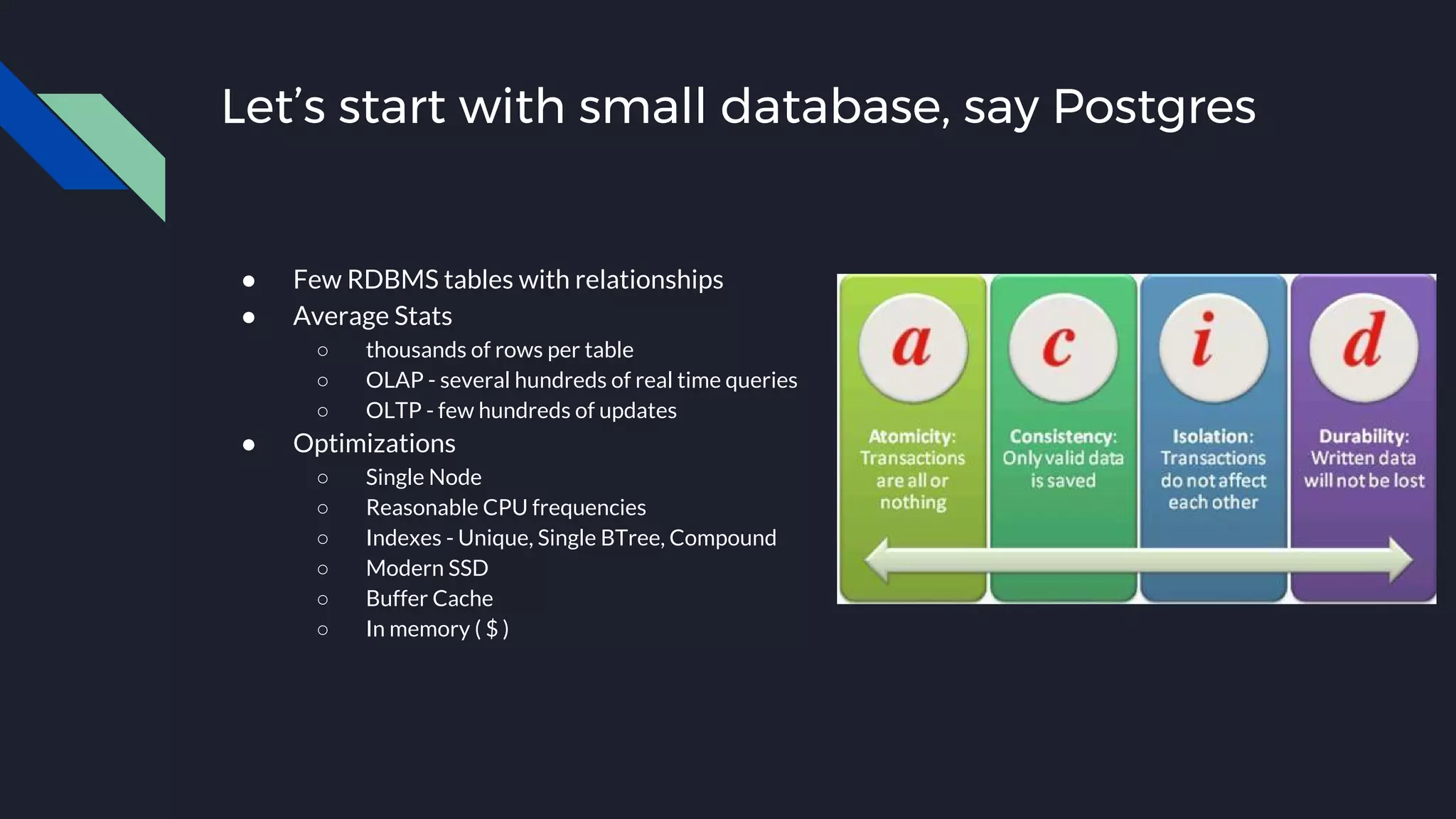
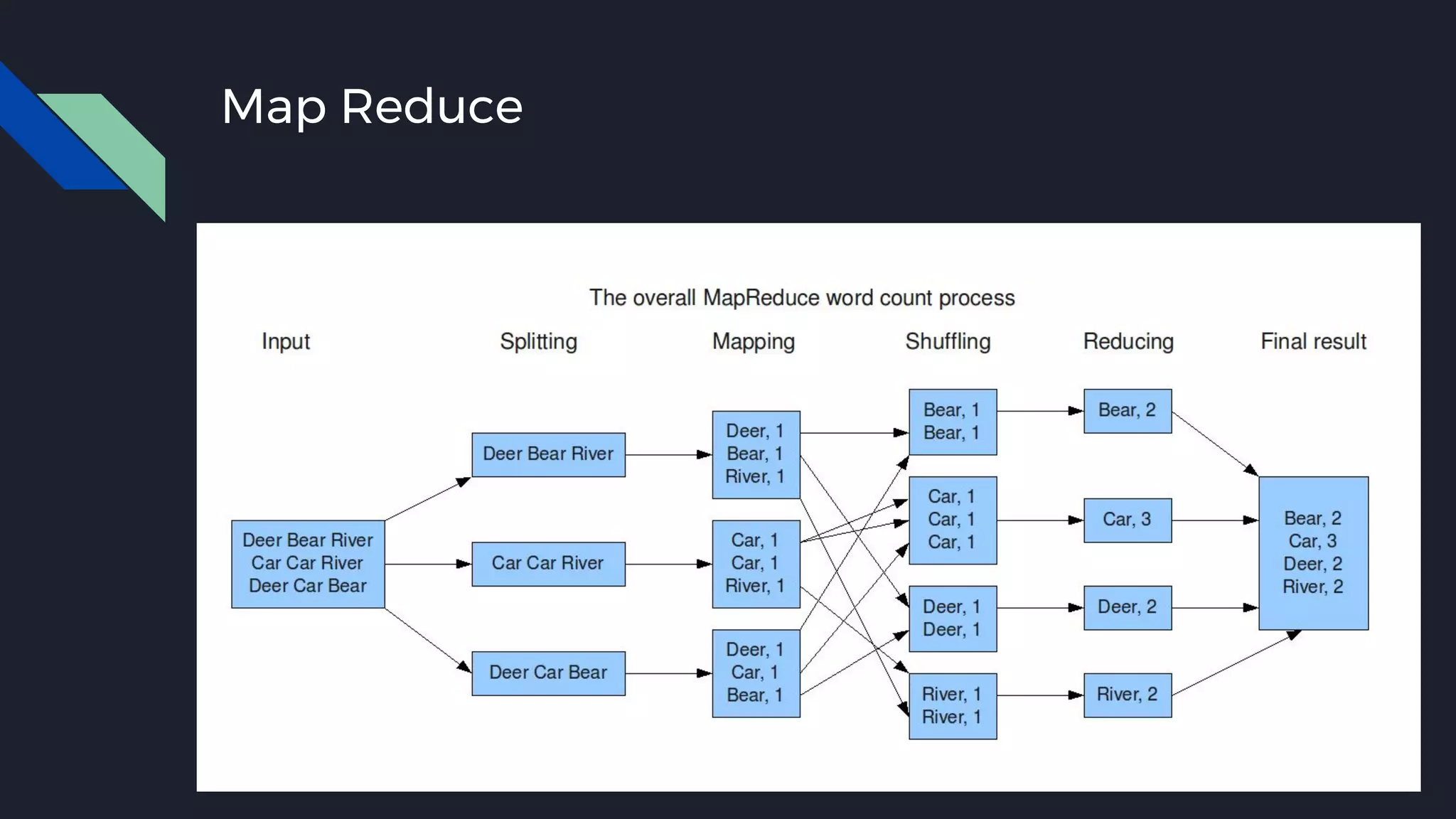
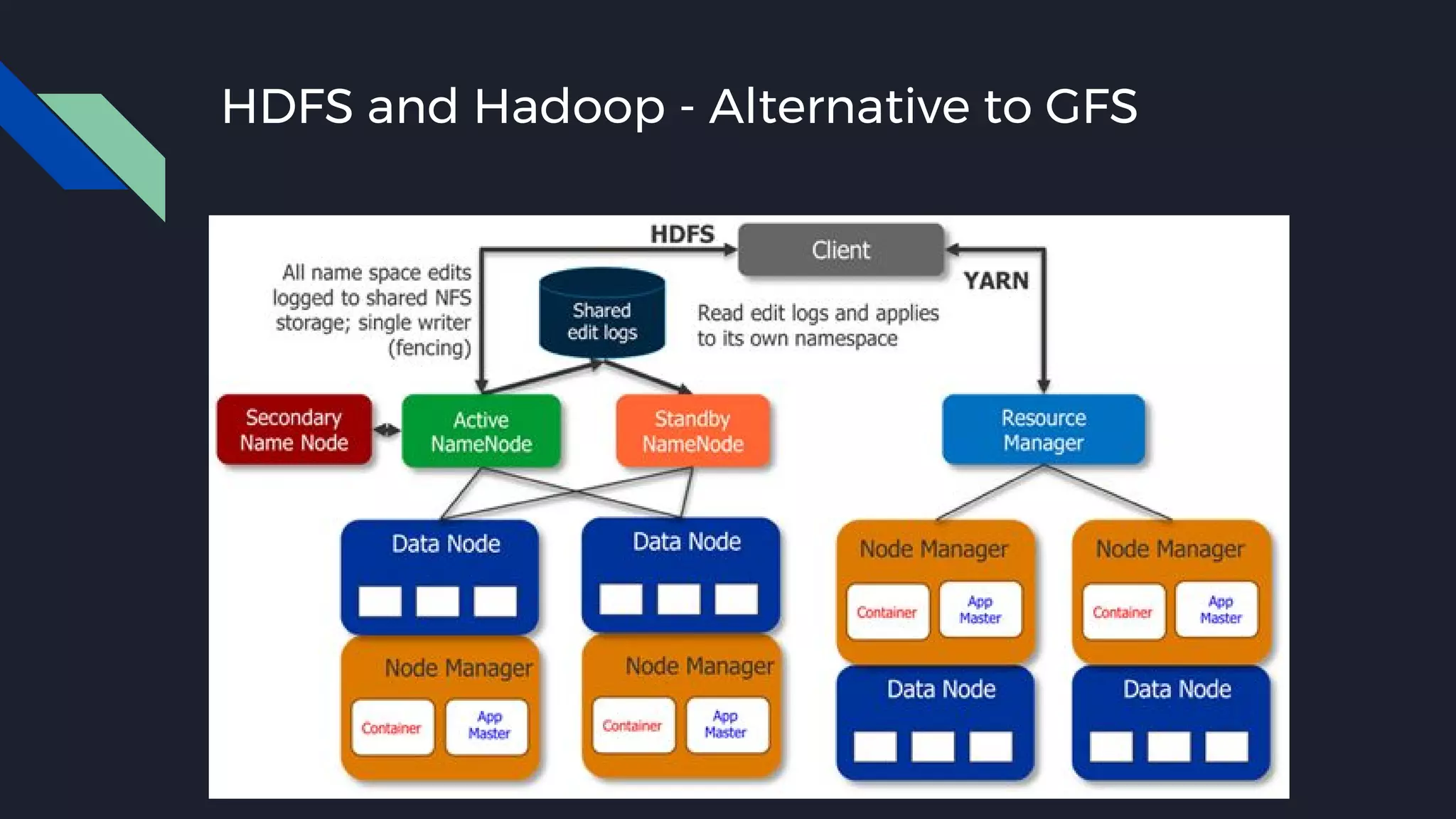
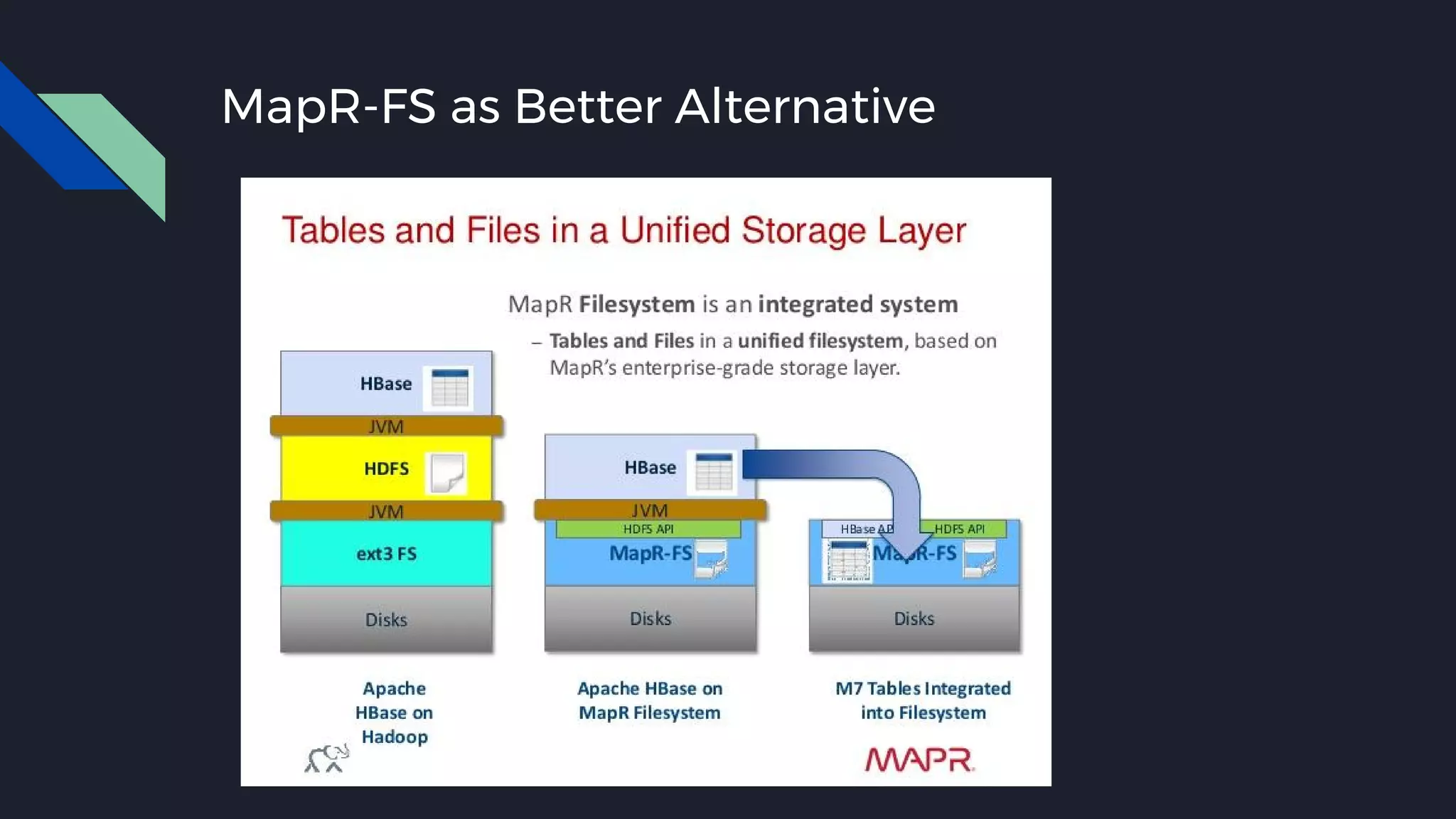
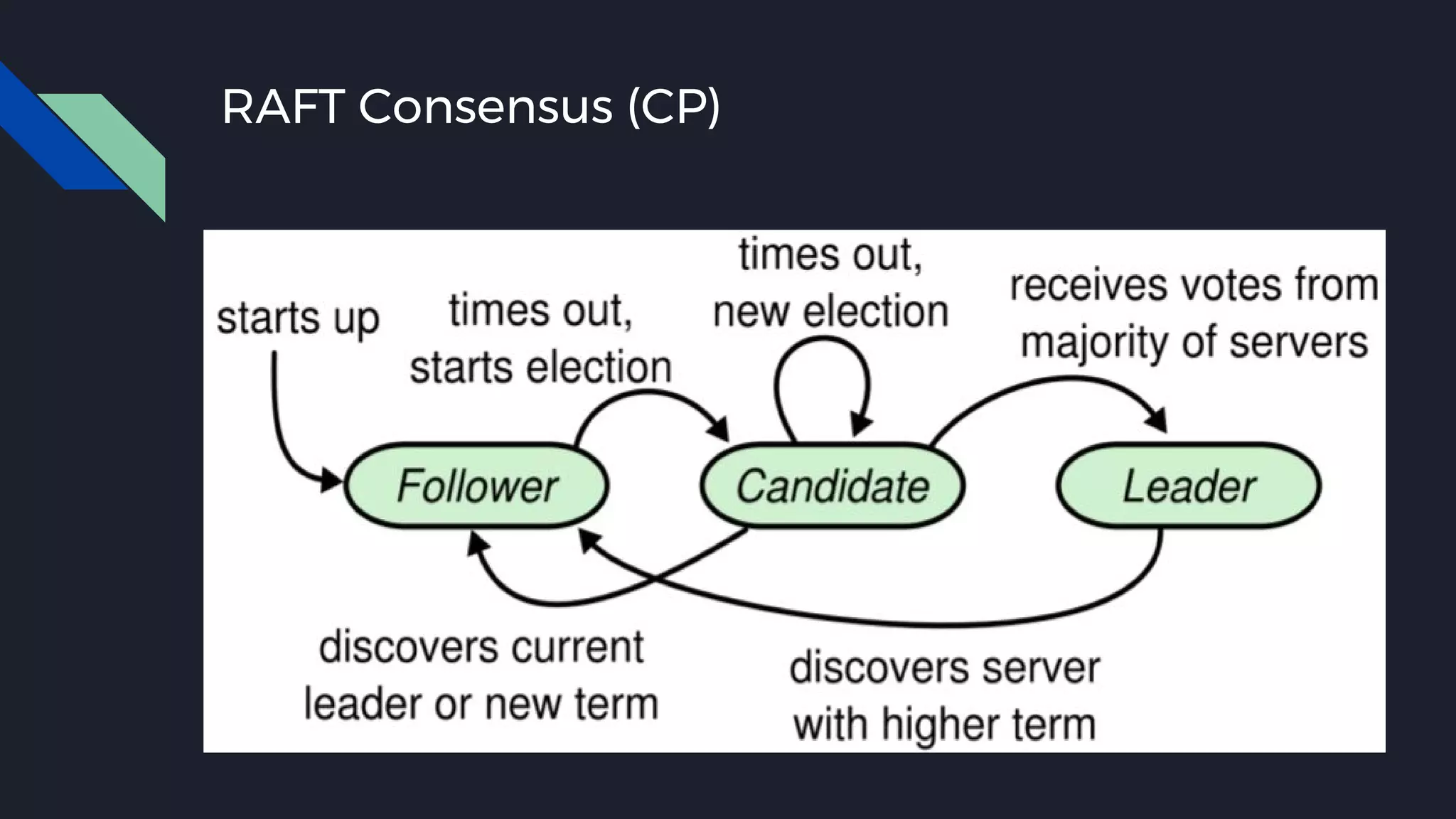
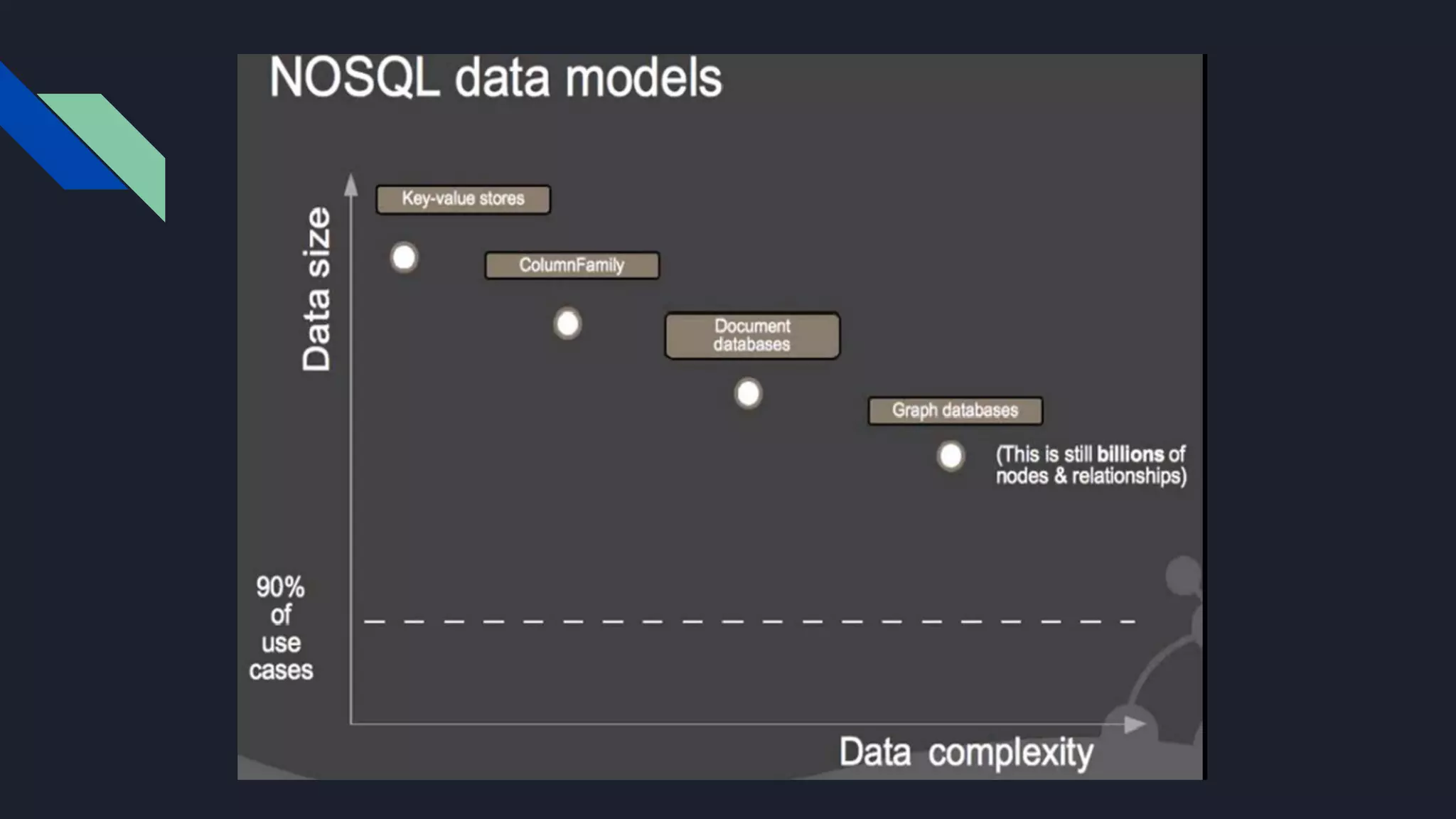
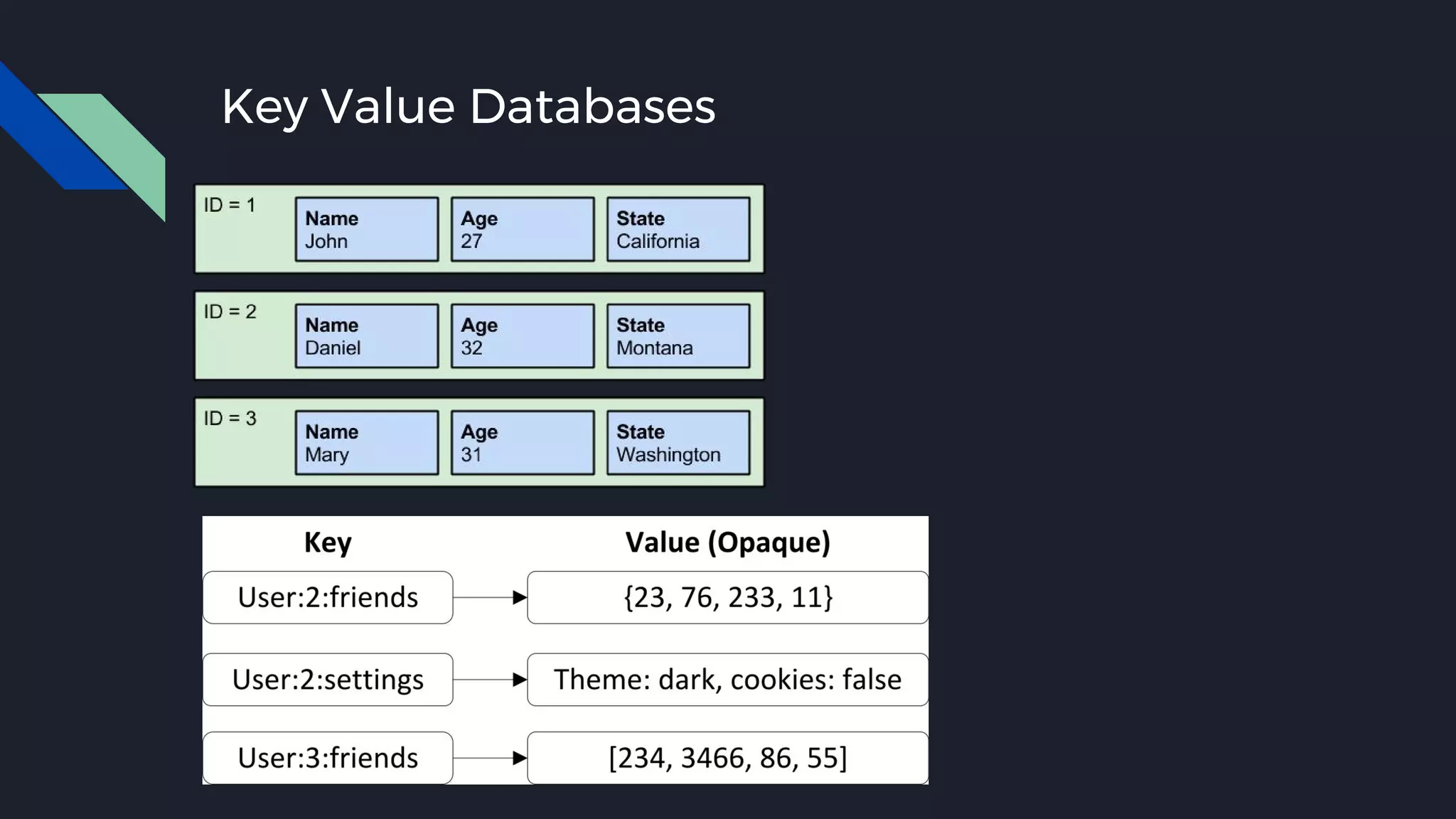
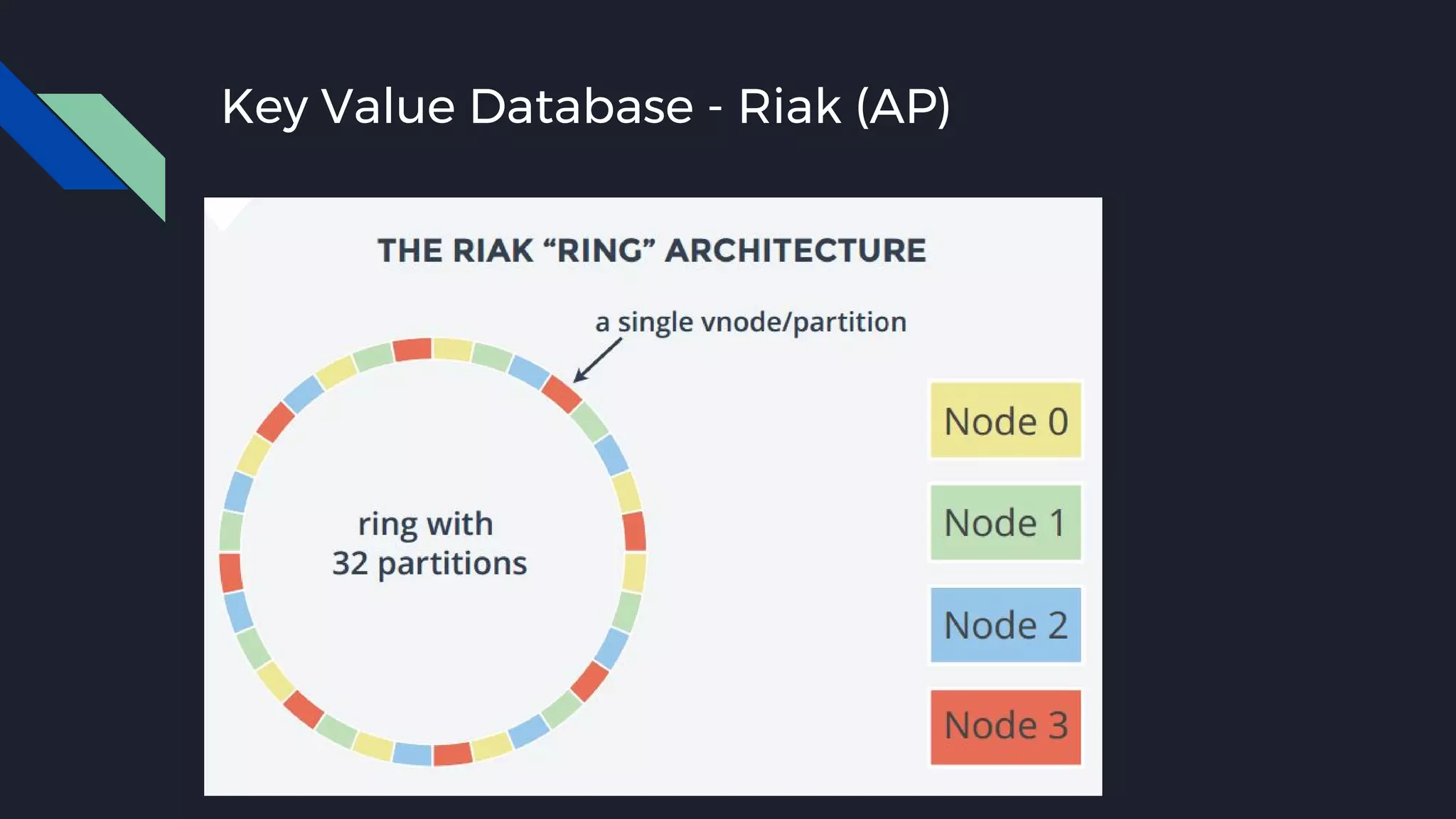
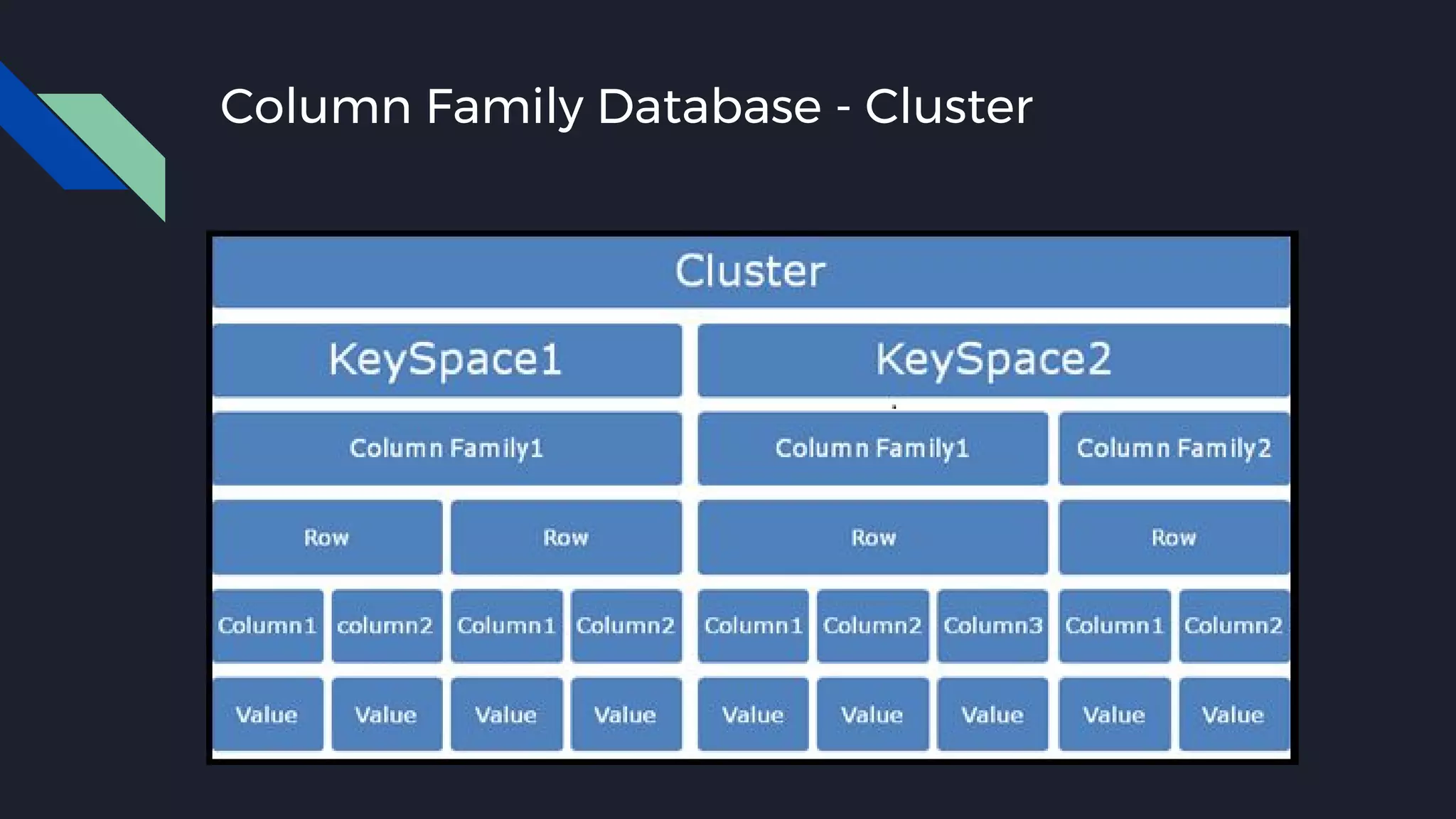
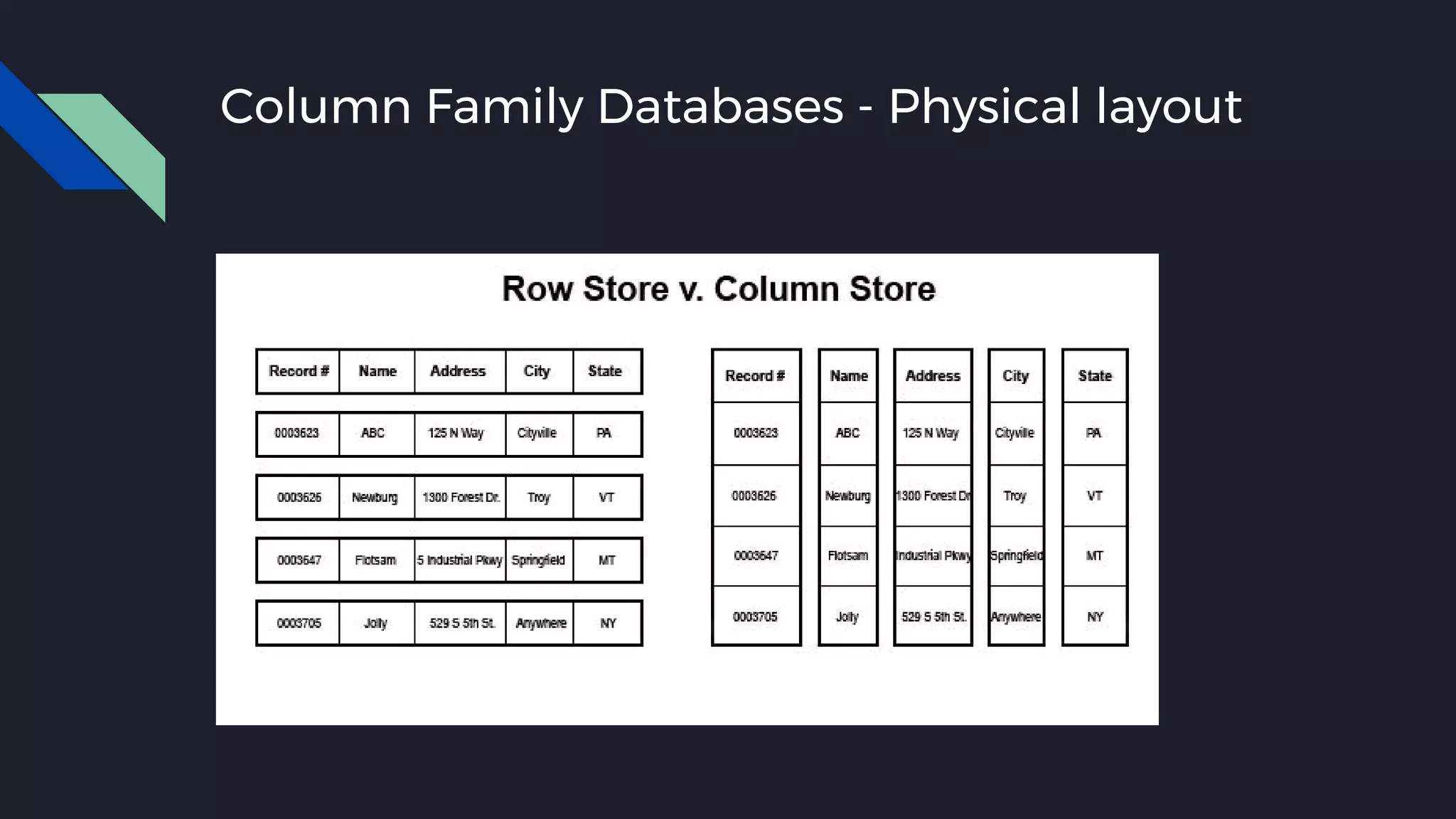
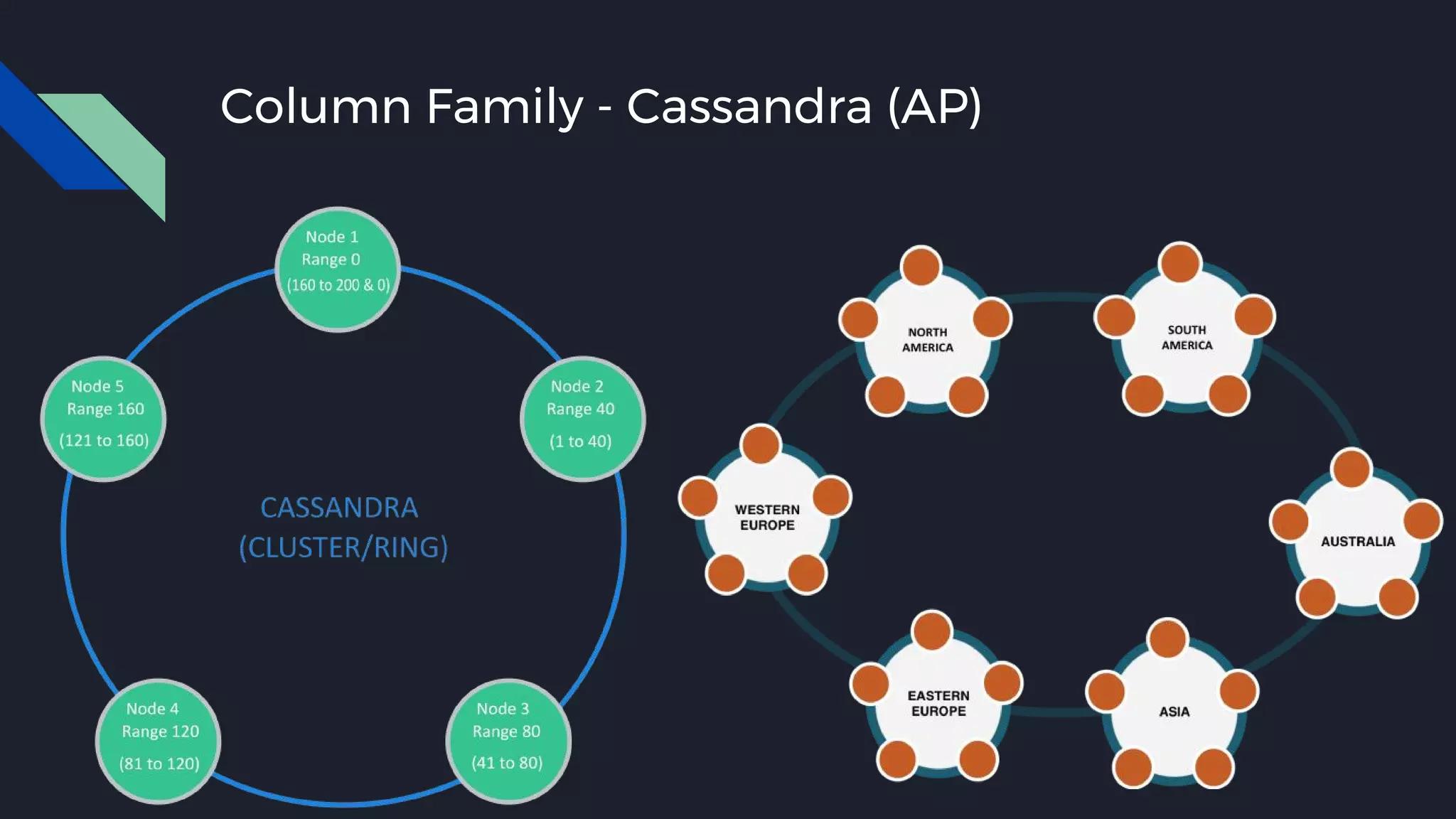
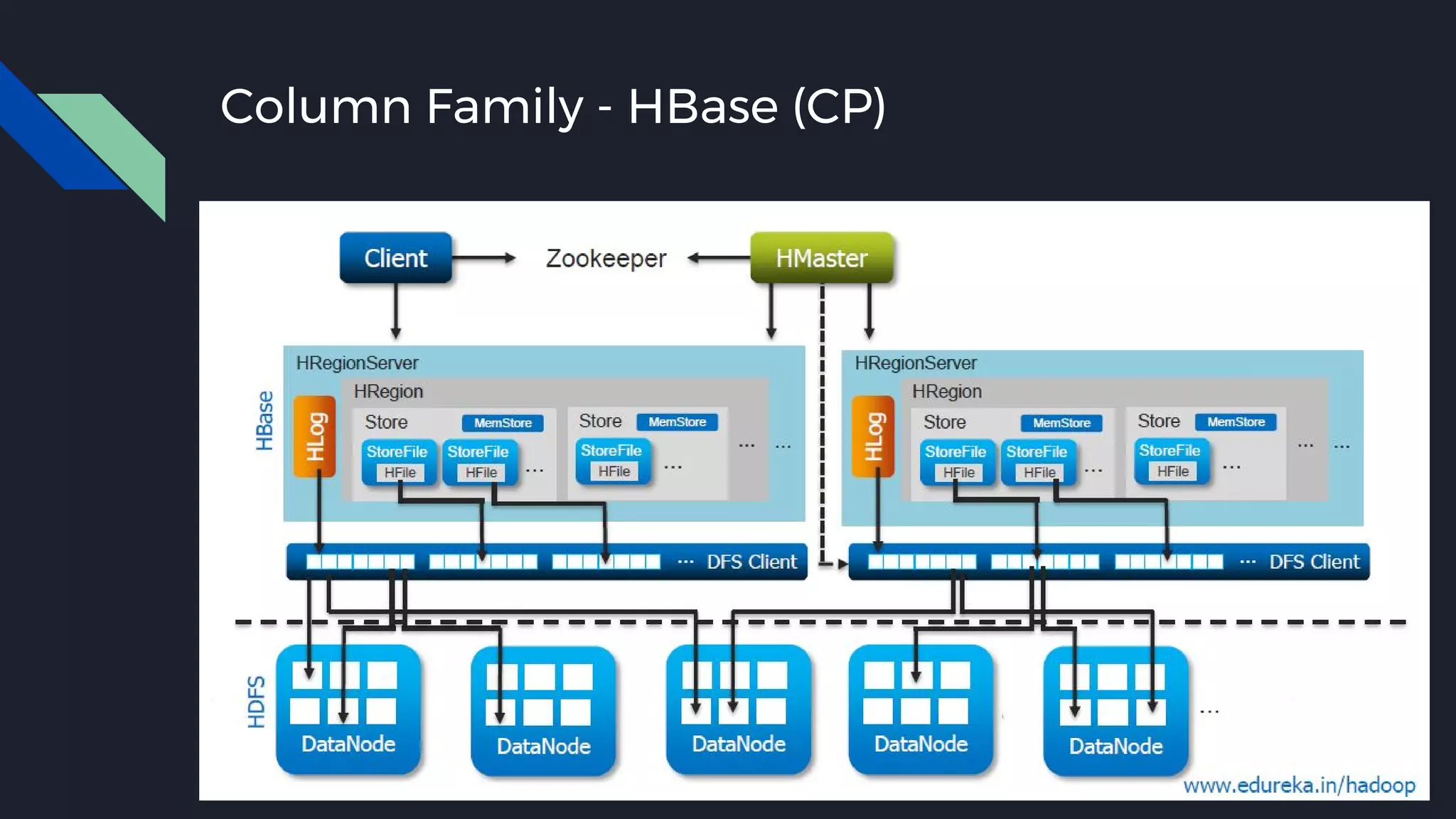
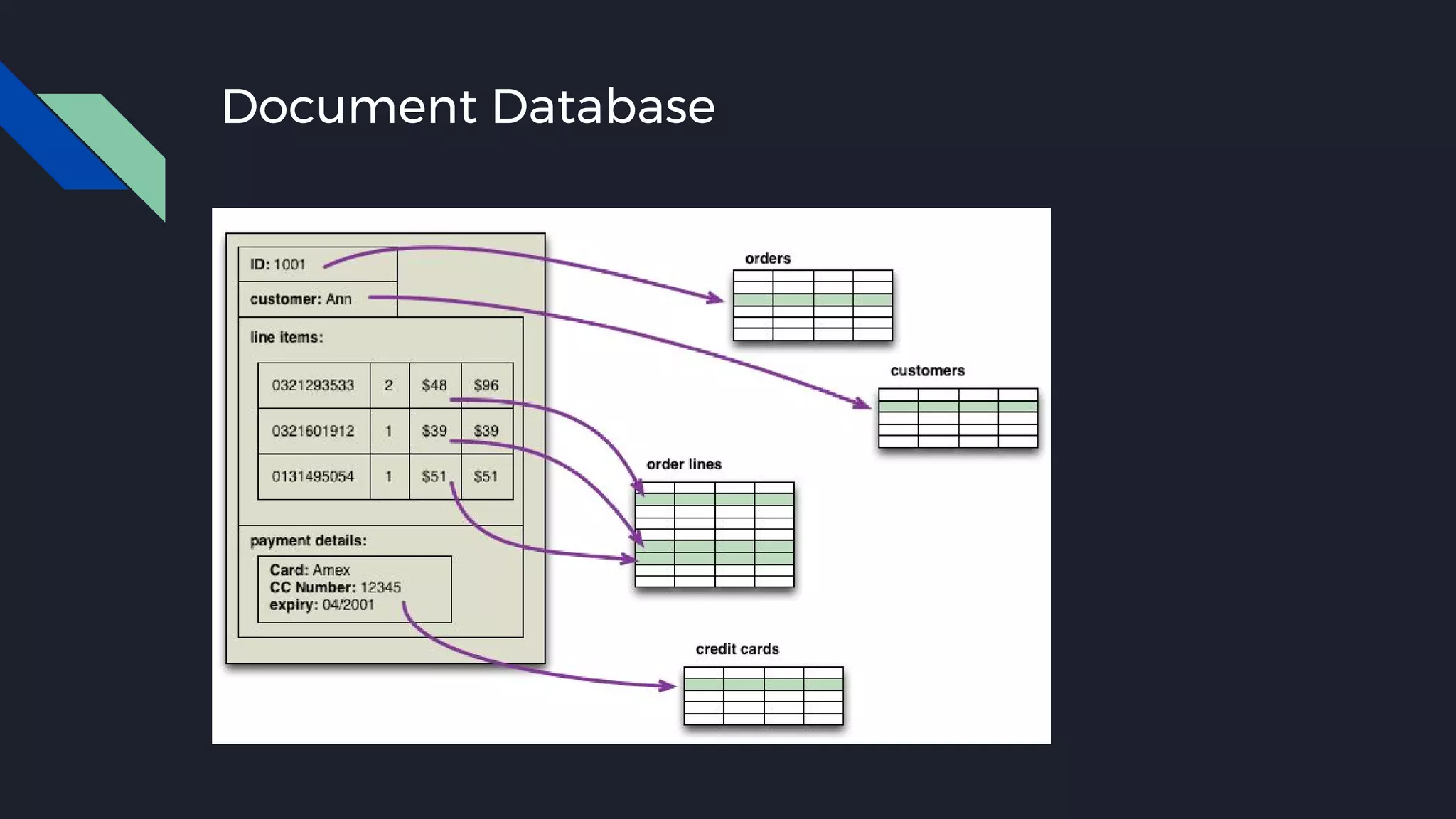
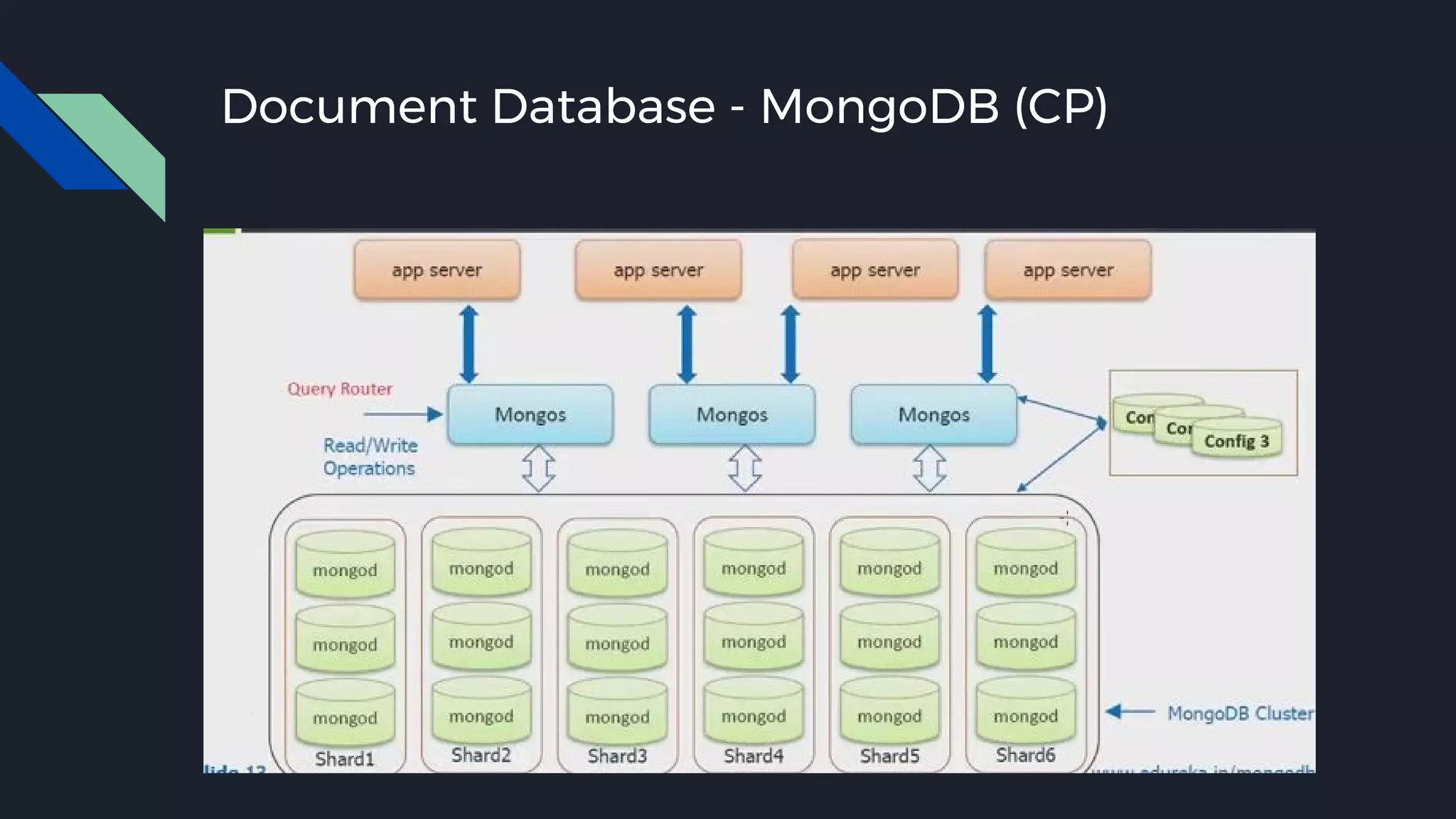
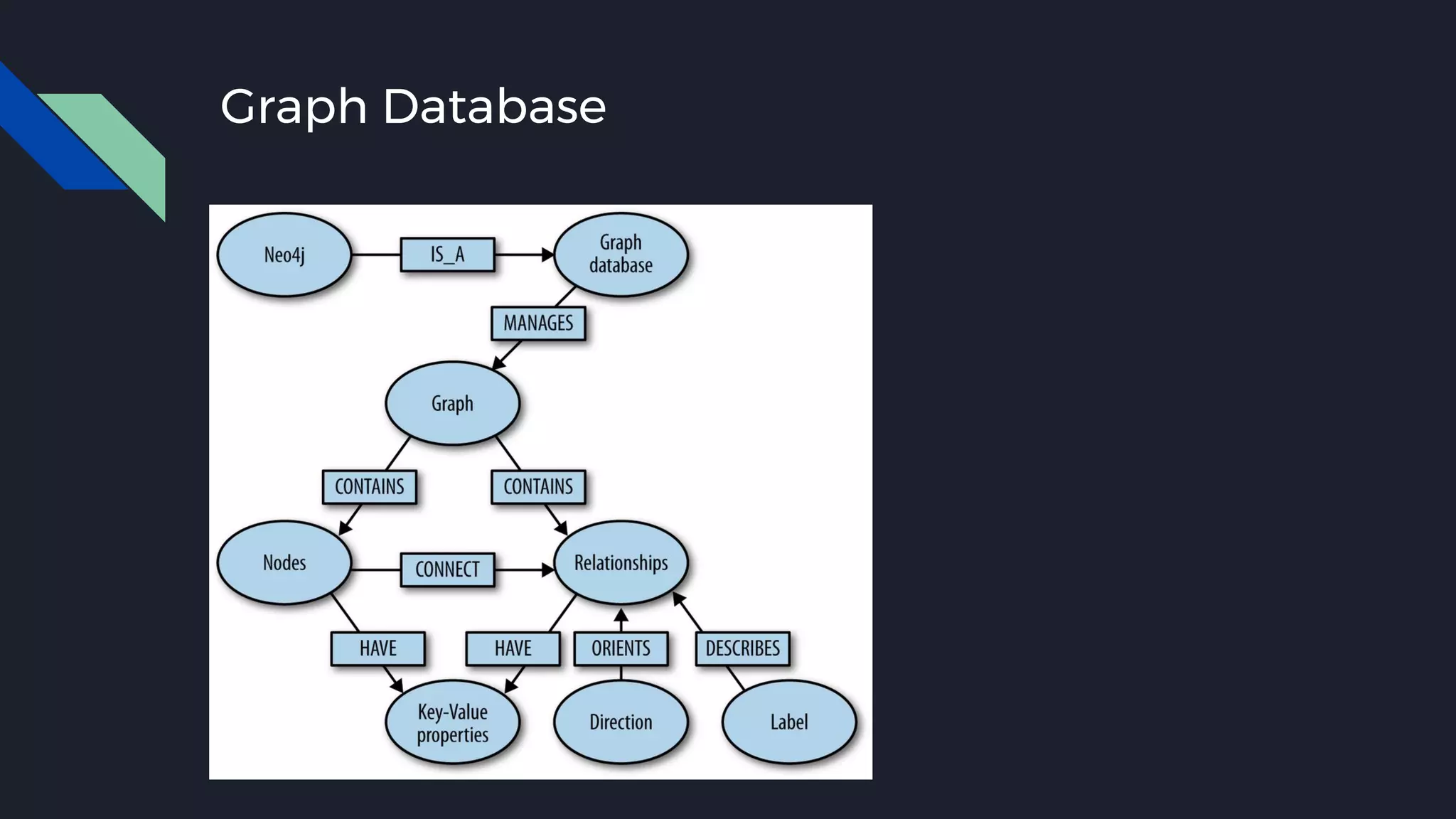
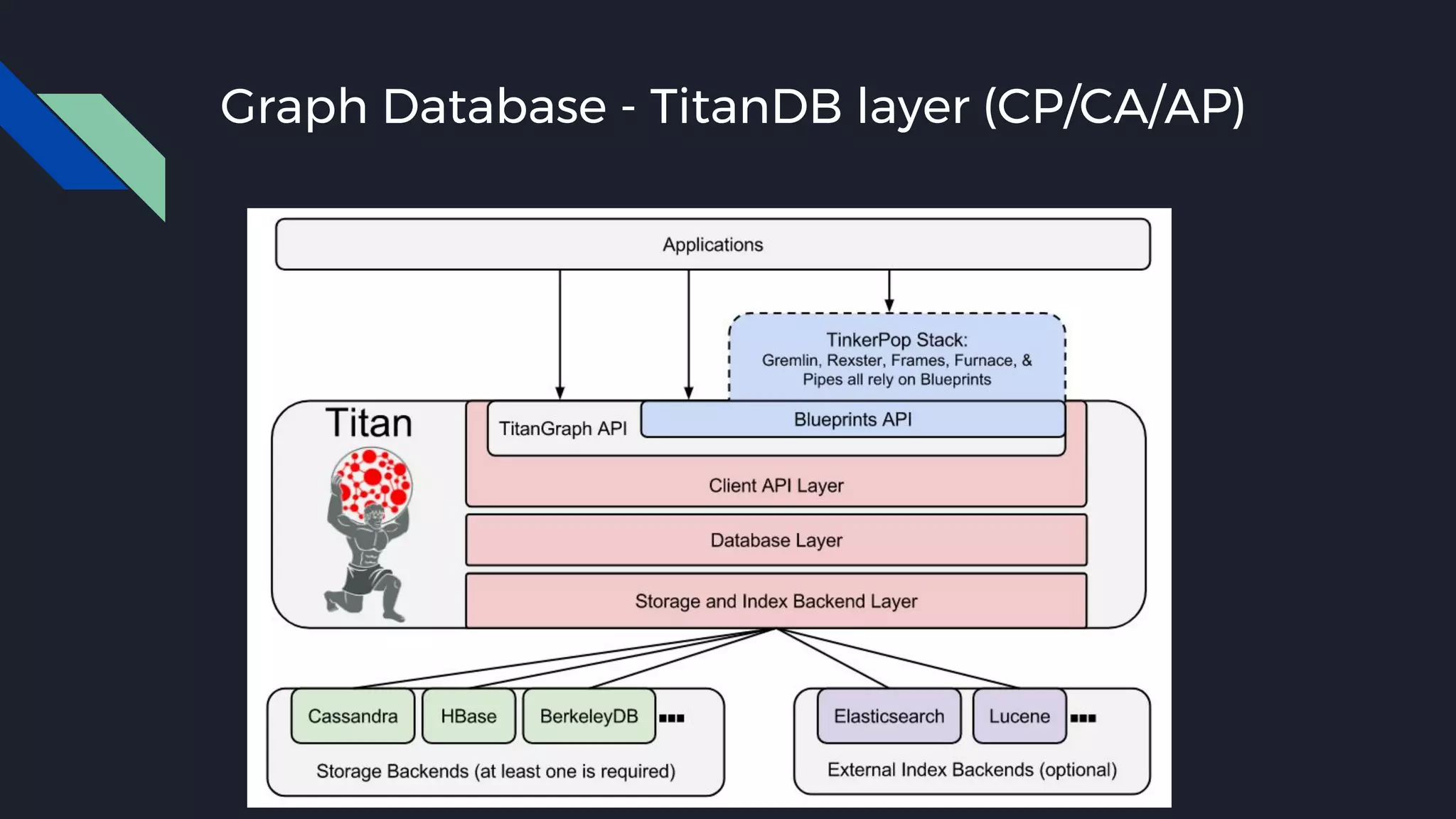
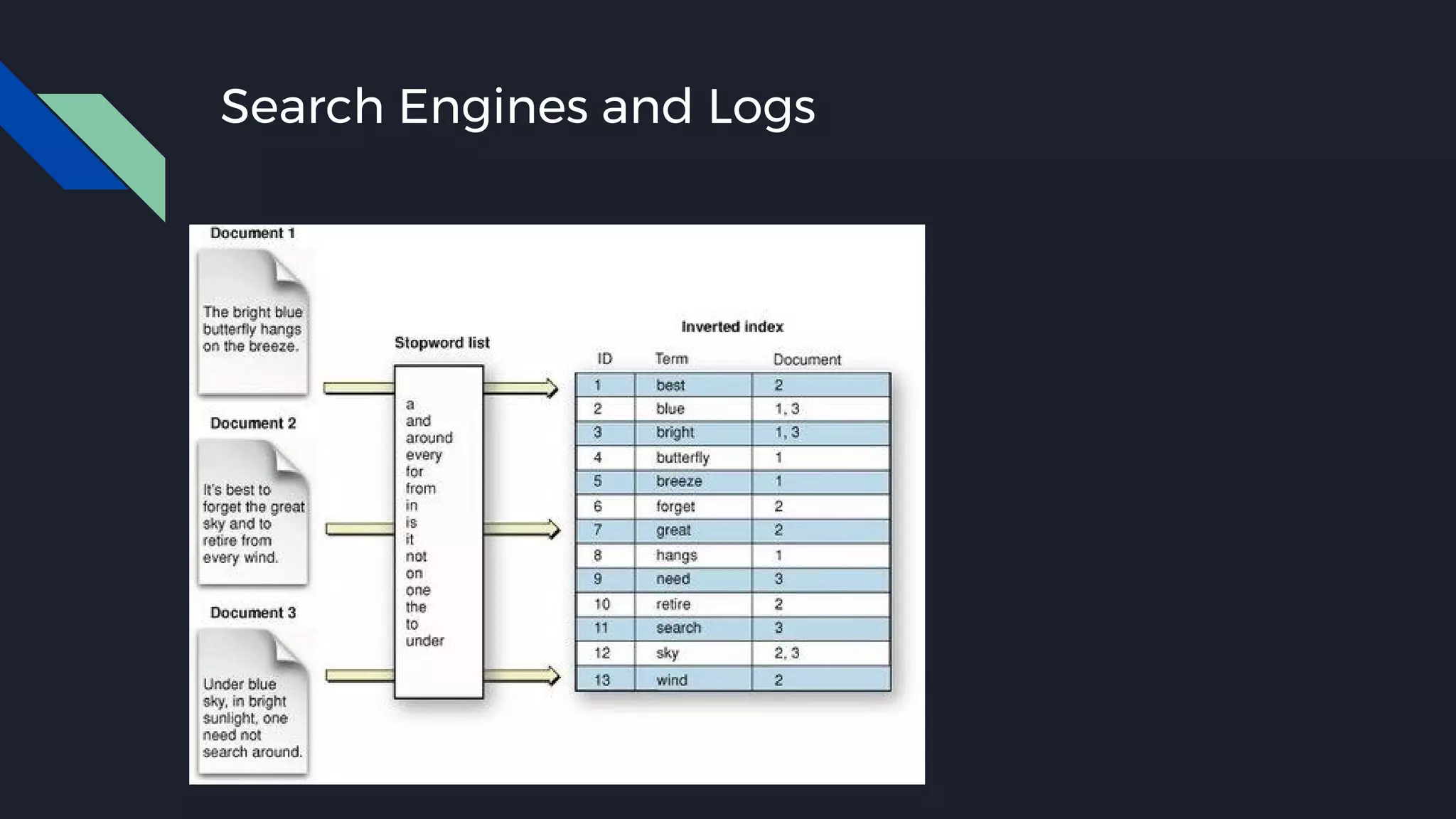
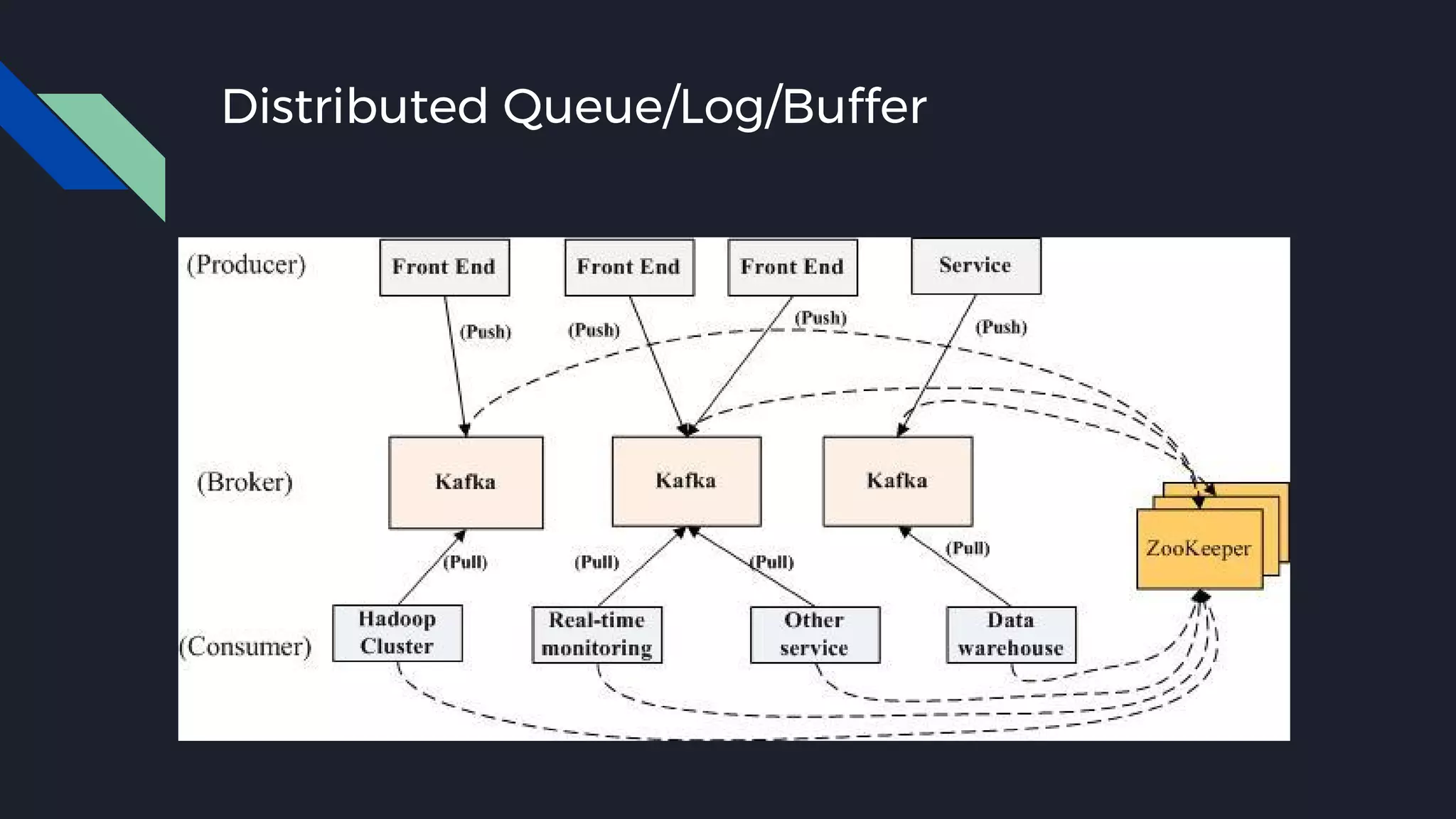
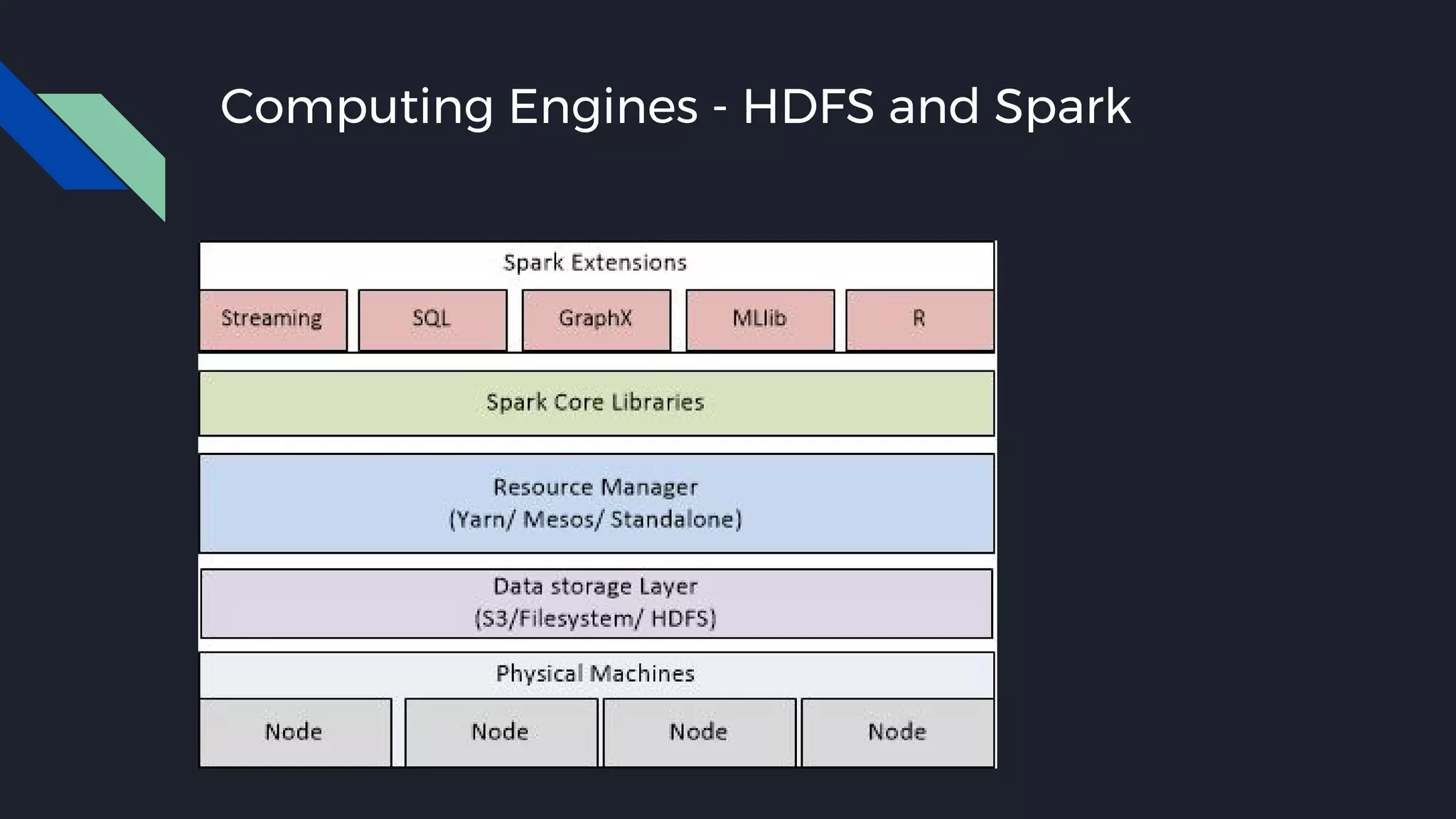
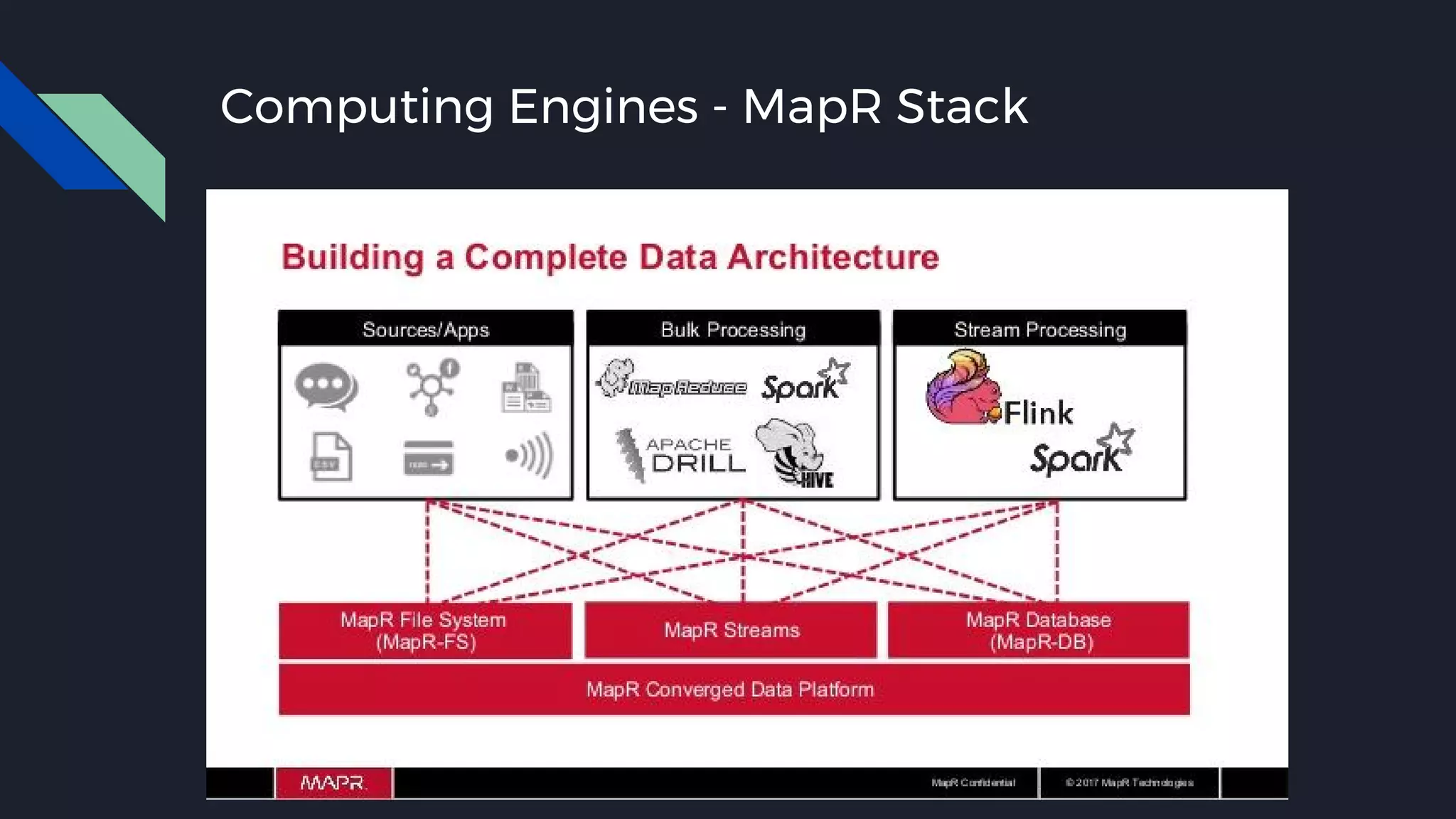
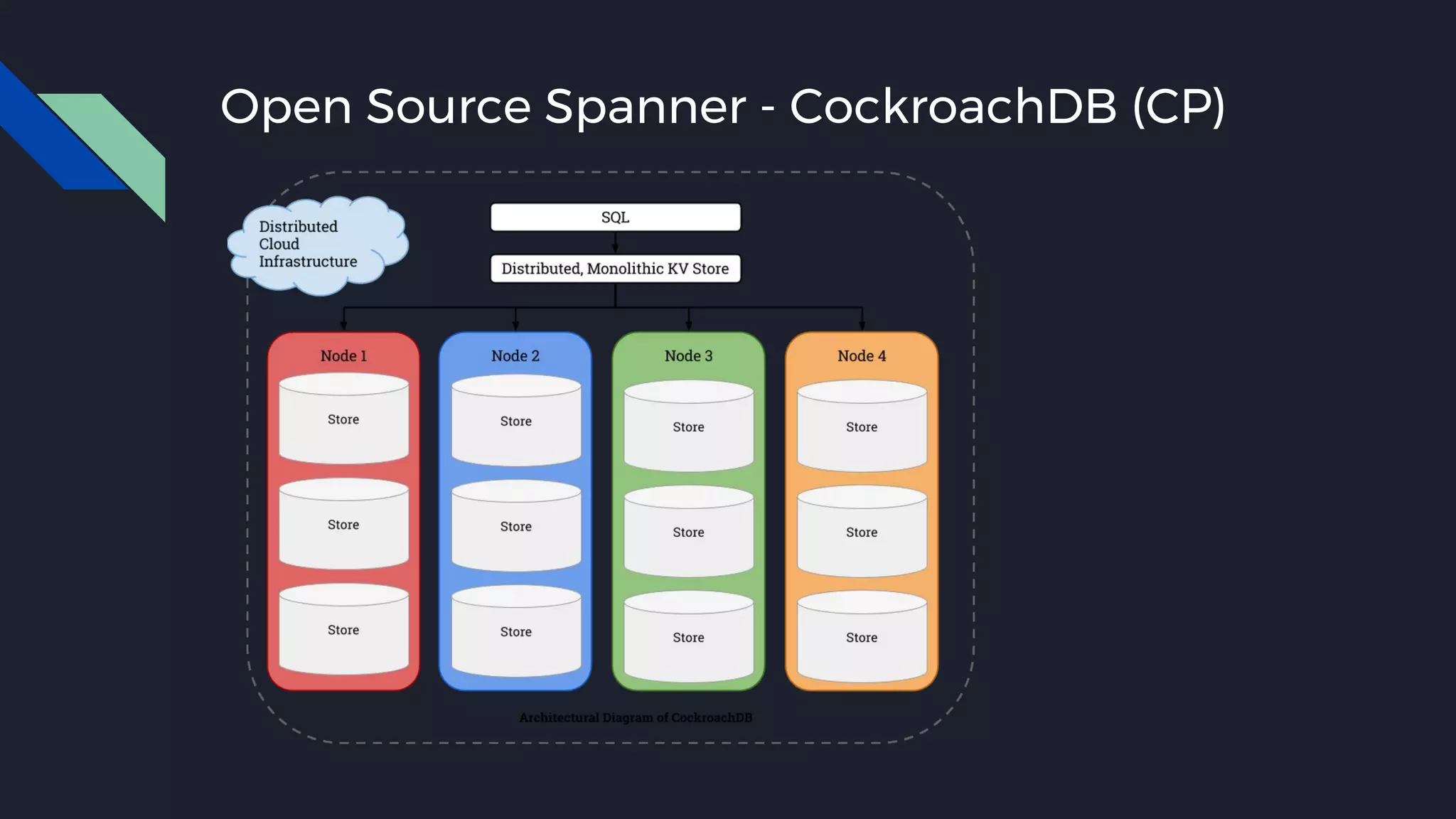
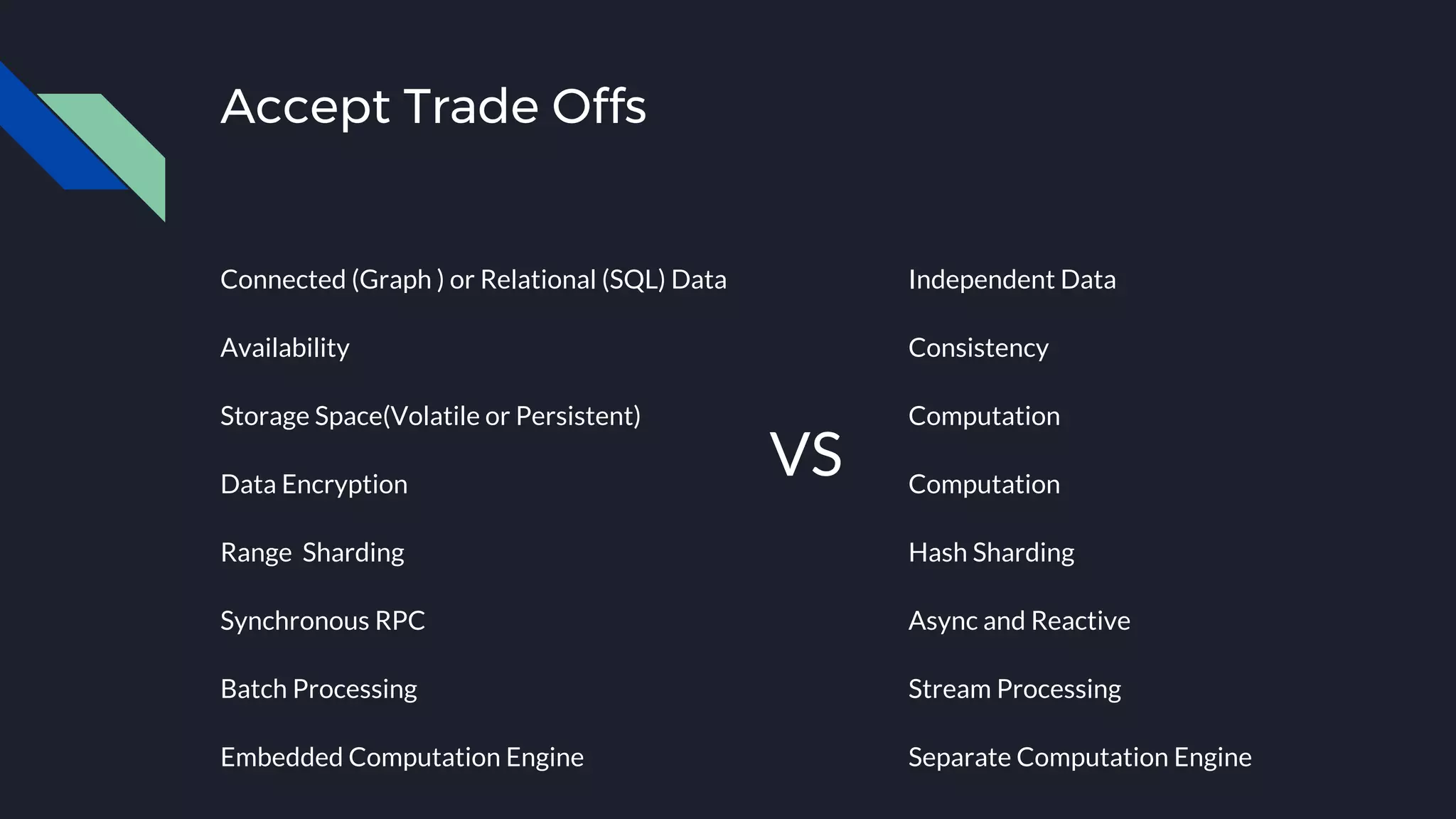
This document discusses strategies for handling large amounts of data as it grows over time. It begins with optimizing a small database on a single node through techniques like indexing and SSD storage. As the data grows larger, it recommends scaling vertically through techniques like replication and partitioning. For very large datasets, it recommends horizontal scaling using distributed systems like HDFS, MapReduce, BigTable and NoSQL databases. It analyzes properties of different database types and recommends systems like MongoDB, CockroachDB, ScyllaDB, Druid and graph databases based on factors like workload and data properties. Scaling choices involve tradeoffs between consistency, availability, computation and costs.