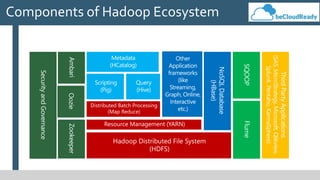
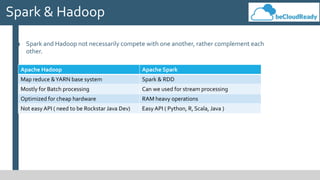
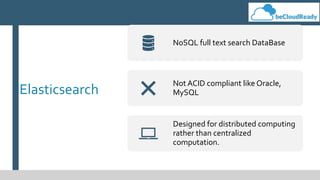
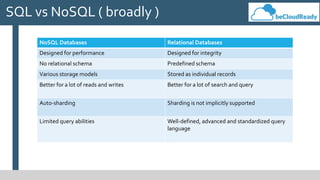
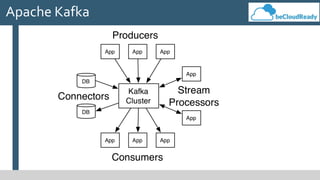
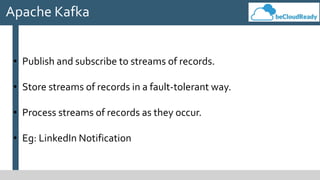
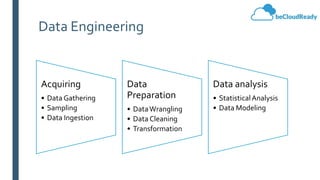
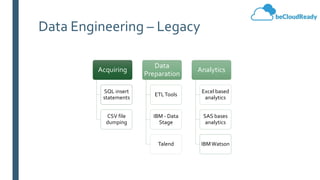
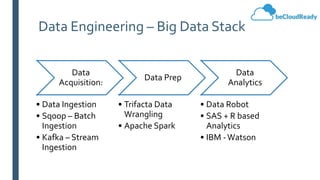
This document provides an overview of big data concepts and related technologies. It discusses what big data is, how Apache Hadoop uses MapReduce for distributed storage and processing of large datasets. Key components of the Hadoop ecosystem are described including HDFS for storage and YARN for resource management. Apache Spark is presented as an alternative to Hadoop for its in-memory computing capabilities and support for stream processing. Spark can complement Hadoop. Elasticsearch is introduced as a NoSQL database for full text search. Apache Kafka is summarized as a system for publishing and processing streams of records. Data engineering processes of acquiring, preparing, and analyzing data are outlined for both legacy and big data systems.