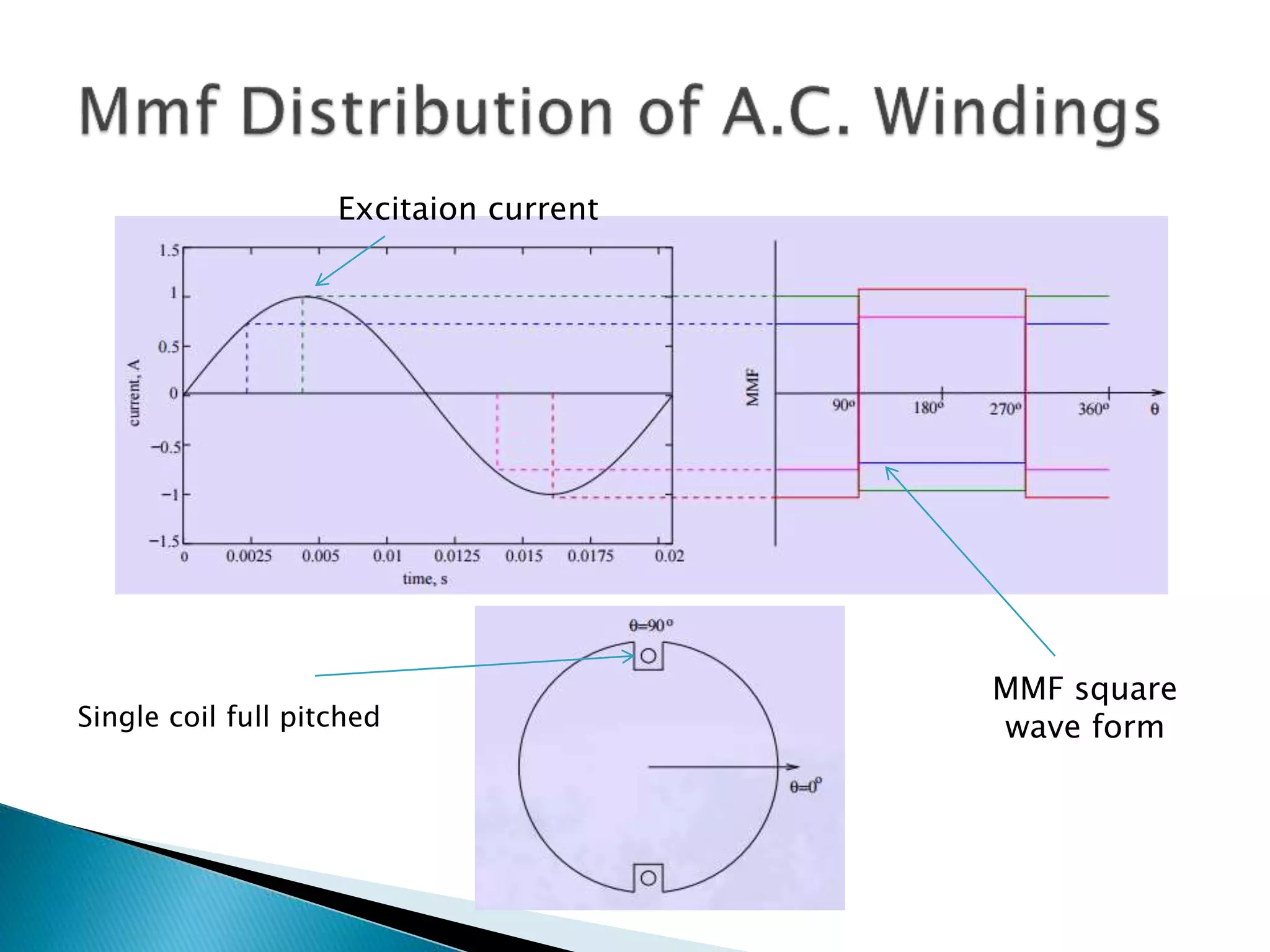
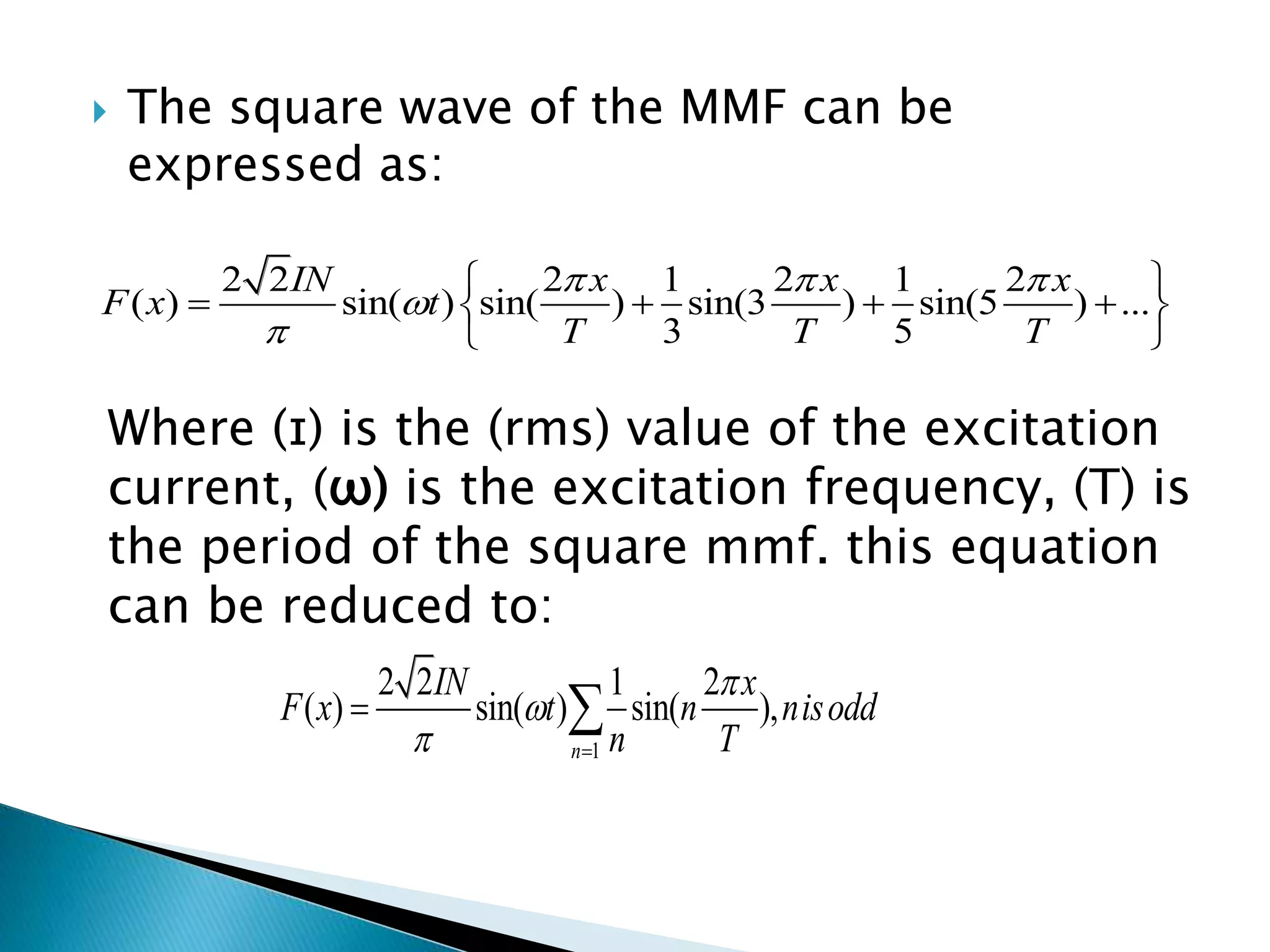
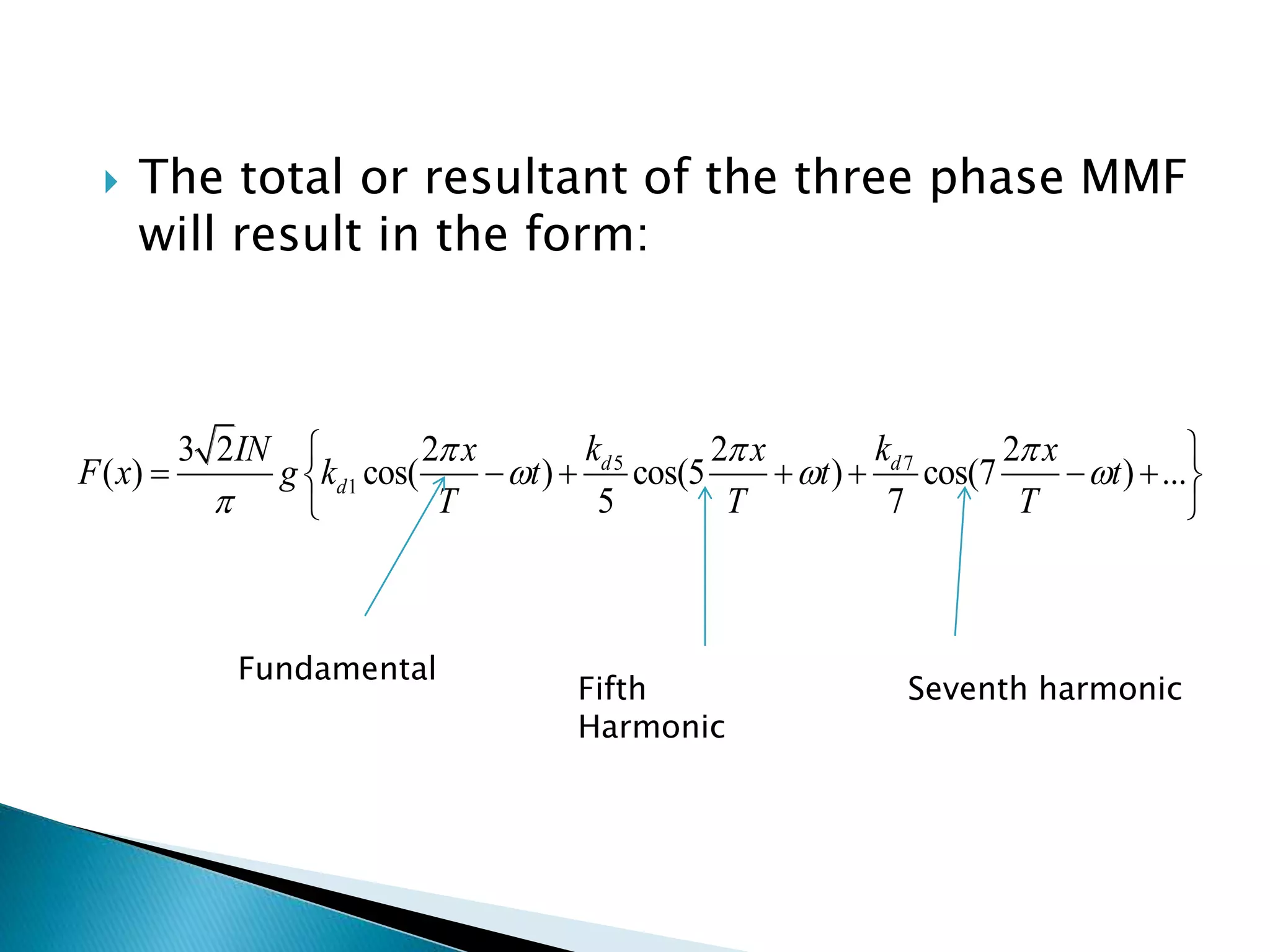
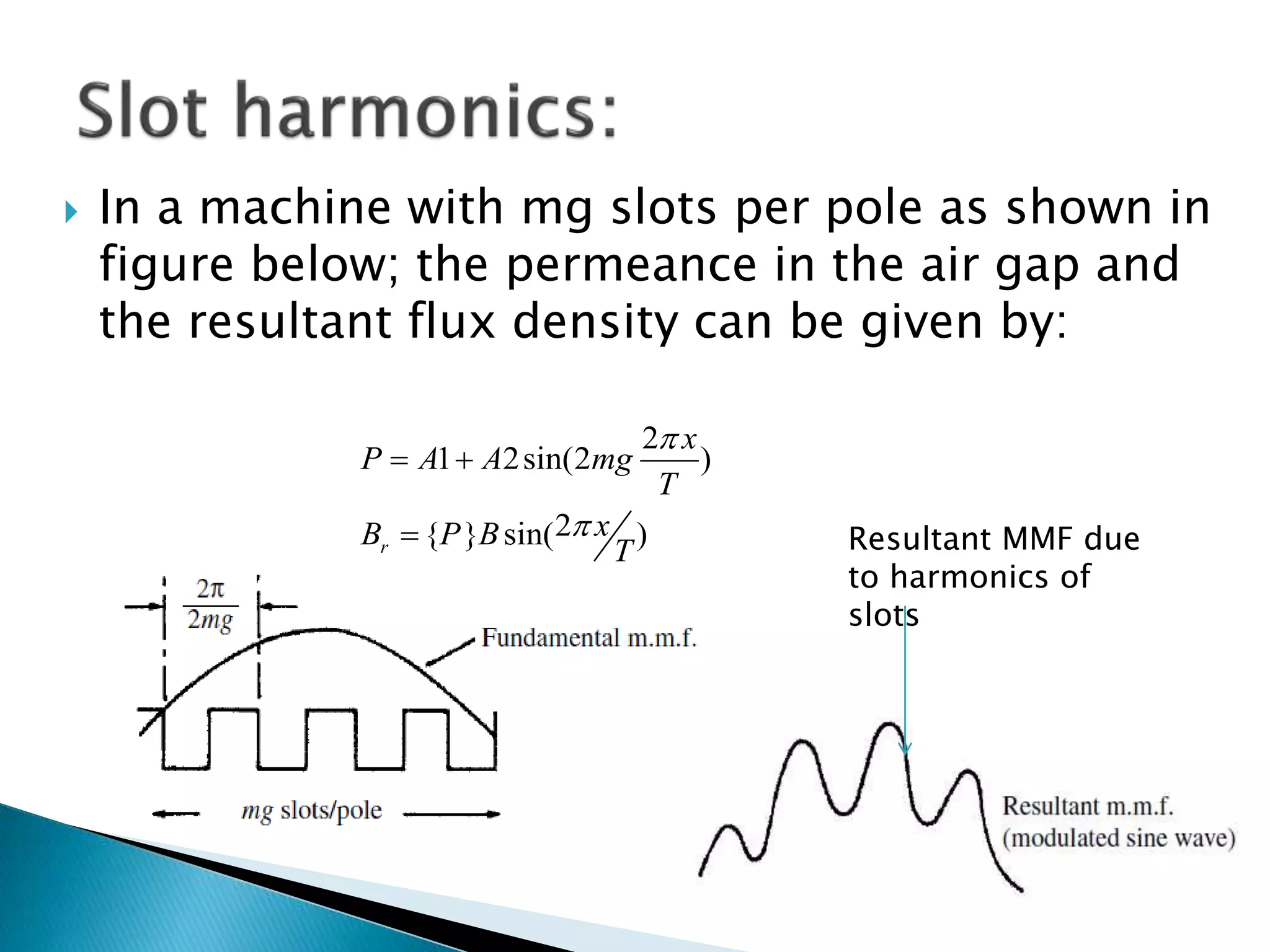
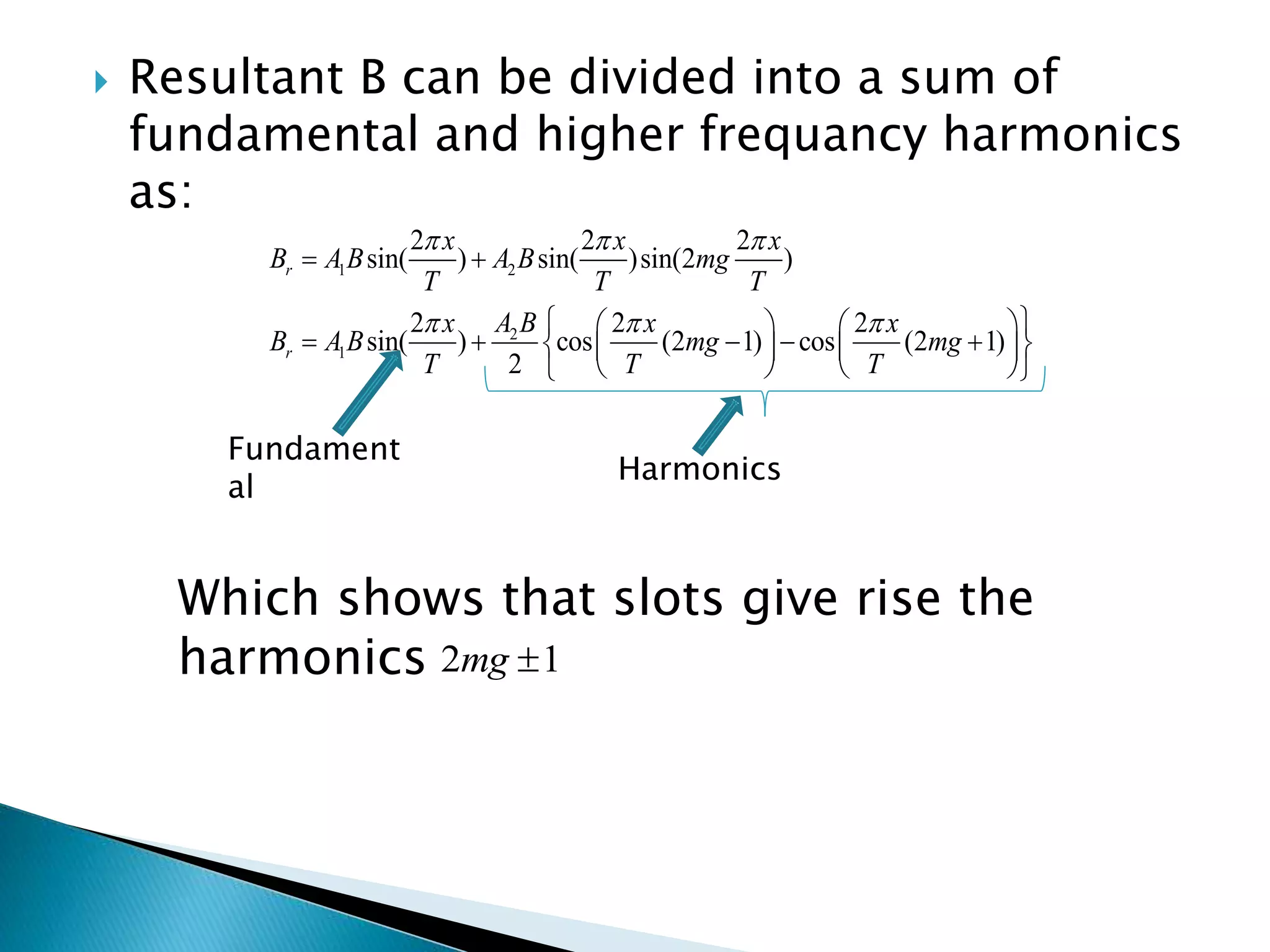
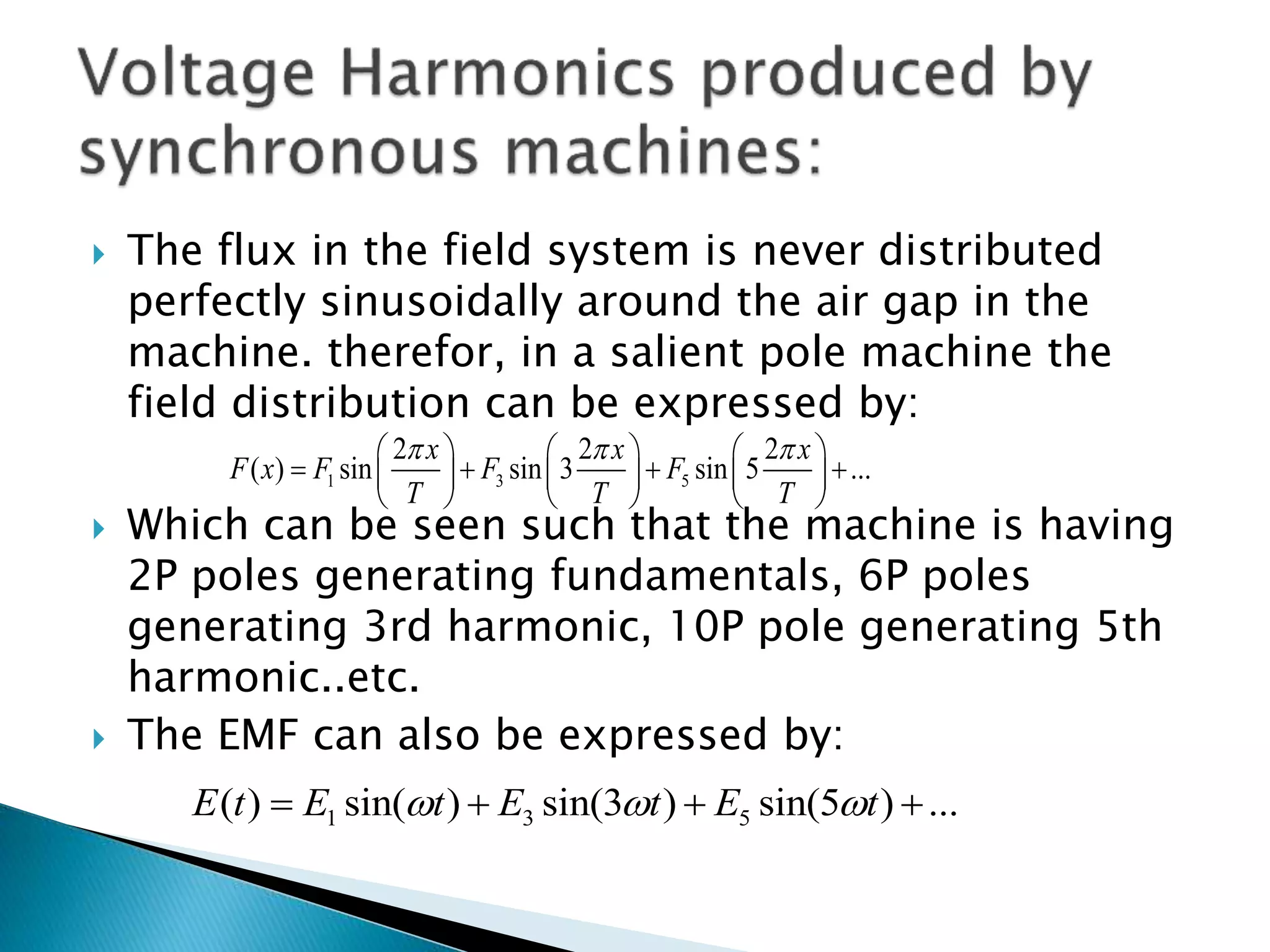
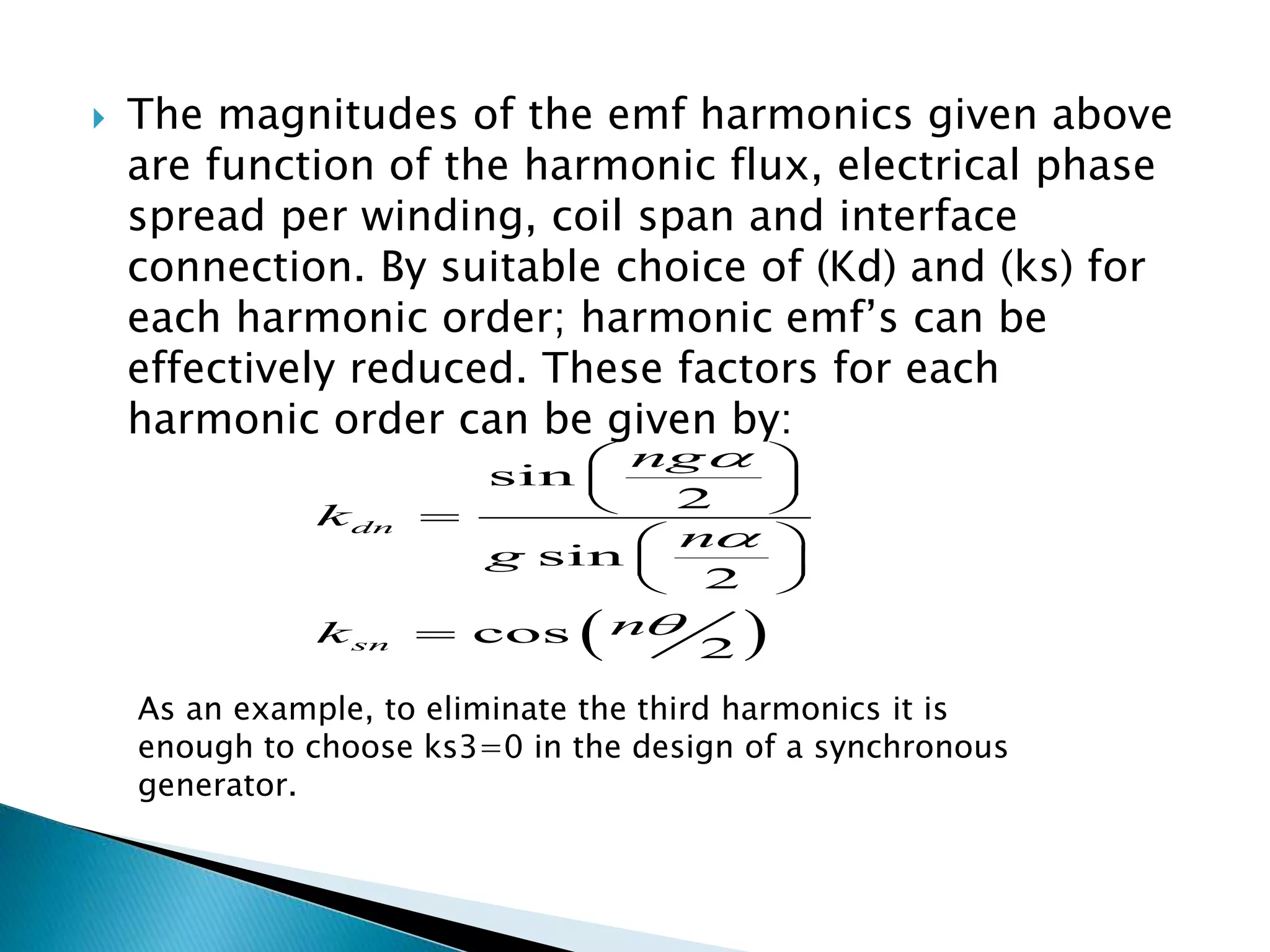
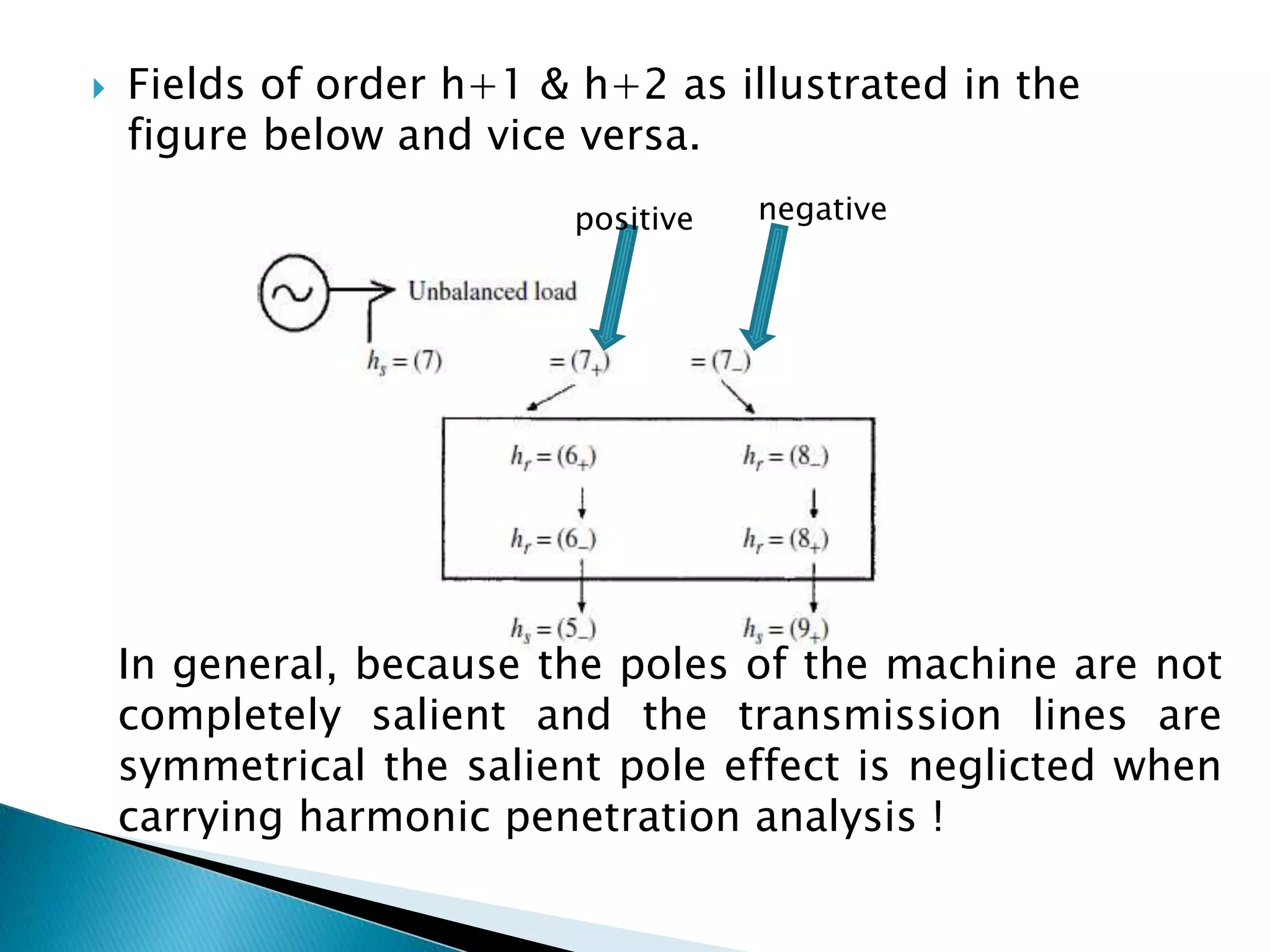
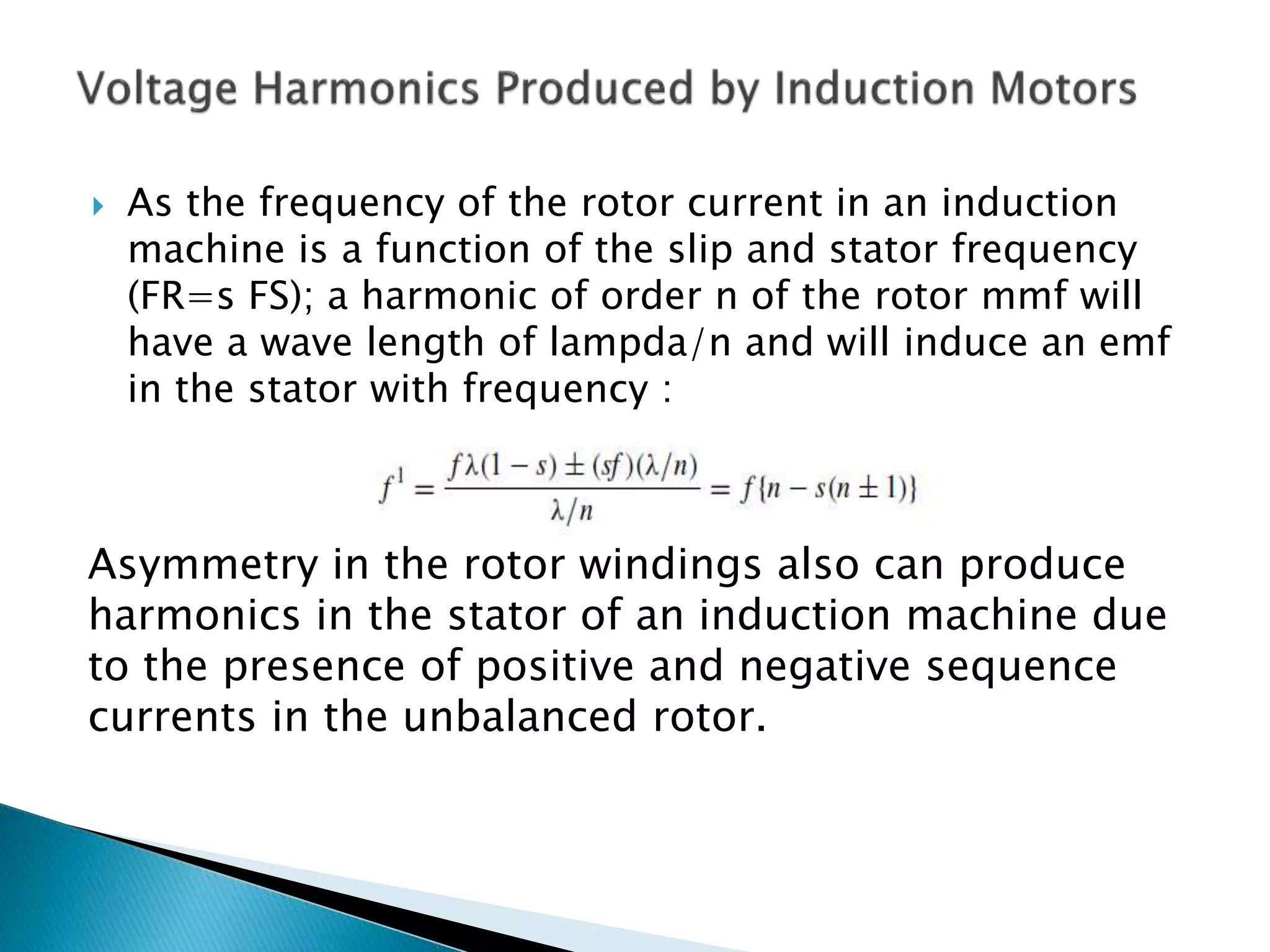
This document discusses harmonics in rotating electrical machines. It explains that the magnetic field produced by windings or slots can be expressed as the sum of the fundamental and higher frequency harmonic components. These harmonics are caused by the non-sinusoidal nature of the magnetic field and can produce unwanted voltages. The magnitudes of the harmonic voltages depend on factors like the coil span and winding configuration, which can be designed to reduce specific harmonics. Harmonics can also be generated through negative and positive sequence currents interacting with the rotor magnetic field.