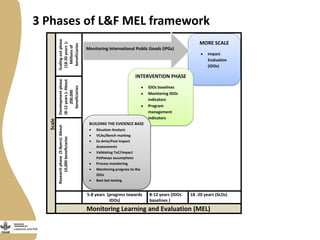
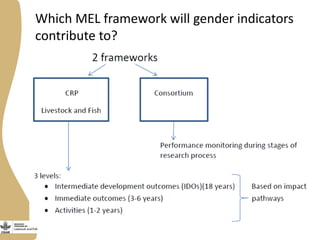
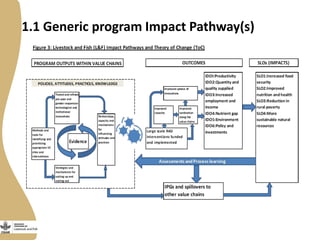
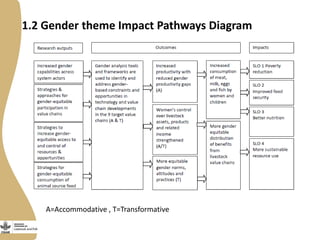
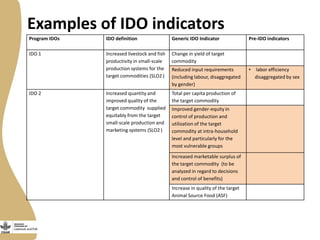
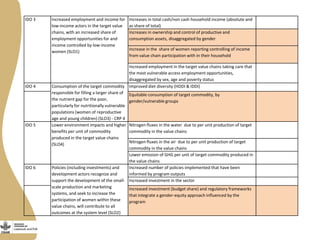
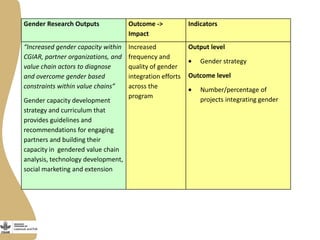
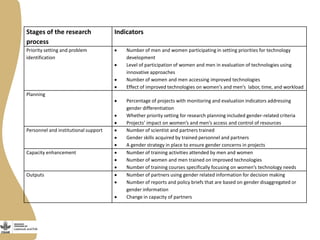
The document discusses the development of gendered monitoring, evaluation, and learning (MEL) indicators for the livestock and fish research program. It outlines the program's objectives to improve productivity in small-scale systems while incorporating gender considerations into MEL frameworks. Key questions and examples of indicators are presented to ensure that gender equity is achieved alongside program goals.