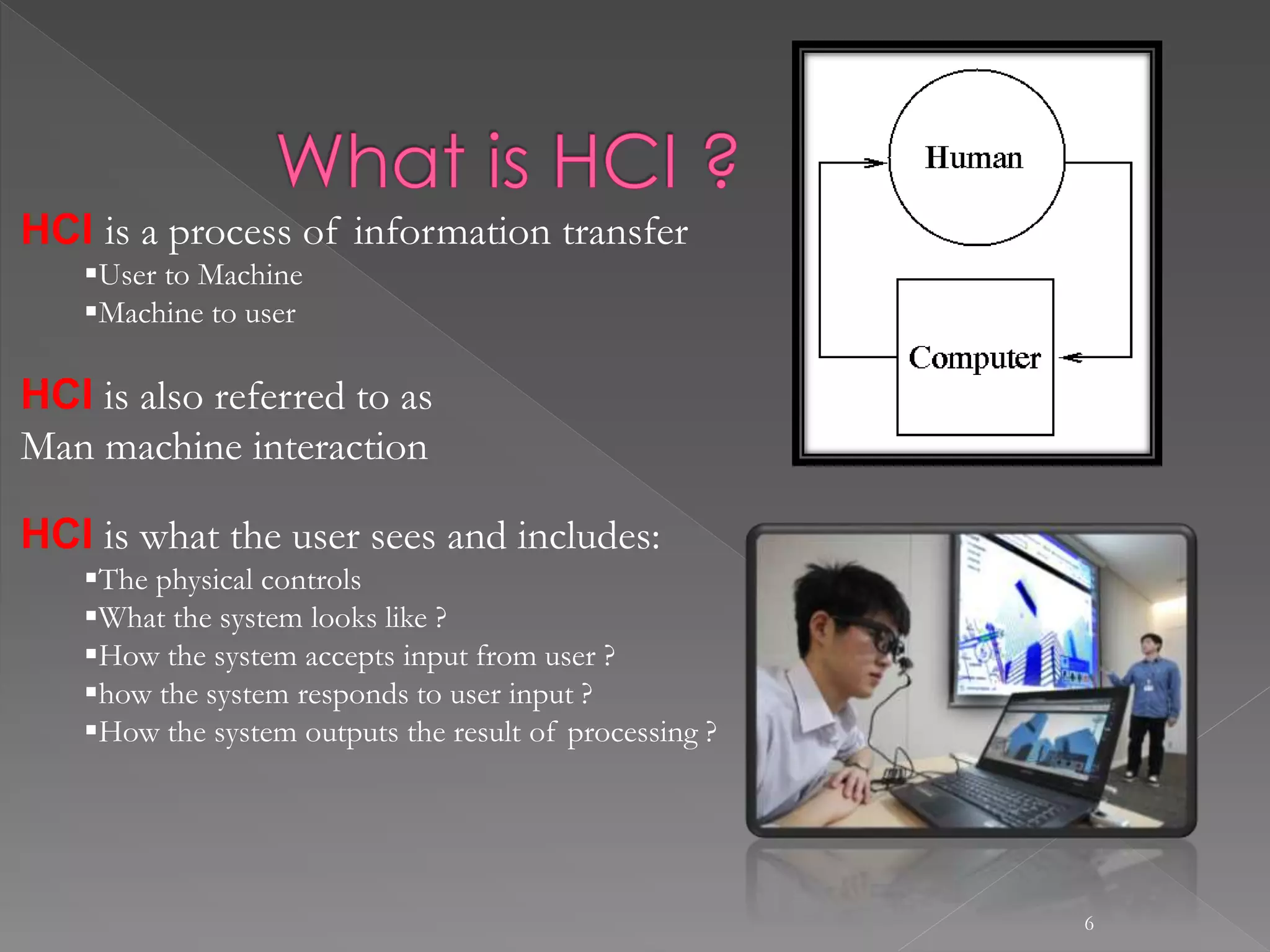
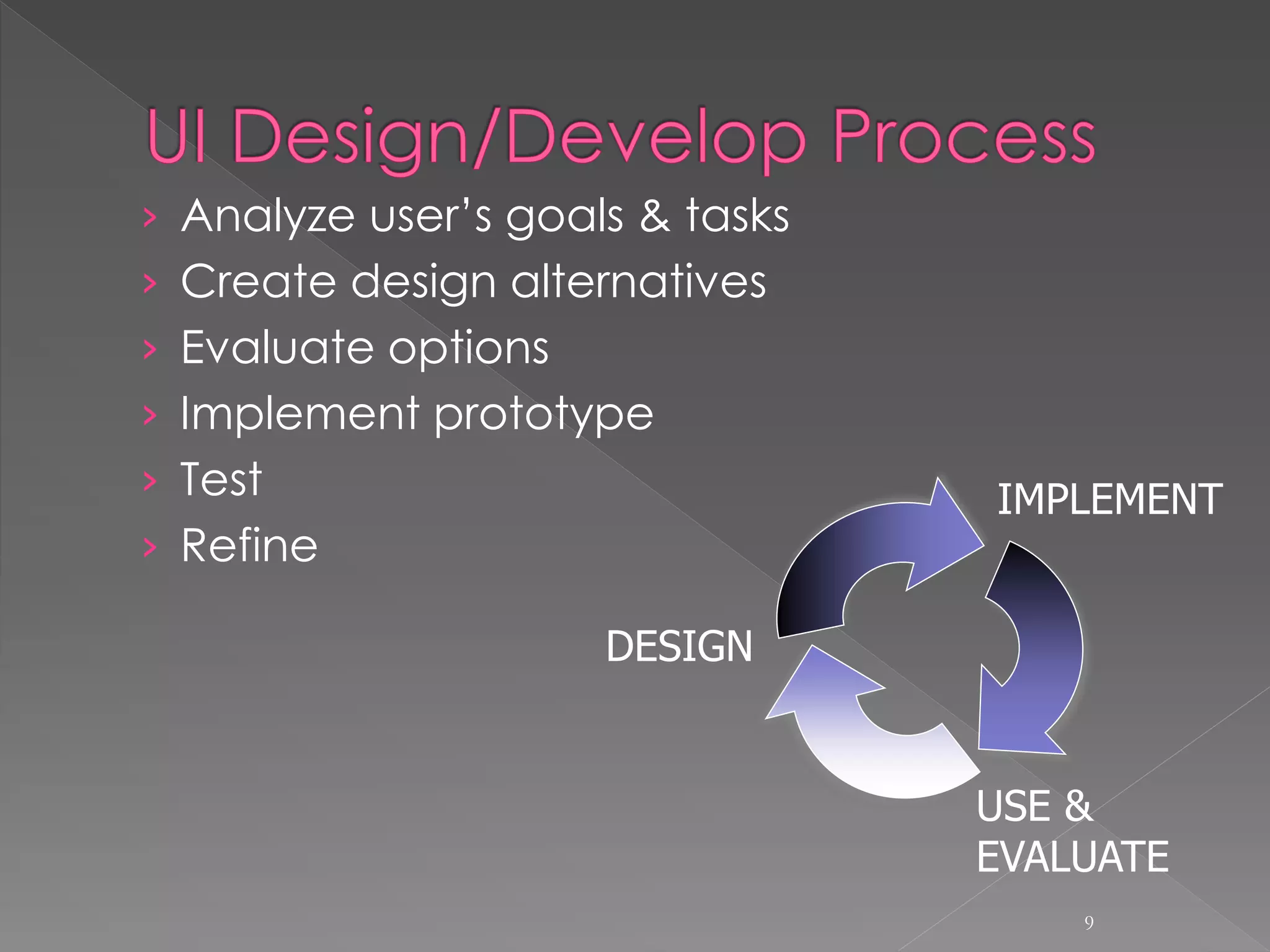
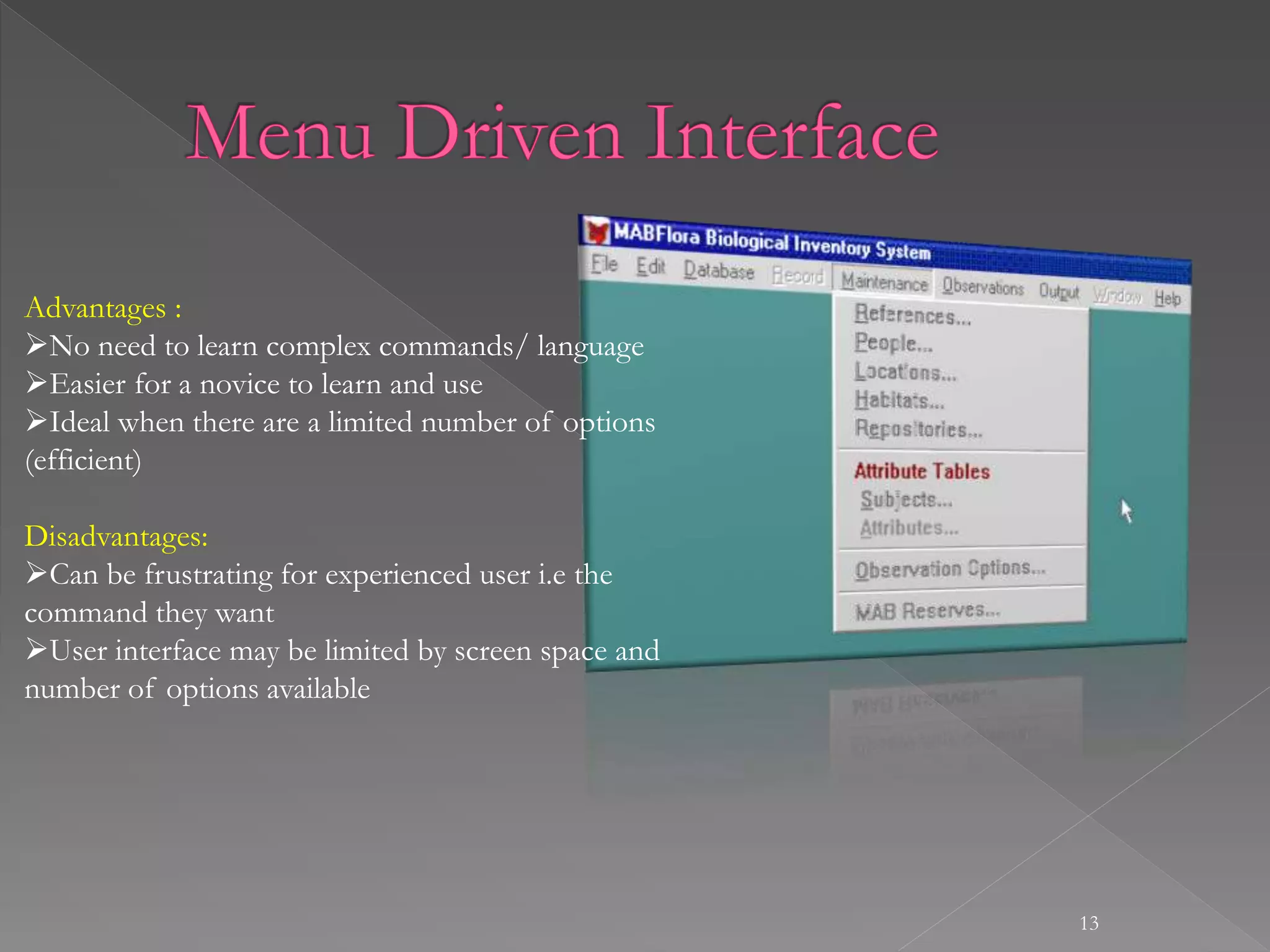
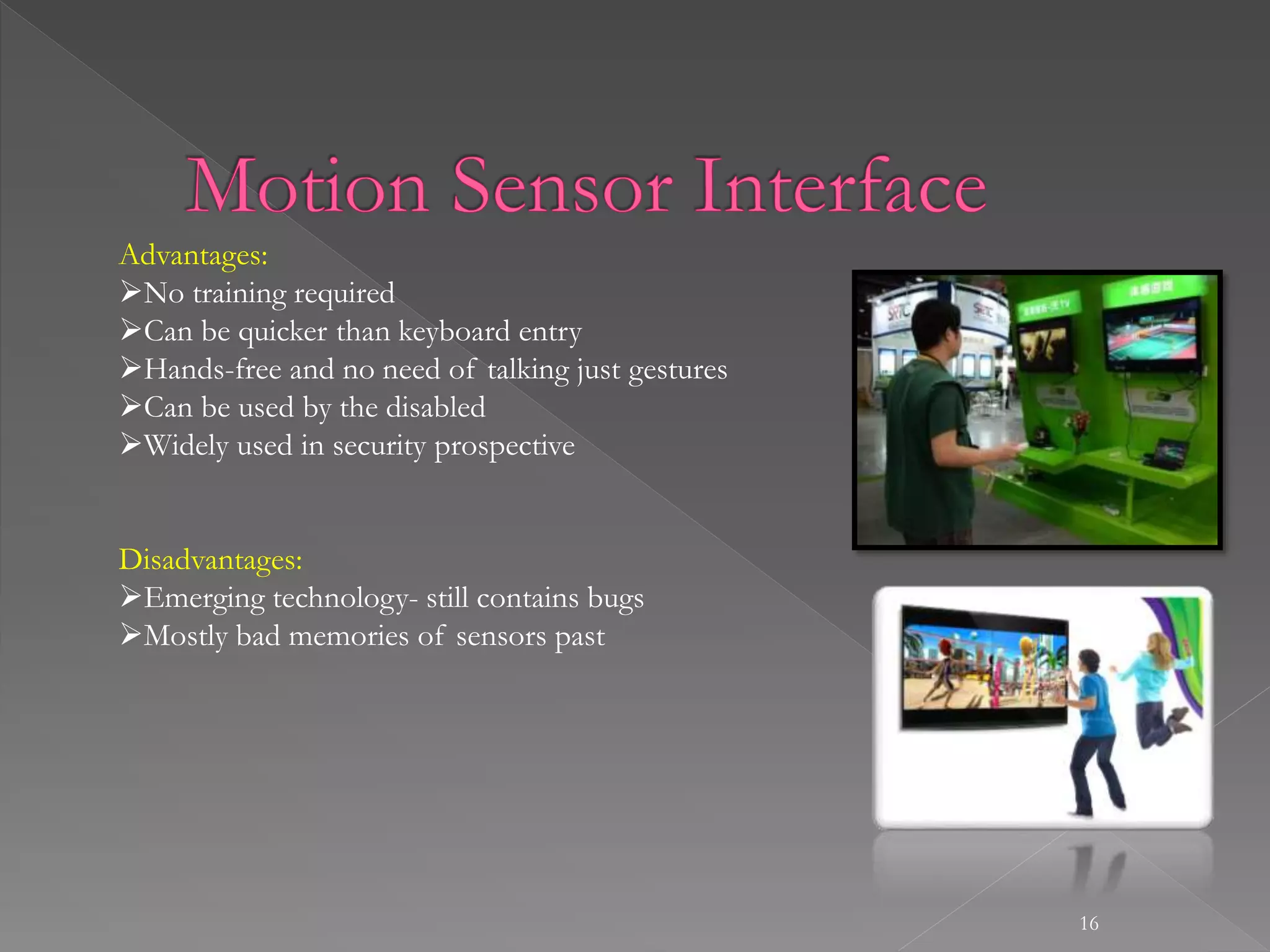
The document provides an overview of human-computer interaction (HCI). It discusses that HCI involves the transfer of information from the user to the machine and vice versa. It also describes different types of interfaces like command line interfaces, menu driven interfaces, graphical user interfaces, natural language interfaces, and motion sensor interfaces. Finally, it lists several disciplines that are involved in HCI, including cognitive psychology, neuroscience, ergonomics, engineering, design, anthropology, sociology, philosophy, linguistics, and artificial intelligence.