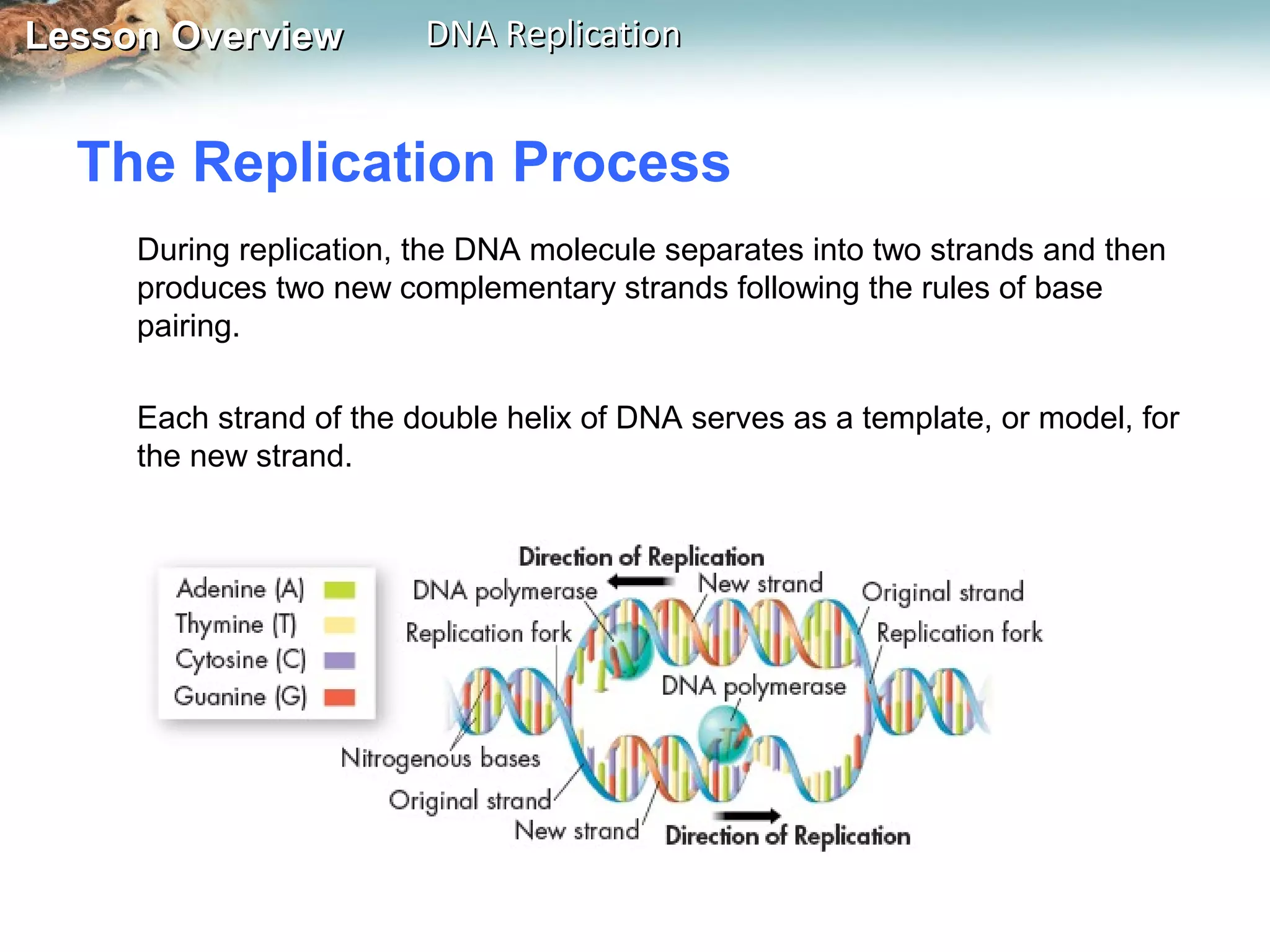
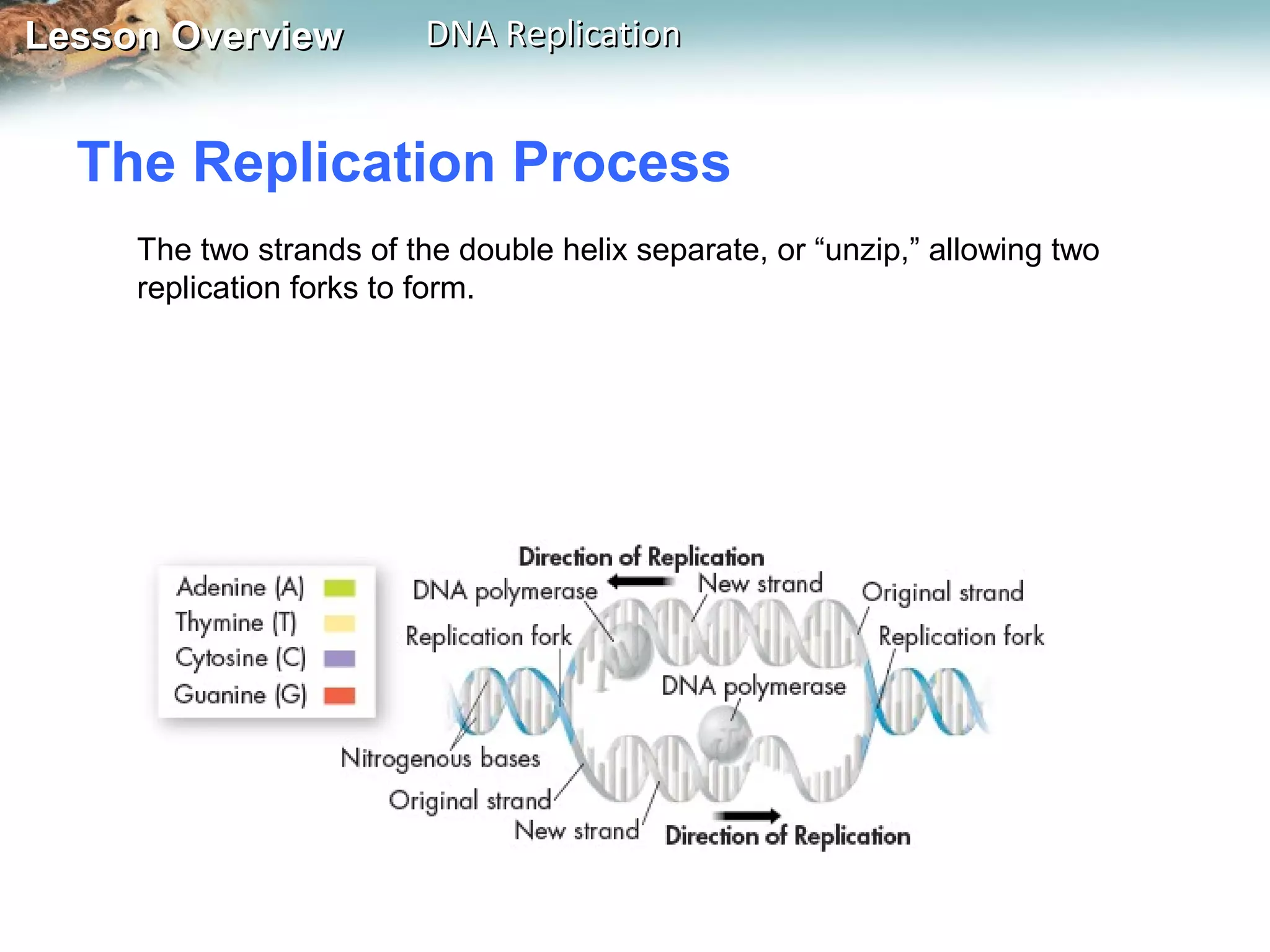
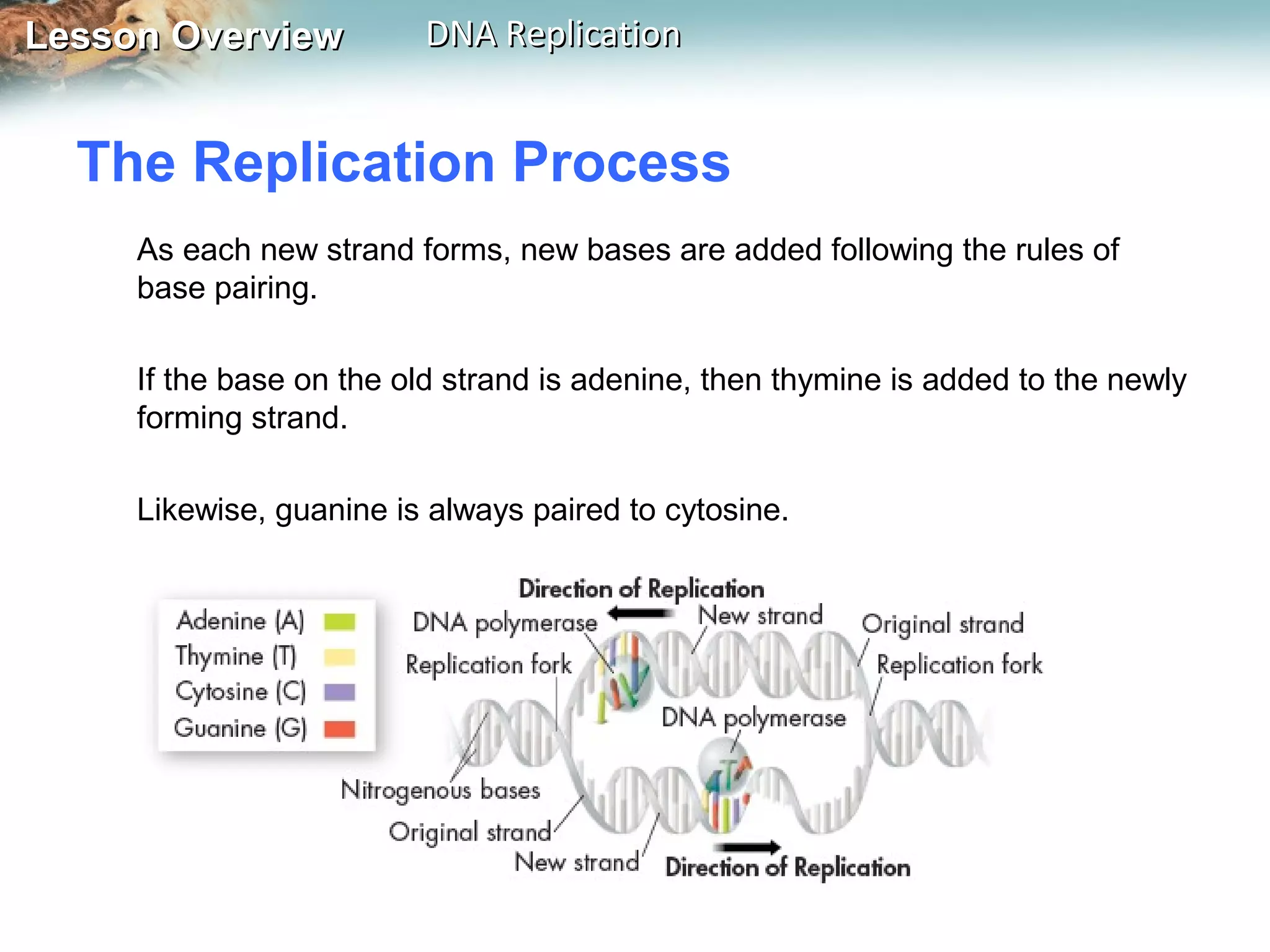
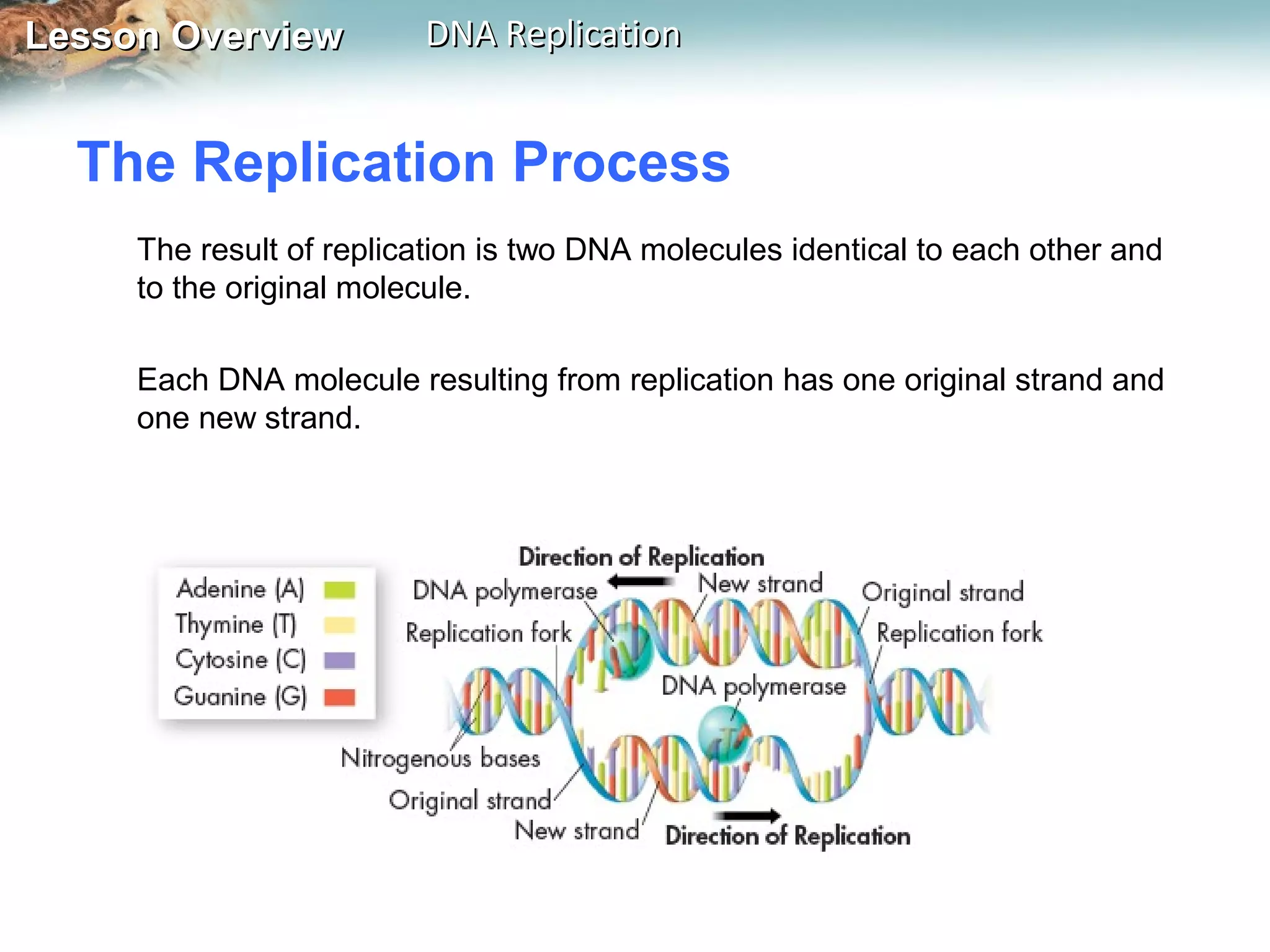
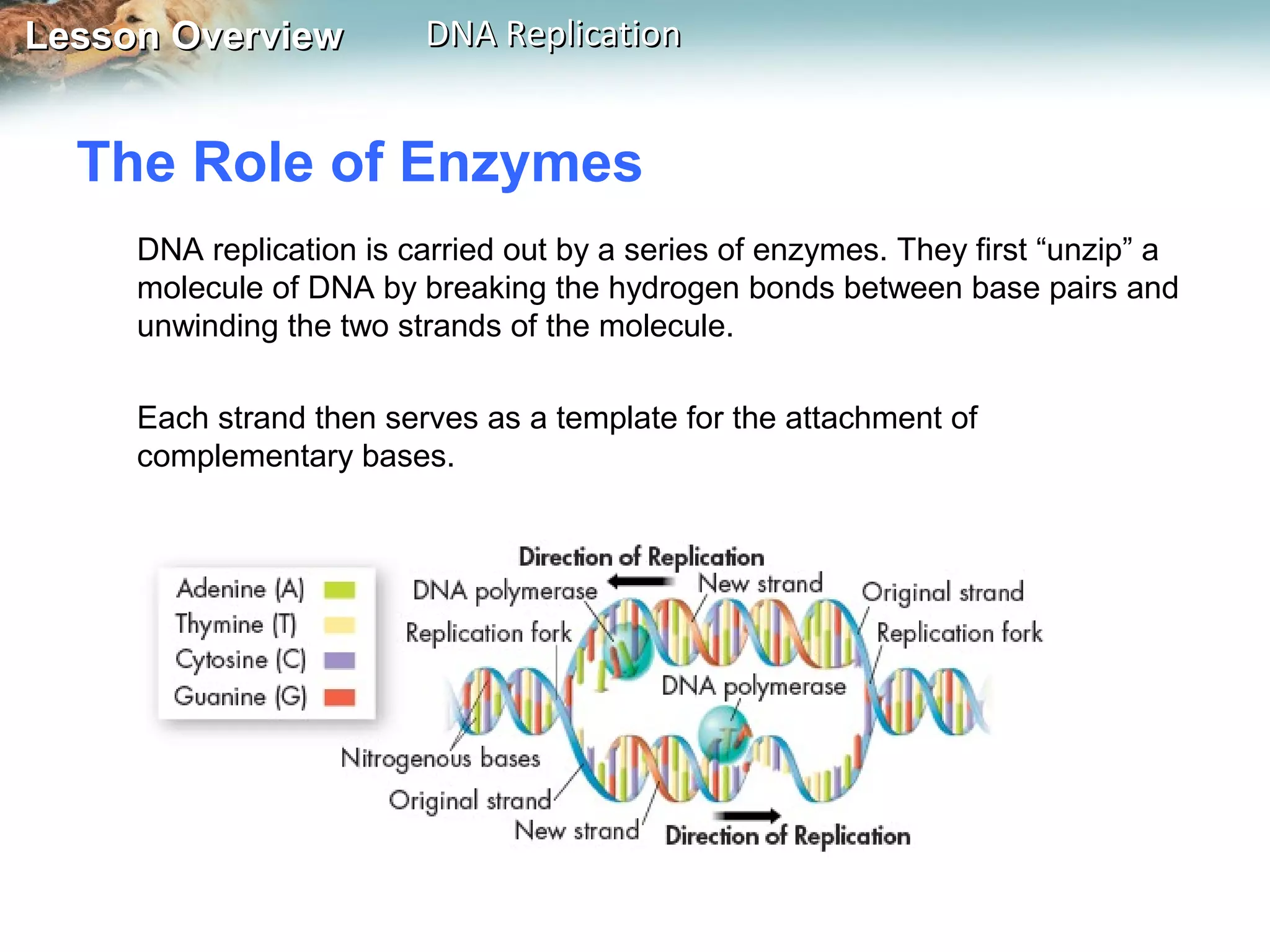
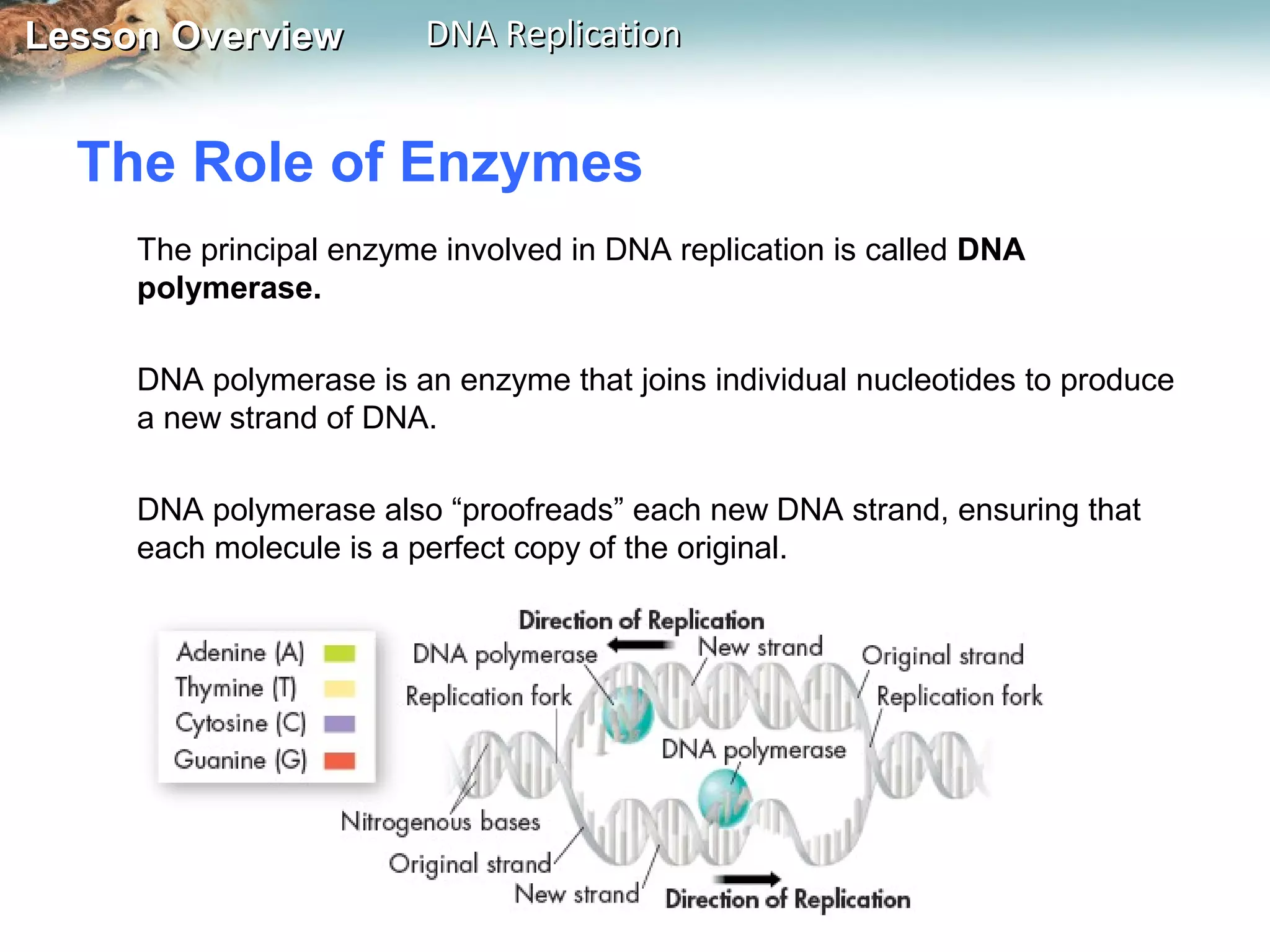
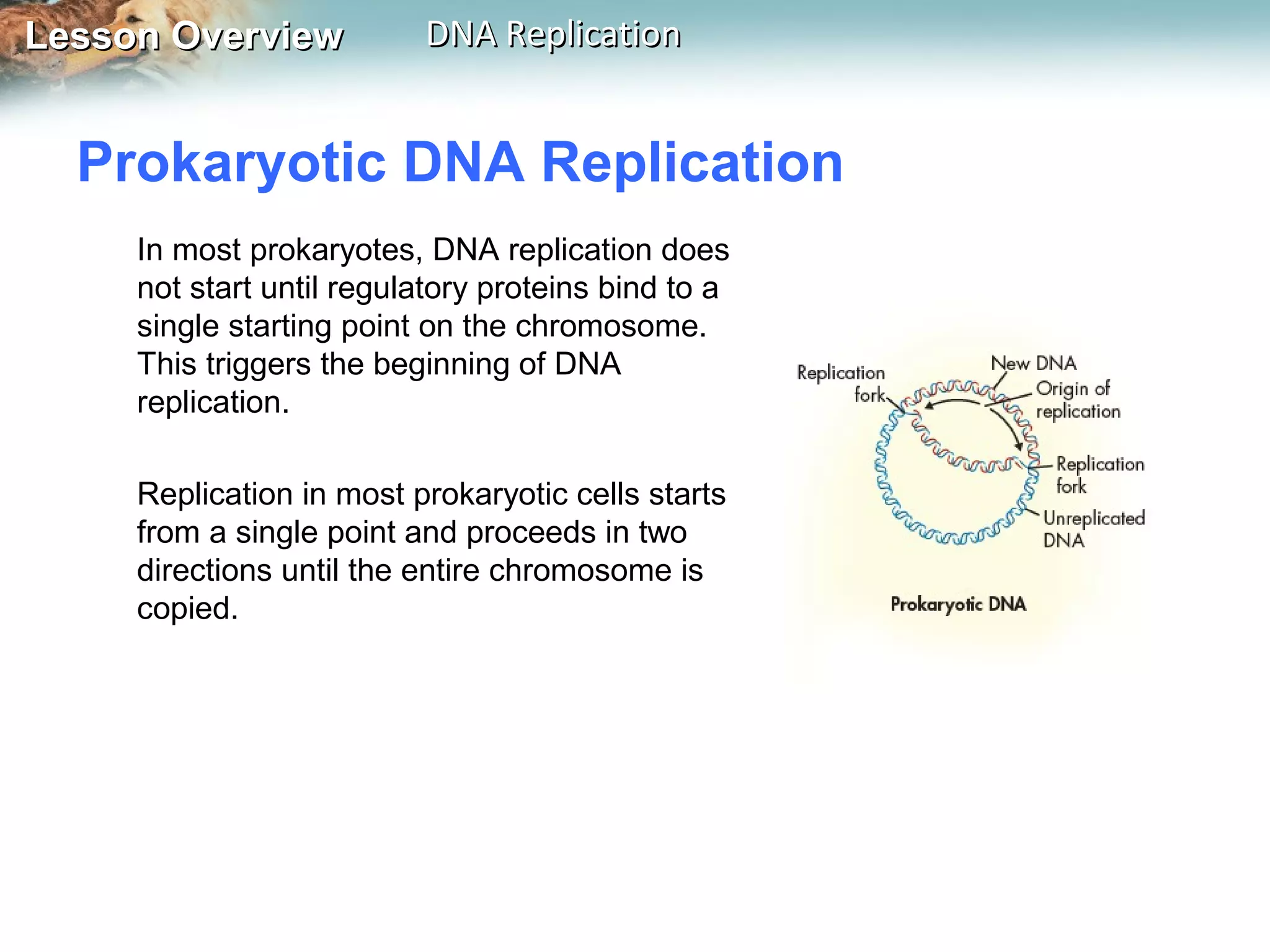
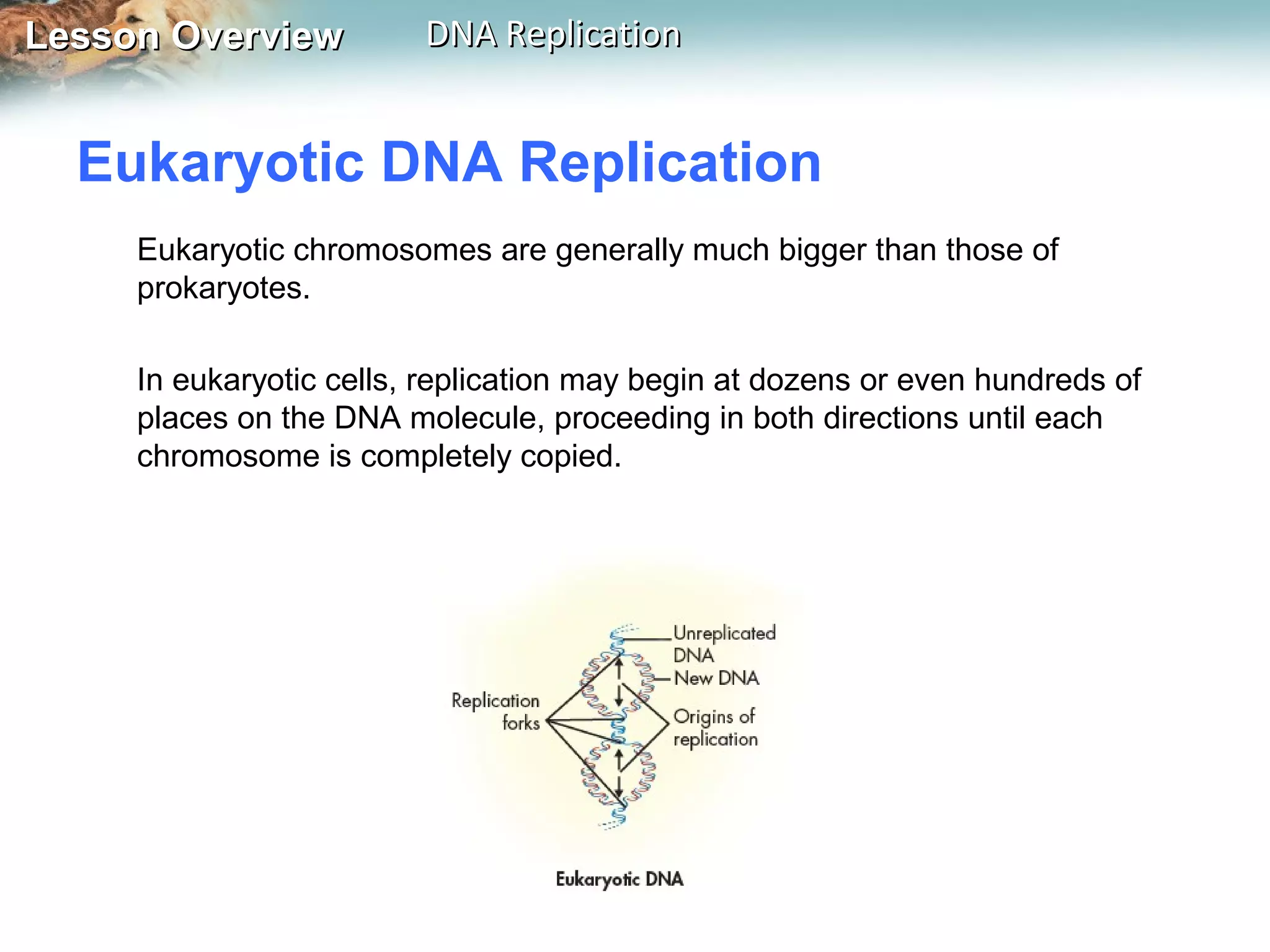
DNA replication is the process where a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. It ensures each new cell has the full DNA content. The double helix structure of DNA allows each strand to serve as a template for copying its complementary strand. In replication, enzymes separate the DNA strands and DNA polymerase enzyme adds complementary nucleotides to each strand to copy it. Replication differs between single-celled prokaryotes, which replicate from one starting point, and eukaryotes, which replicate from multiple starting points along each chromosome.