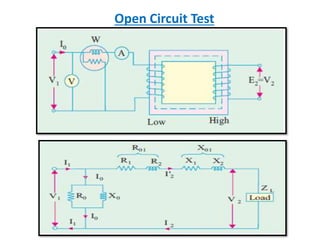
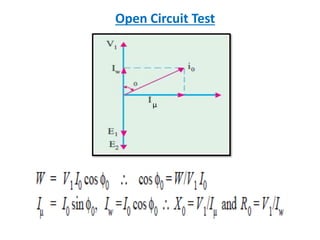
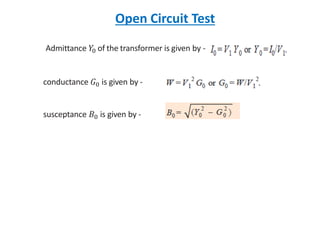
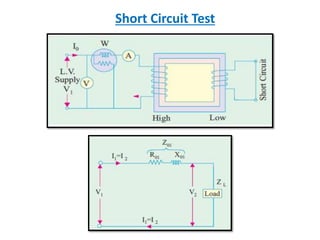
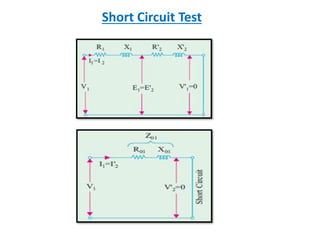
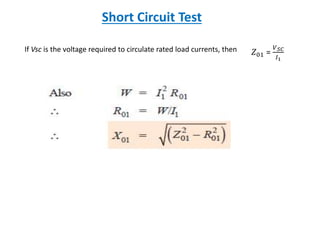
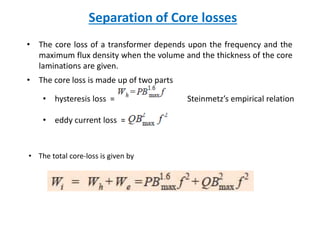
This document discusses transformer tests, including open circuit and short circuit tests. It explains that these tests are done to determine the equivalent circuit parameters, impedance, currents, efficiency, and losses of a transformer. The open circuit test is used to determine the core or iron losses, while the short circuit test determines the copper losses. Examples of calculations for each test are provided.