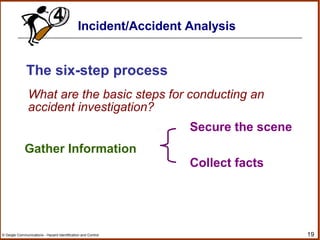
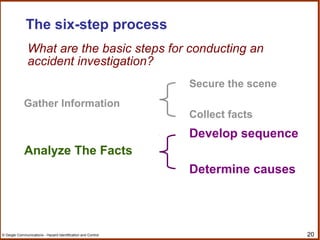
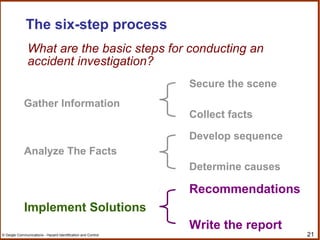
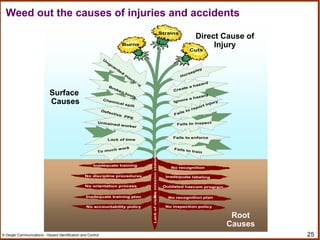
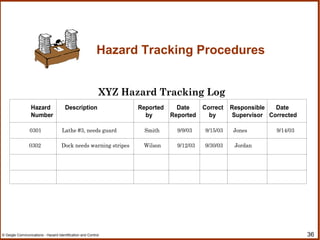
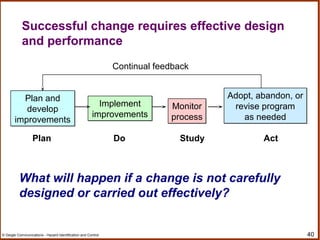
The document outlines a workshop on hazard identification and control. It discusses identifying hazards, exposure, root causes of accidents, and controlling hazards. It covers inspection, observation, job hazard analysis, incident investigation, risk analysis, and continual improvement of safety management systems. The overall goals are to explore effective hazard identification and control programs and discuss the identification and control process.