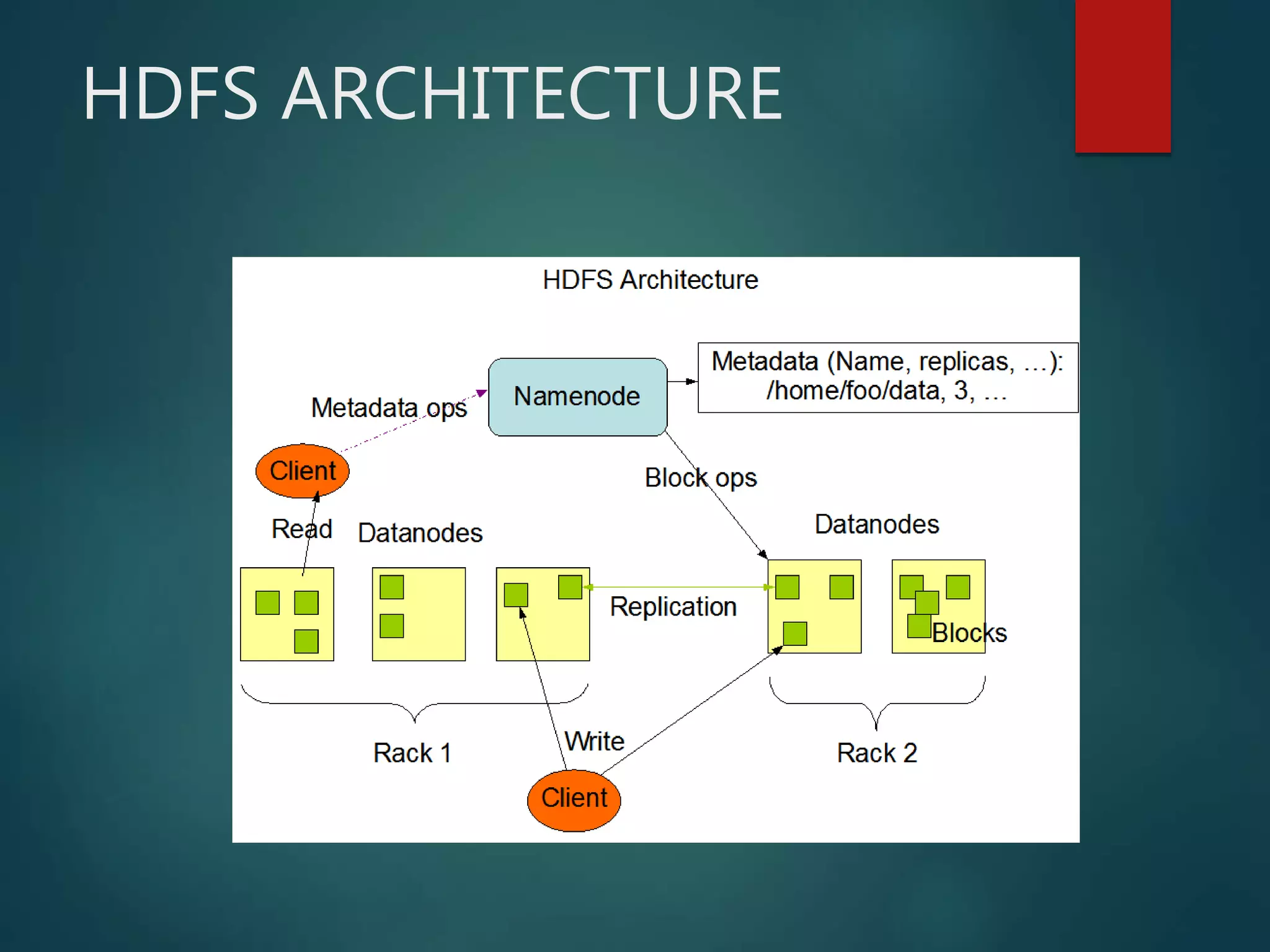
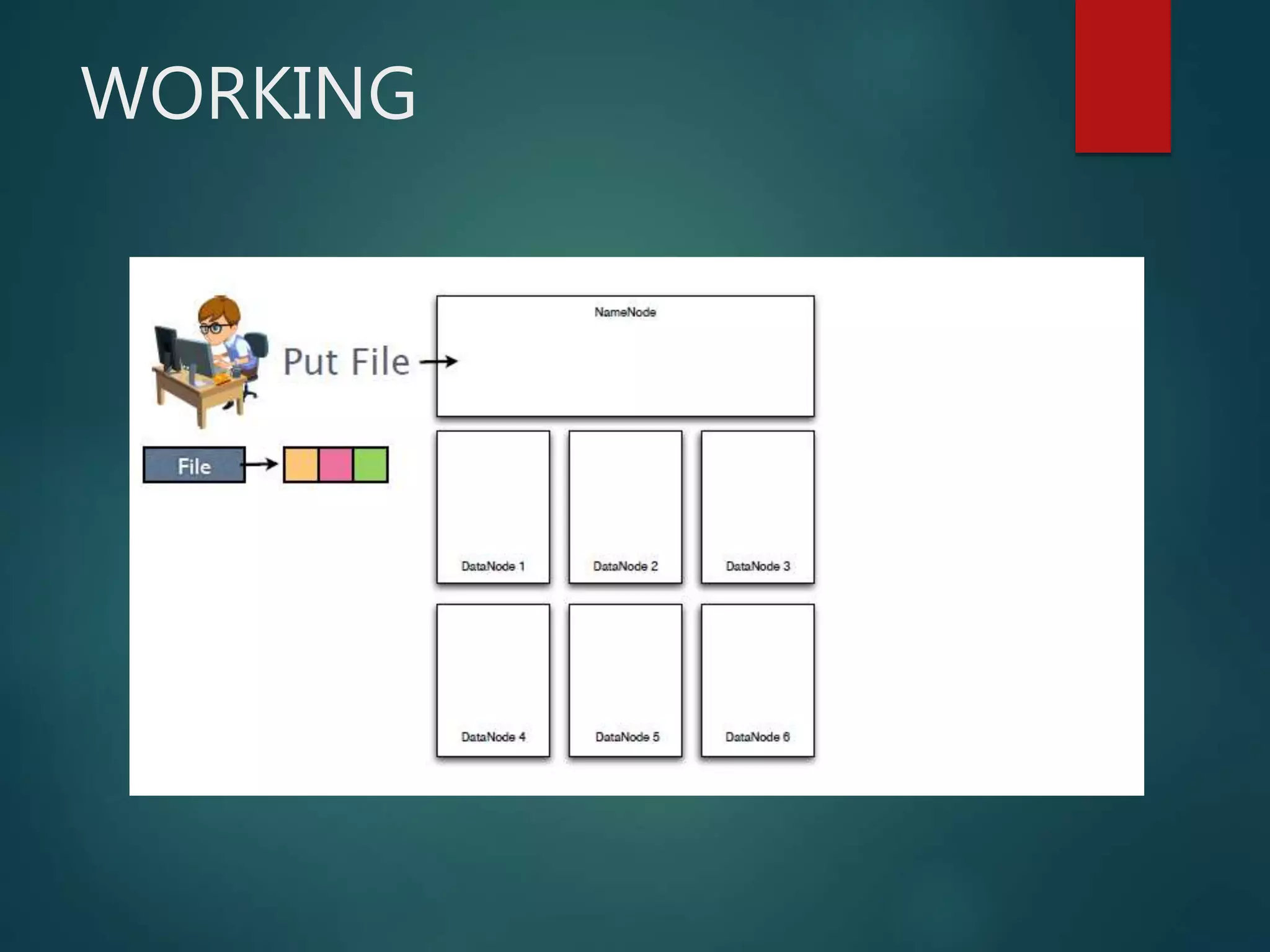
Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) is an open-source software framework that provides distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of commodity hardware. HDFS has two main components - HDFS for storage and MapReduce for distributed processing. HDFS uses a master-slave architecture with a NameNode master and DataNodes slaves. The NameNode manages the file system namespace and metadata, while DataNodes store data blocks and report to the NameNode.