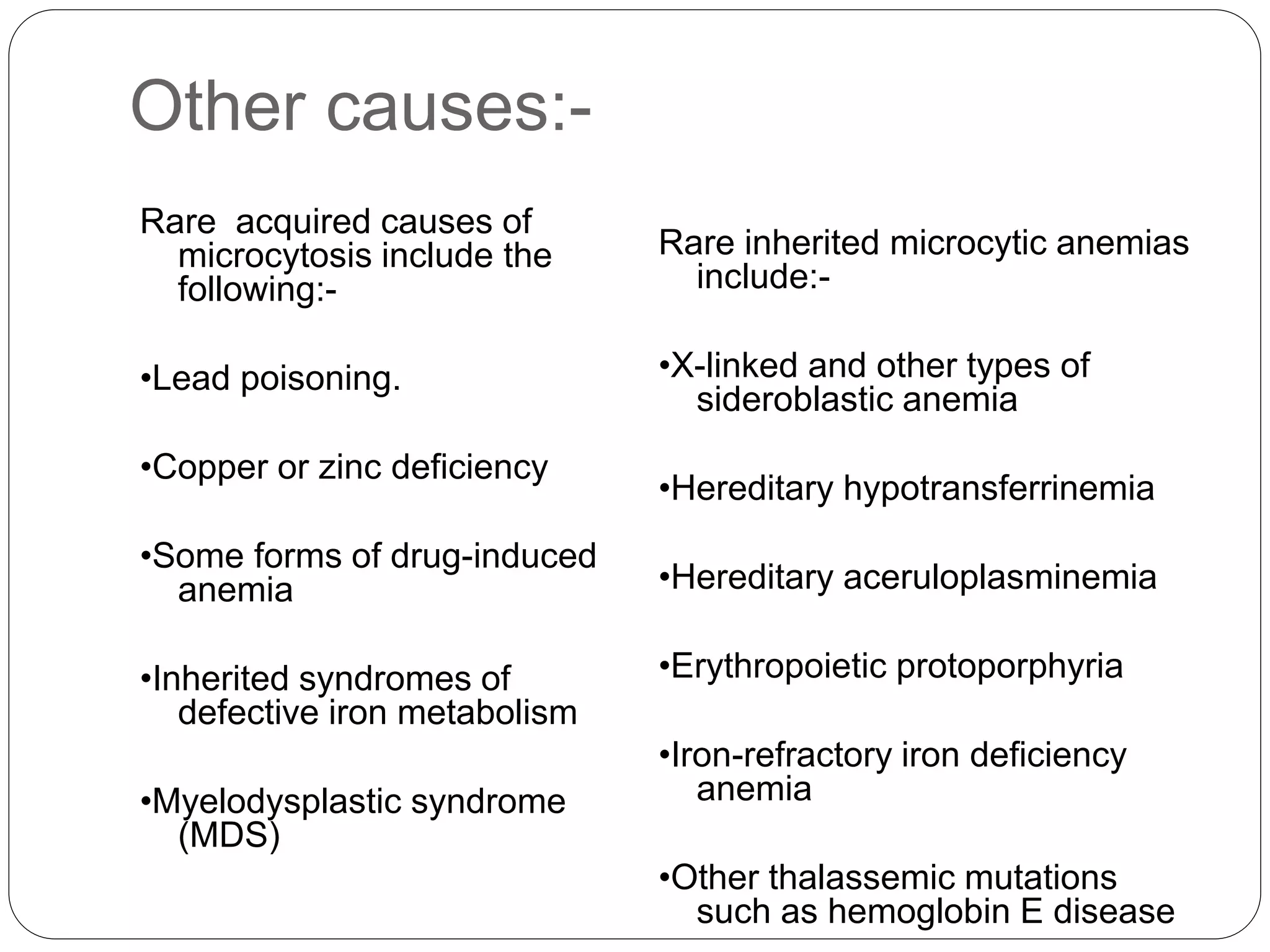
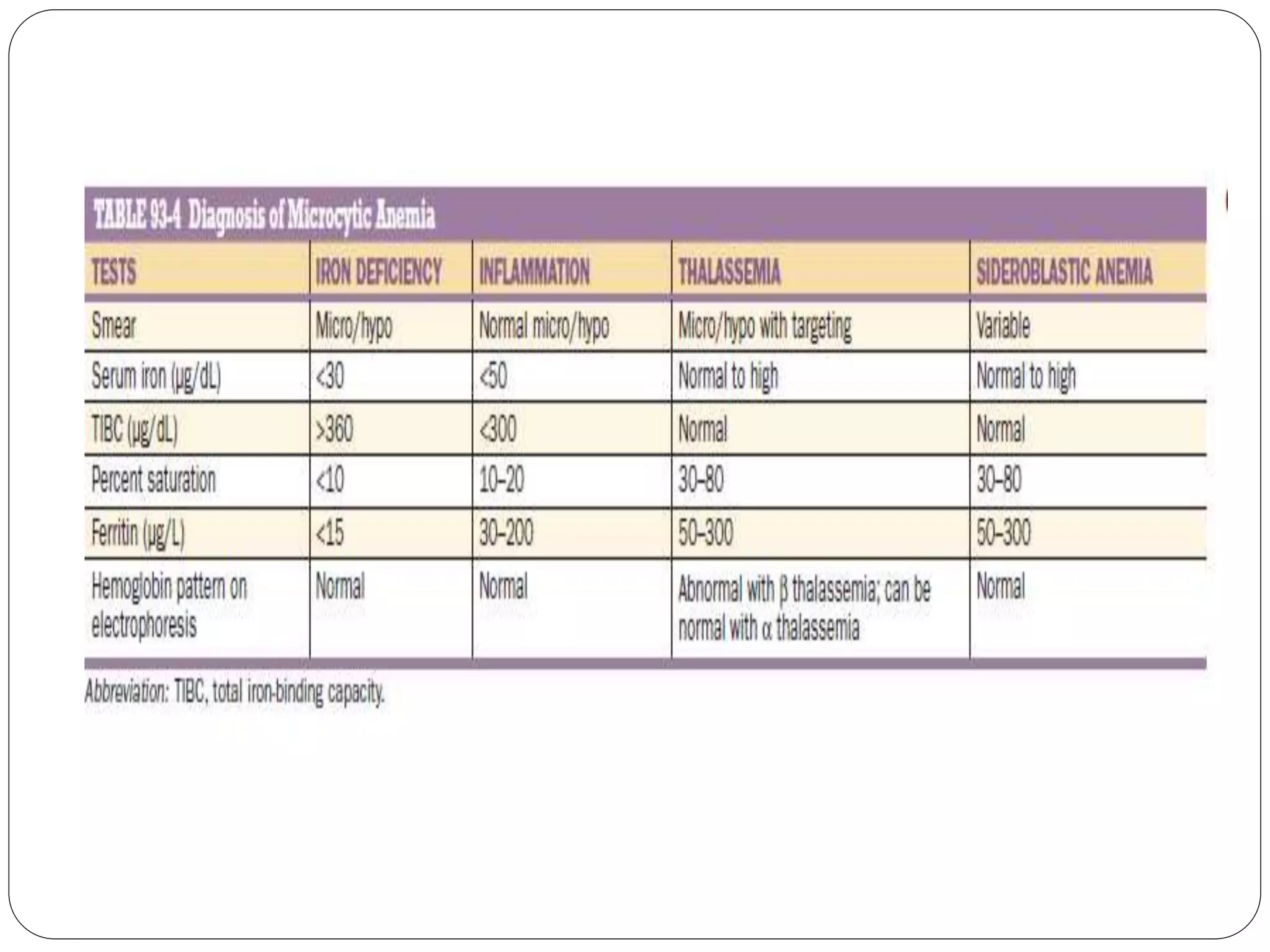
1. Microcytic anemia can be identified by a low MCV on a CBC, small RBCs on a blood smear, or an increased RDW. The most common causes are iron deficiency anemia and thalassemia.
2. Iron deficiency anemia is usually caused by inadequate dietary iron intake or increased needs. It often affects young children, women, and pregnant women. Ferritin levels below 15 ng/mL indicate iron deficiency.
3. Thalassemia involves a genetic defect in hemoglobin production and is more common in those of Mediterranean, Southeast Asian, and African descent. Beta-thalassemia trait causes mild anemia while alpha-thalassemia trait
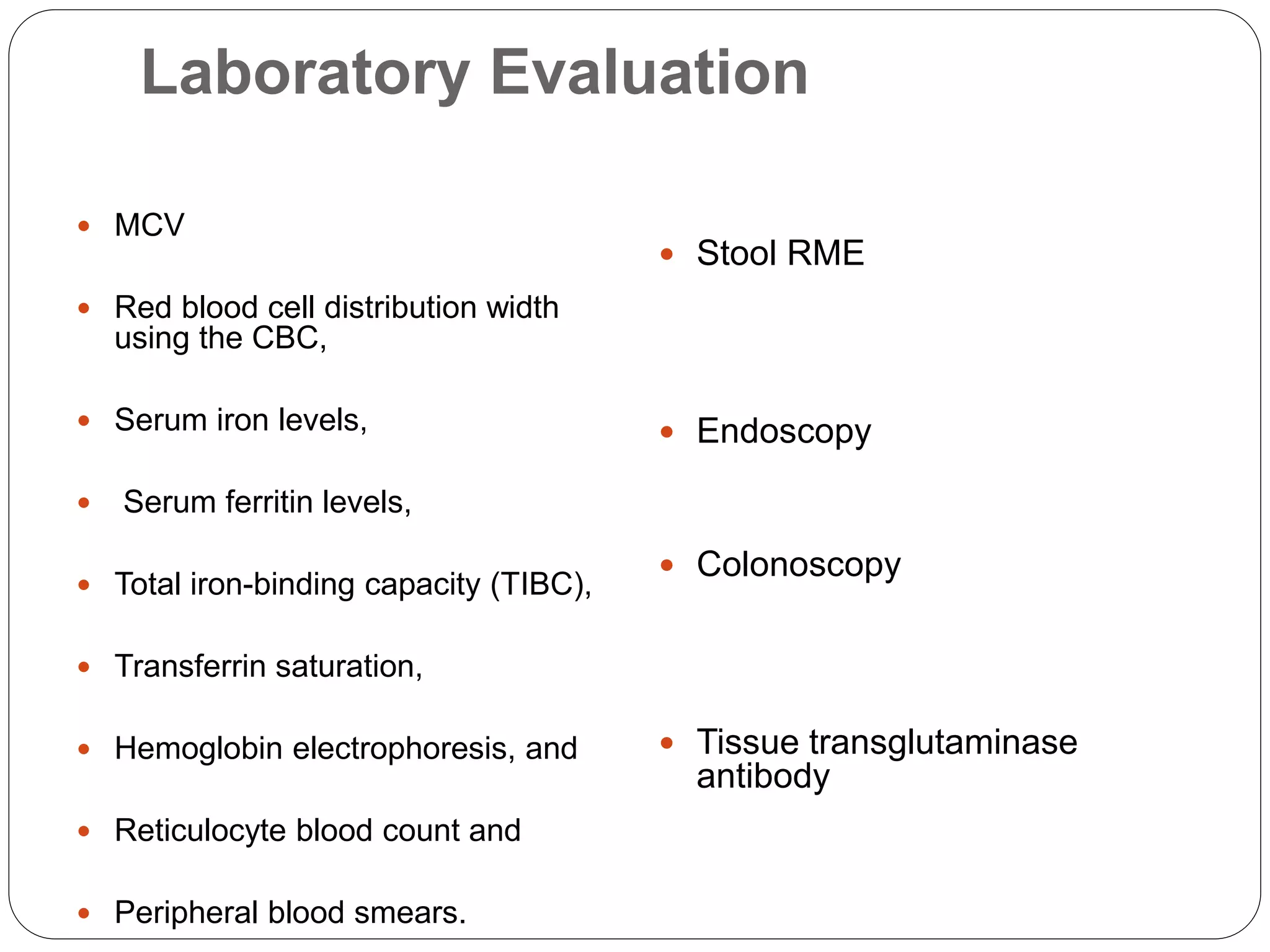
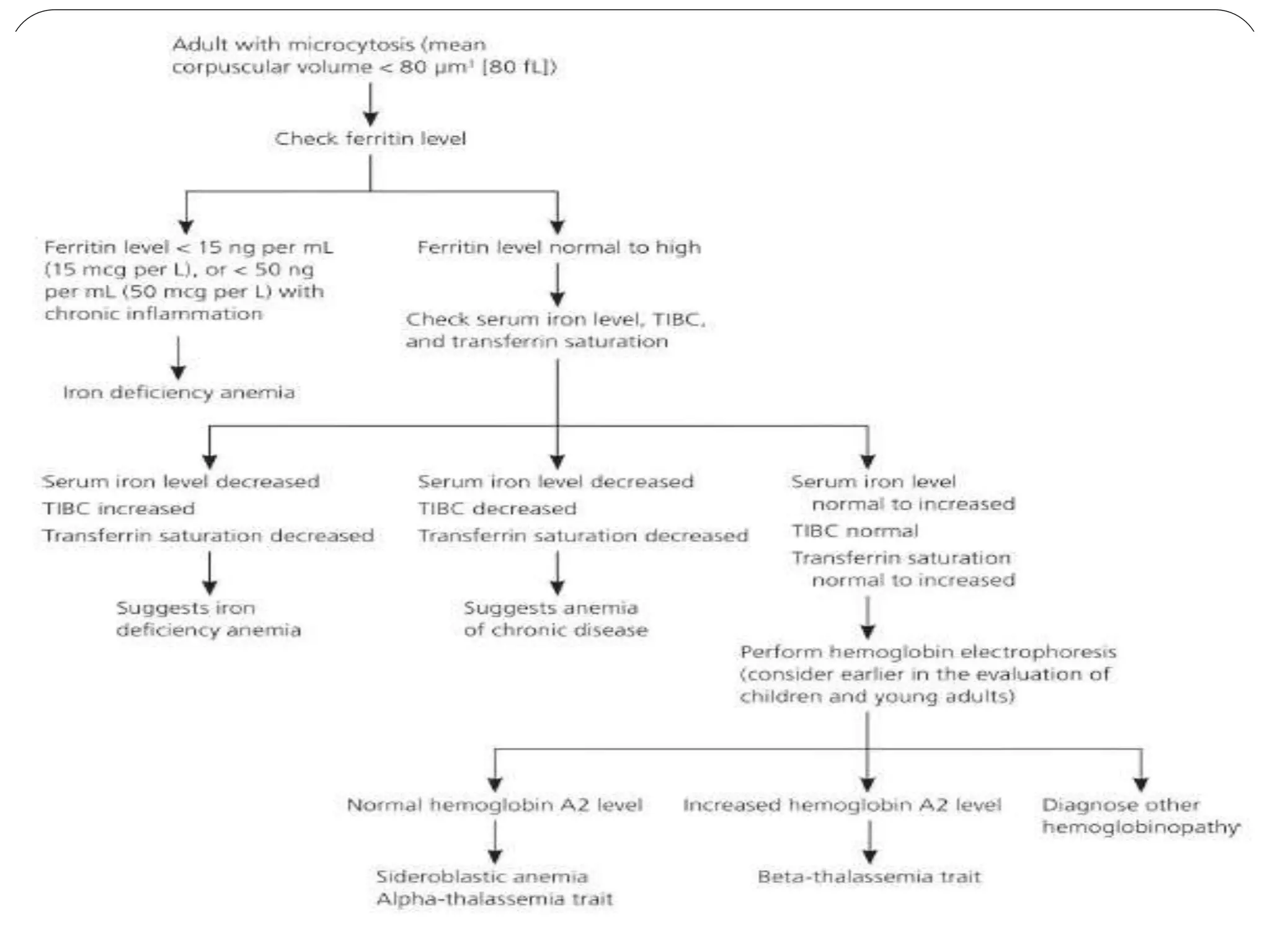
![Microcytosis can be documented from
1. the mean cell volume (MCV) on an automated hematology instrument (ie, MCV
below 80 femtoliters [fL] for an adult or below the age-appropriate value for children) or
2. from examination of the peripheral blood smear. Variation in cell size can be
assessed from the red blood cell (RBC) distribution width (RDW) or
3. from observing the degree of anisocytosis on the blood smear.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtomicrocyticanemia-200827155645/75/Approach-to-microcytic-anemia-2-2048.jpg)




![THALASSEMIA:-
Most patients with beta-thalassemia trait have mild
anemia (hemoglobin level is rarely less than 9.3 g per
dL [93 g per L]).
In addition, the mean corpuscular volume can
sometimes reach much lower levels than with iron
deficiency anemia alone.
Ultimately, the diagnosis of beta-thalassemia trait is
made when hemoglobin electrophoresis shows a
slight increase in hemoglobin A2.
Coexisting iron deficiency anemia can lower
hemoglobin A2 levels; therefore, iron deficiency
anemia must be corrected before hemoglobin
electrophoresis results can be appropriately
evaluated.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approachtomicrocyticanemia-200827155645/75/Approach-to-microcytic-anemia-7-2048.jpg)