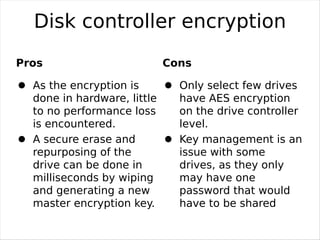
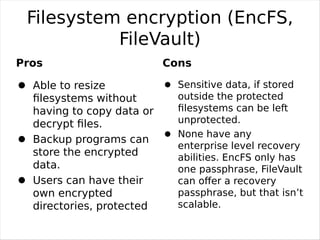
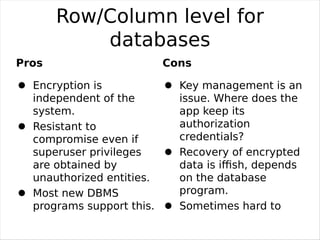
Full Hard Disk Encryption allows encrypting the entire contents of a hard disk for security and privacy. Disk encryption software encrypts every bit of data as it is written to the disk, including the operating system partitions. This prevents unauthorized access to data storage even if the computer is lost or stolen. Disk encryption can be done through hardware or software methods at different levels from the disk controller to individual files. While providing security benefits, disk encryption also has some potential downsides like additional management overhead and possible performance impacts. Open source encryption tools are available to easily enable disk encryption with minimal effects on usability or speed.