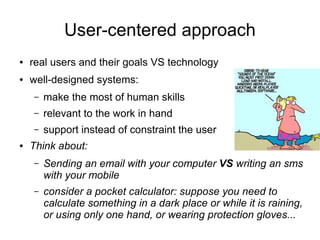
This document provides an introduction to human-computer interaction (HCI). It discusses key concepts in HCI such as taking a user-centered design approach, focusing on users and their tasks early in the design process, employing iterative design through prototyping and testing, and using empirical measurement to evaluate designs with real users. The document outlines steps in the HCI design process including establishing requirements, conceptual and physical design, building interactive prototypes, and evaluating designs based on user experience. It also provides examples of prototyping tools and techniques for storyboarding interactions and designing new tasks.



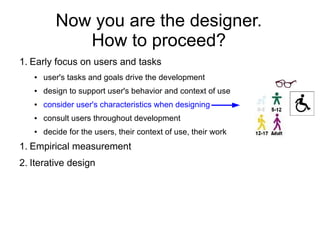

![How to proceed?
1. Early focus on users and tasks
1. Empirical measurement
2. Iterative design
Establish
● identify needs / establish requirements requirements [*]
for user experience
● cycle: design, test, measure, re-design
(re)Design Test +
● develop alternative designs: [**] Measure
conceptual and physical design
● build interactive versions of the Build
designs: paper-based, role-playing, or interactive
software version
● evaluate w.r.t. user experiences Final
product
[*] requirements = user needs
[**] how to invent many designs?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hci-introtask-111212031953-phpapp02/85/Hci-intro-task-8-320.jpg)