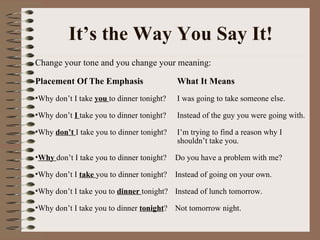
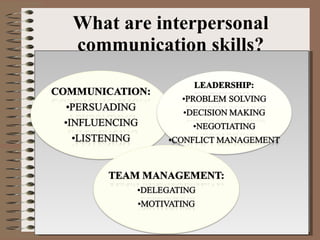
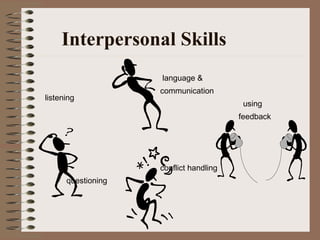
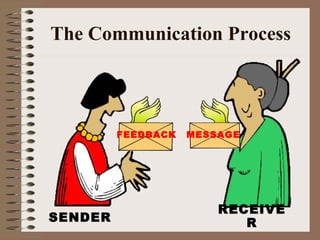
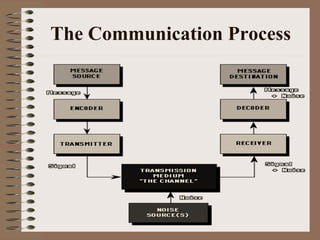
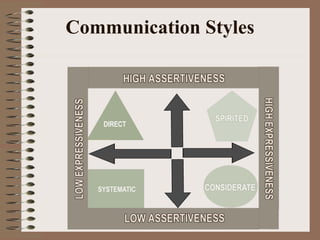
Effective communication involves using language appropriate to the audience's understanding level, ensuring the intended message is received, and developing open and honest relationships. Interpersonal communication skills include listening, questioning, providing feedback, and handling conflict. Such skills help develop self-awareness, acknowledge others' interests, and manage diversity to get the best from team members. Barriers like lack of skills, interest or feedback can interrupt the communication process between a sender and receiver.