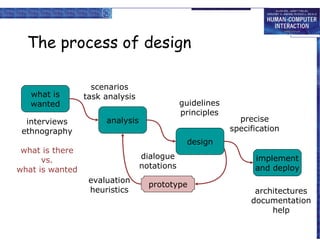
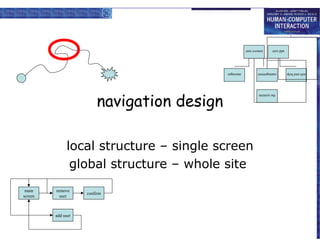
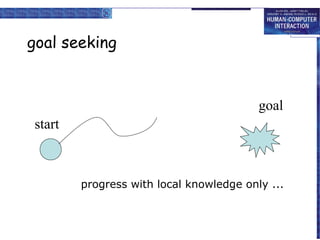
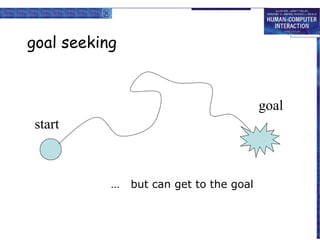
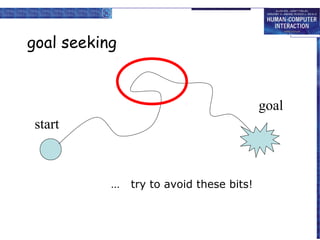
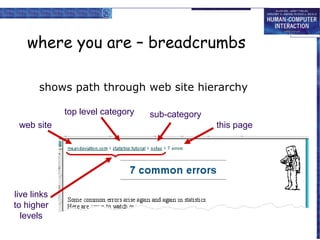
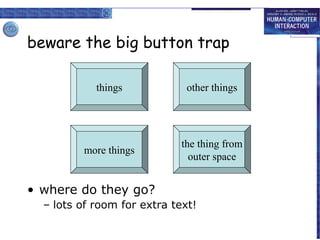
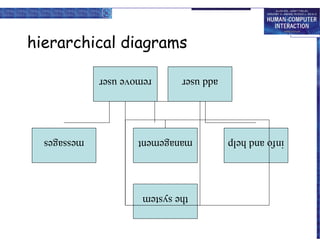
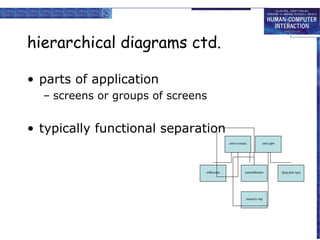
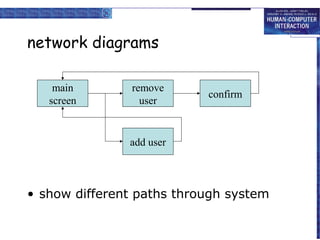
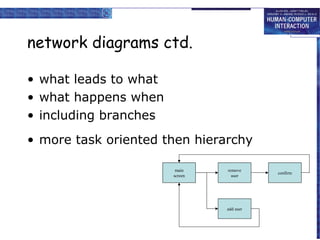
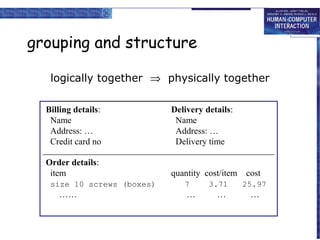
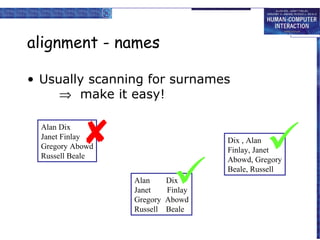
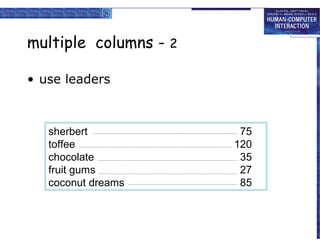
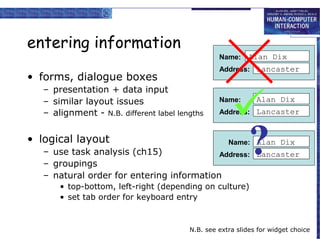
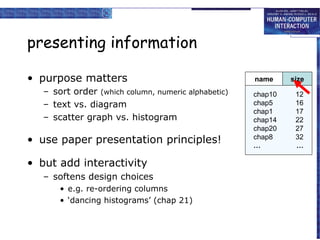
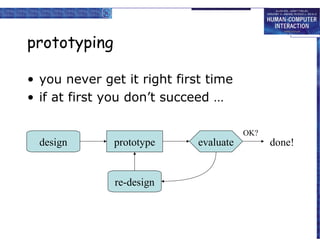
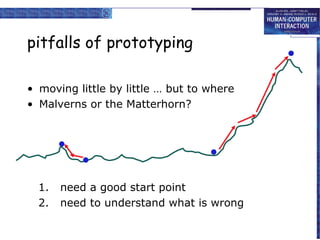
The document discusses interaction design basics and principles. It covers the design process, understanding users through personas and cultural probes, using scenarios to illustrate interactions, and considering navigation and structure at both the local screen level and global application level. Iteration and prototyping are important to refine designs based on user research and testing. The focus is on understanding users and designing interactions rather than just interfaces.