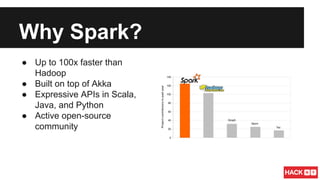
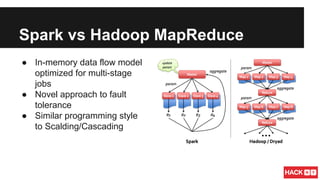
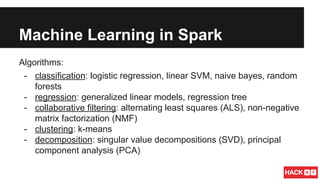
This document summarizes a presentation about scalable machine learning with Apache Spark. It introduces Apache Spark and its advantages over Hadoop MapReduce like being up to 100x faster. It provides examples of using Spark for word count, k-means clustering, and gradient descent. It also gives an overview of machine learning algorithms supported in Spark's MLlib like classification, regression, collaborative filtering, and clustering.