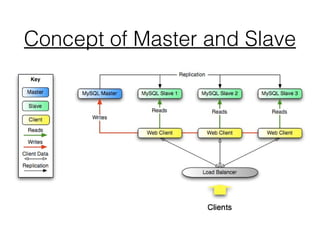
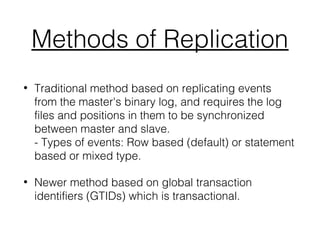
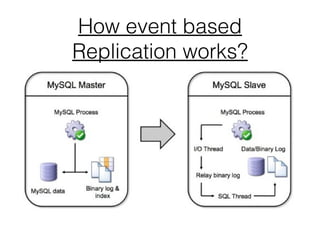
This document provides an introduction to MySQL master-slave replication. It defines replication as copying data from a master database server to one or more slave servers. The key concepts of master and slave are explained. Advantages of replication include scaling out solutions, increasing data security, enabling analytics, and distributing data over long distances. Event-based and GTID-based replication methods are described. The document also demonstrates setting up master-slave replication between two AWS MySQL instances and provides guidance on when replication is best used, such as for systems with many reads and few writes.