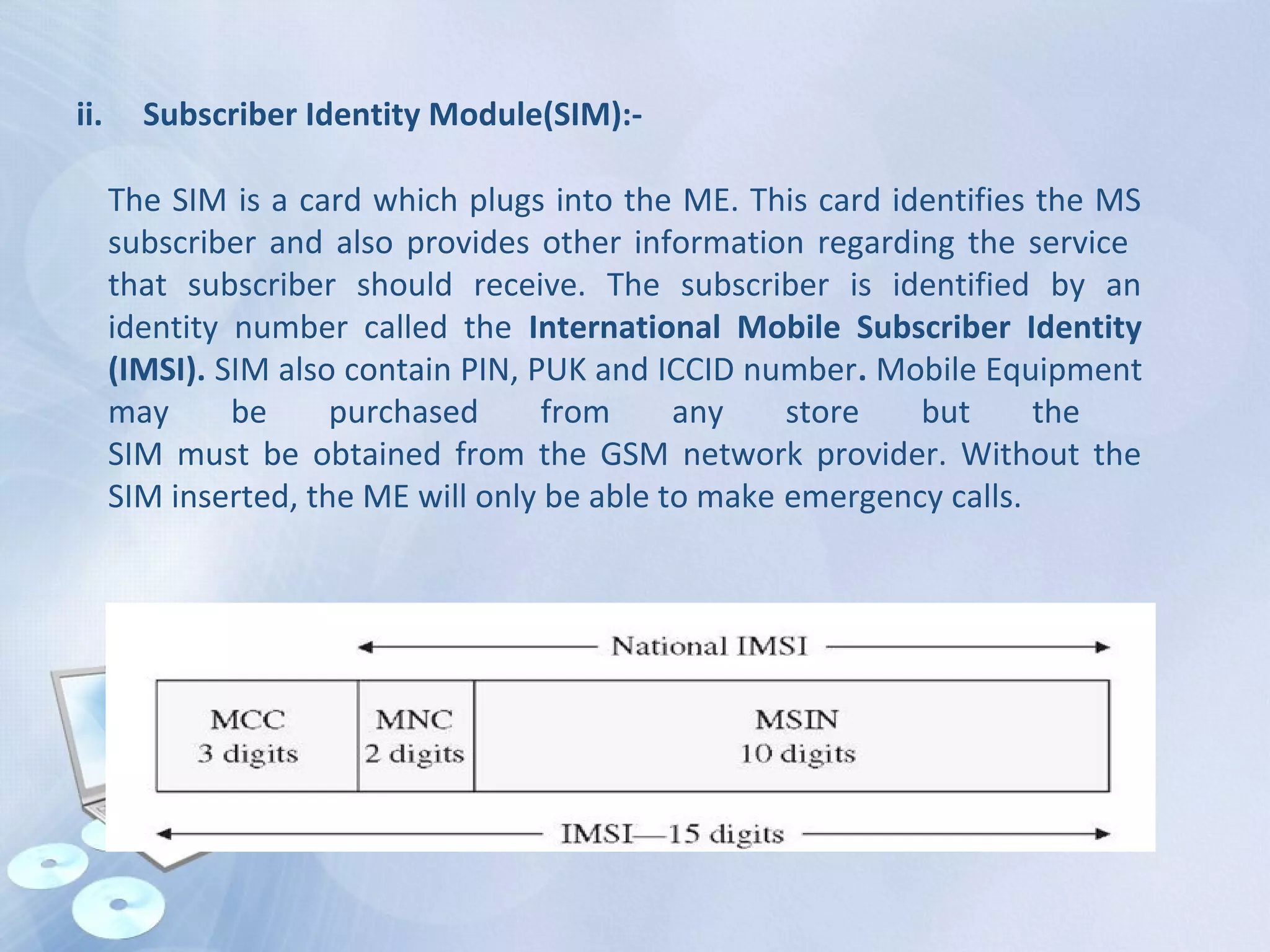
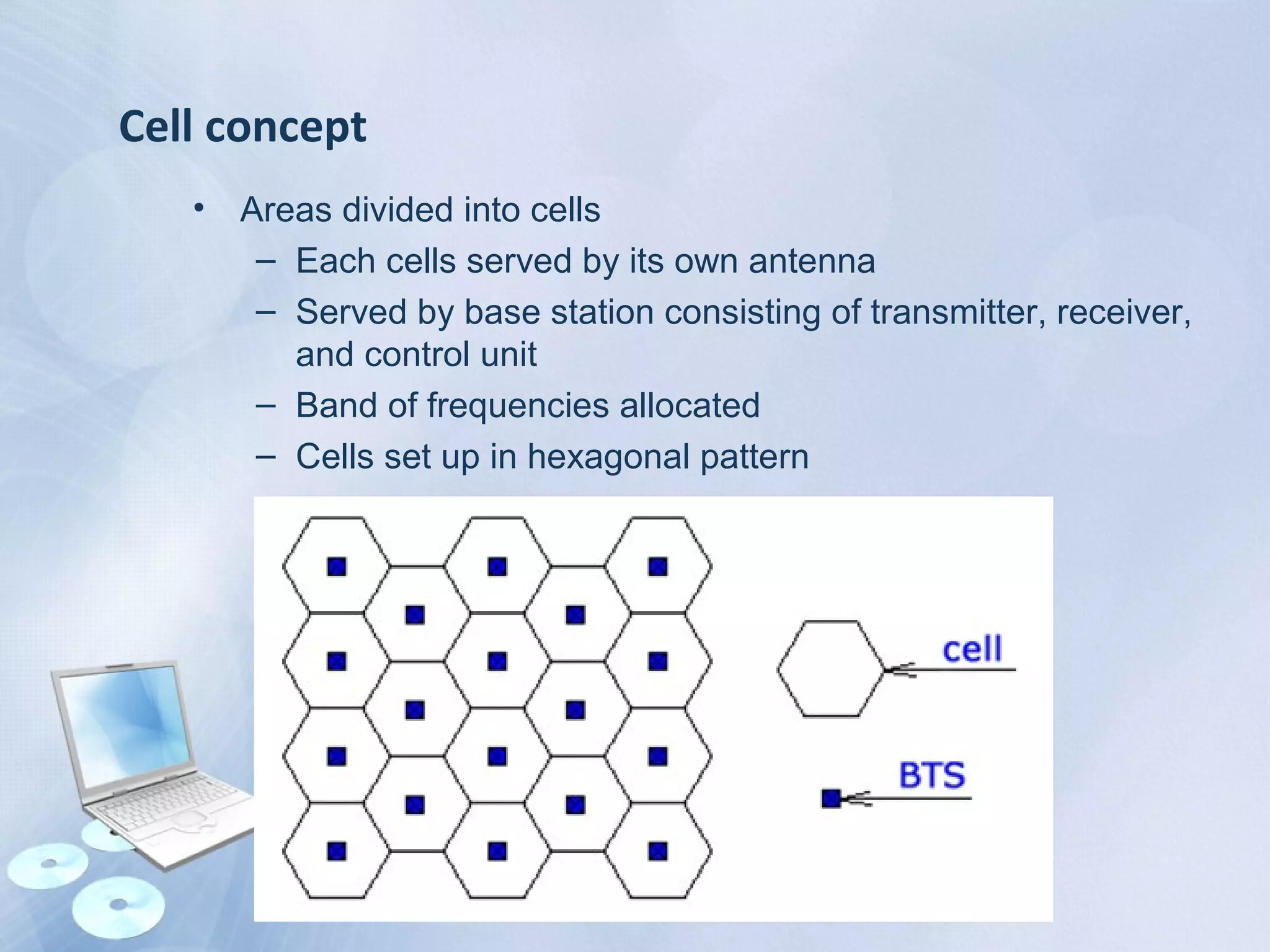
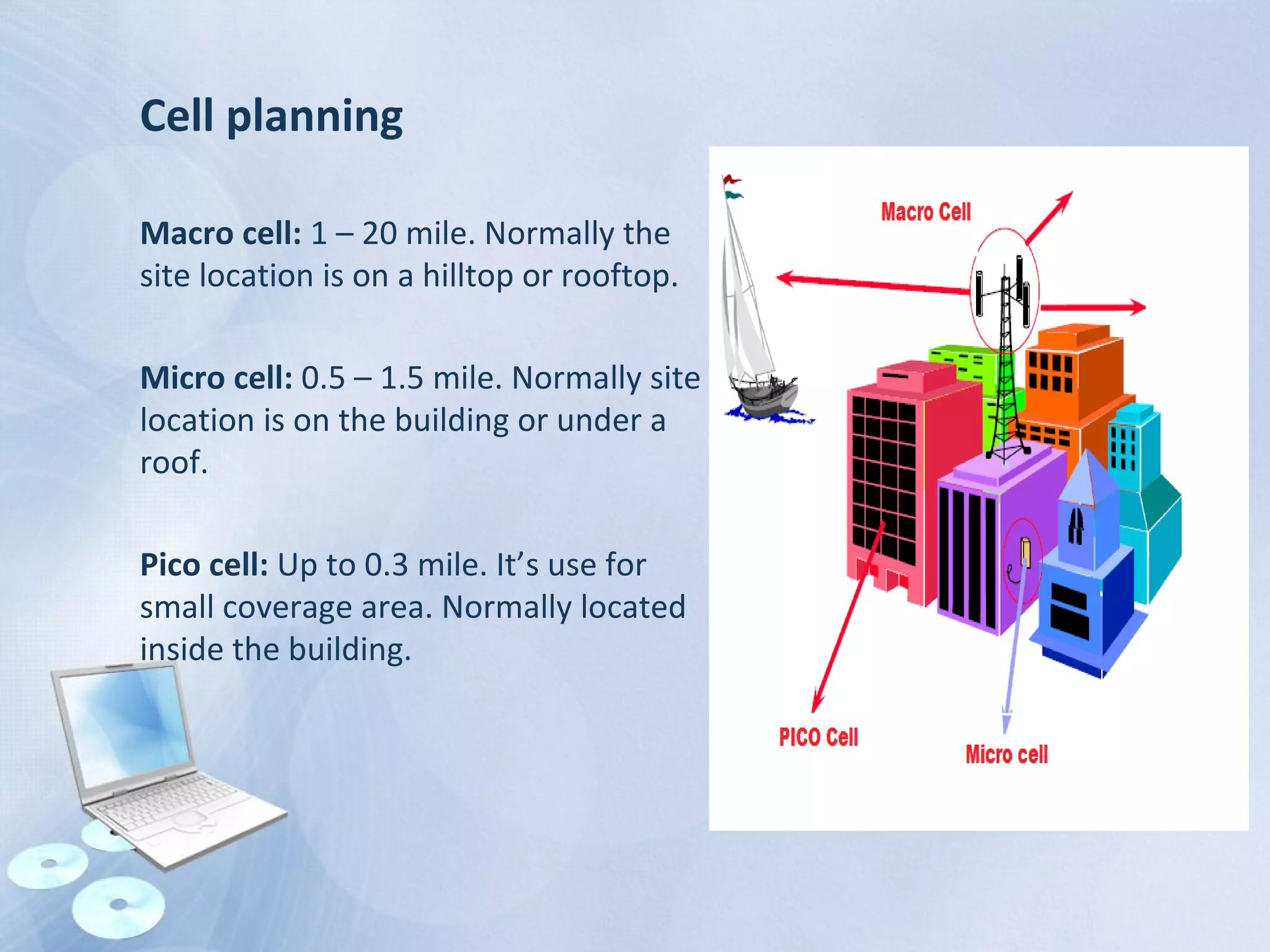
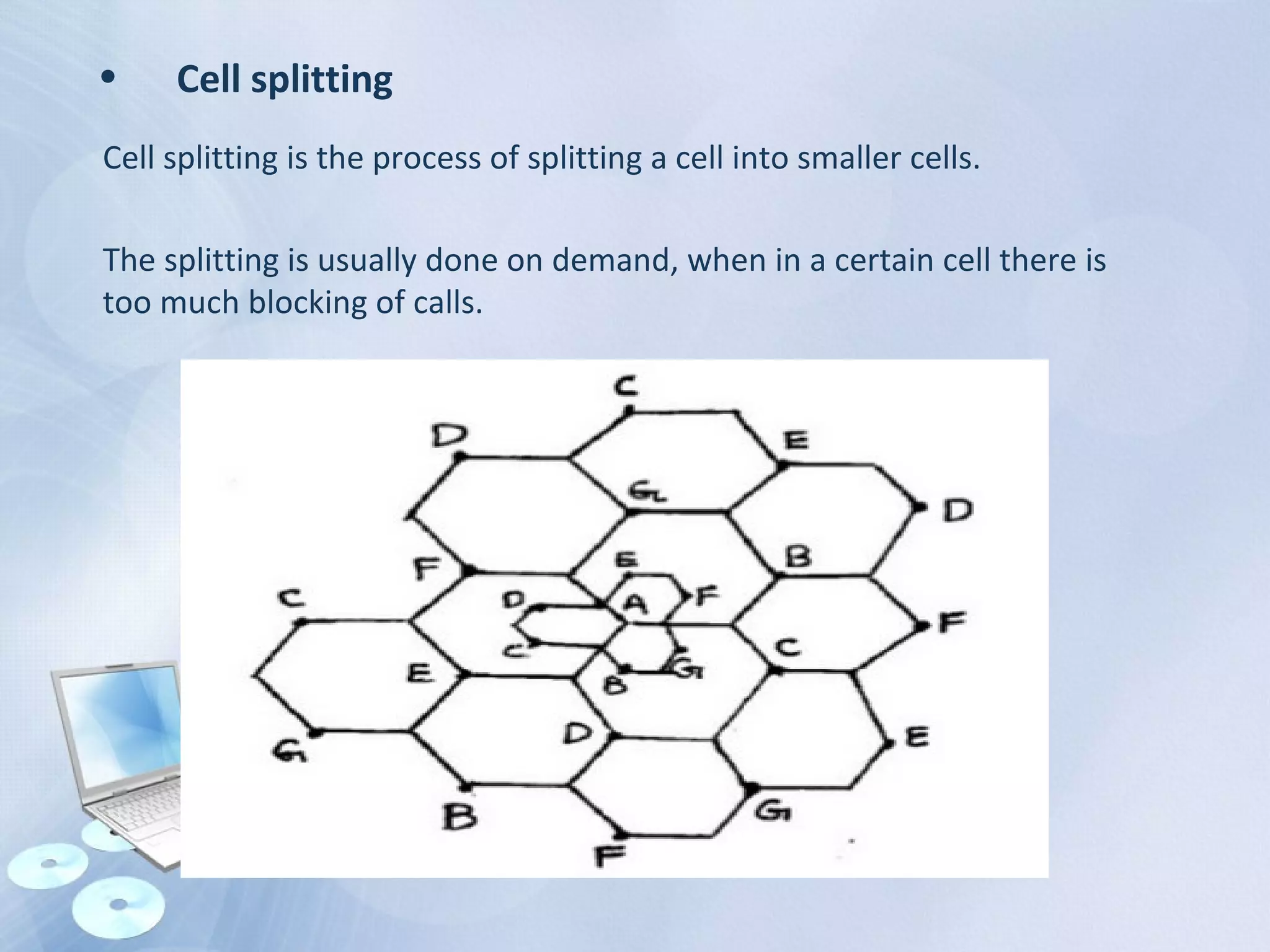
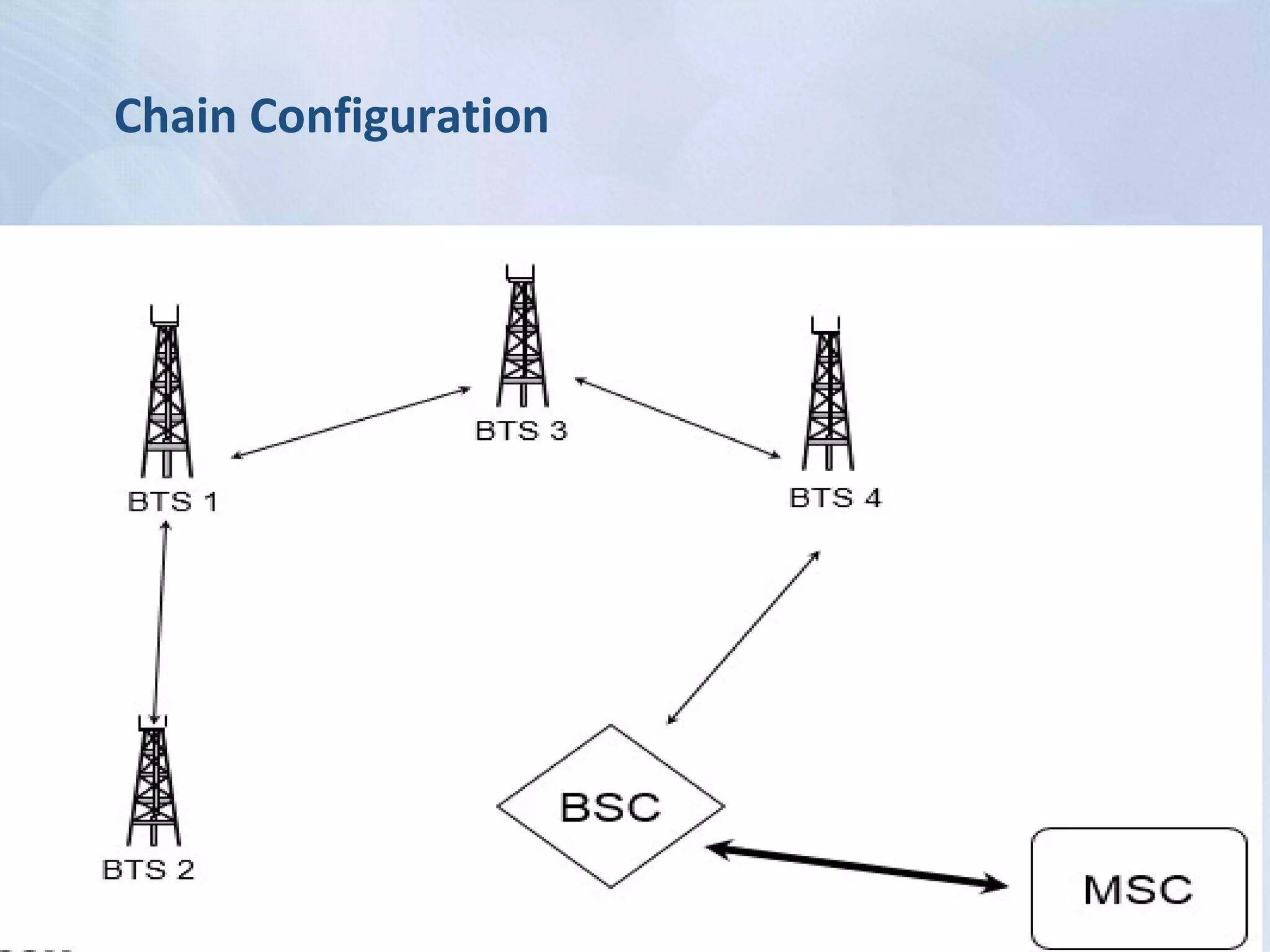
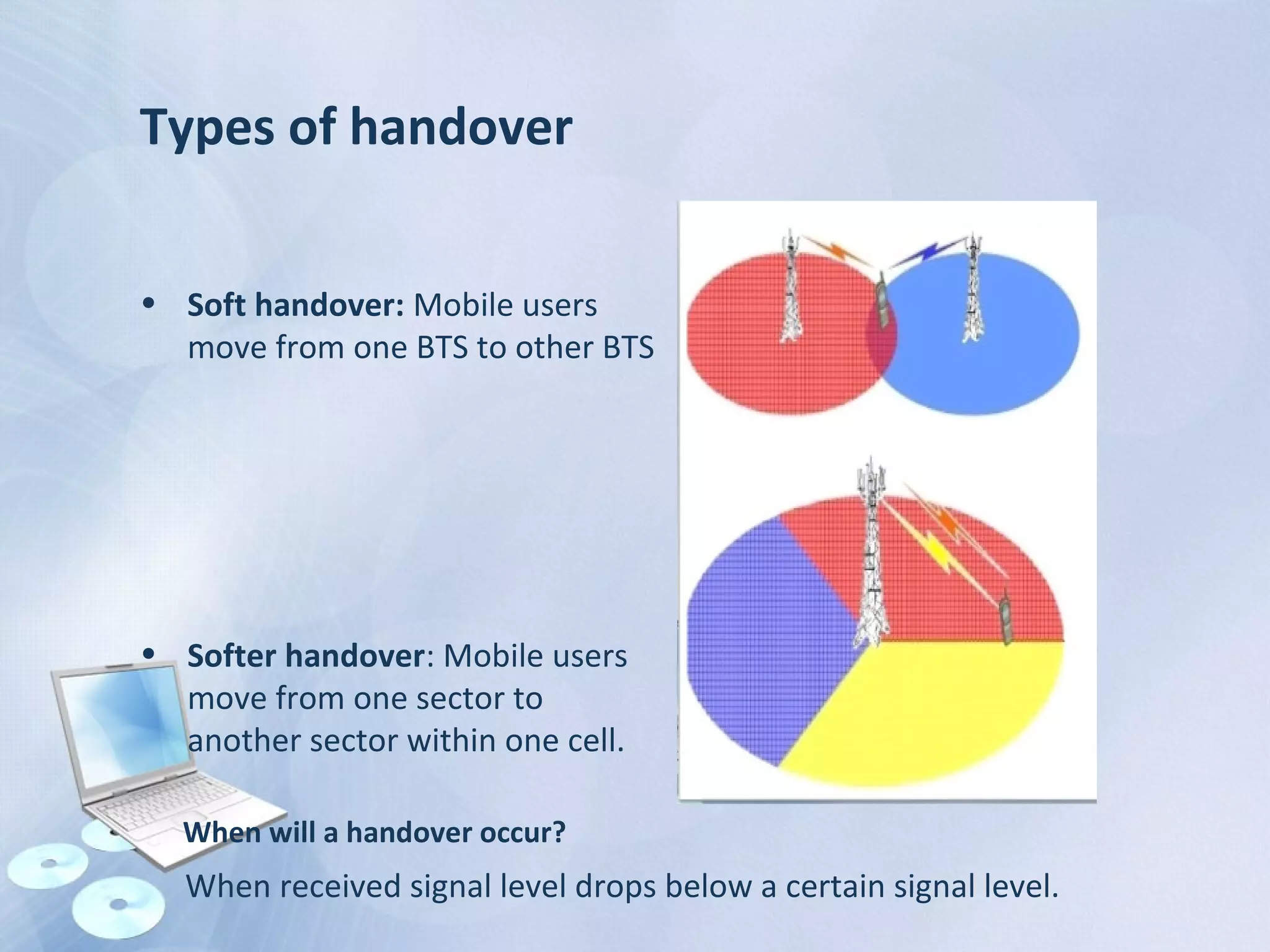
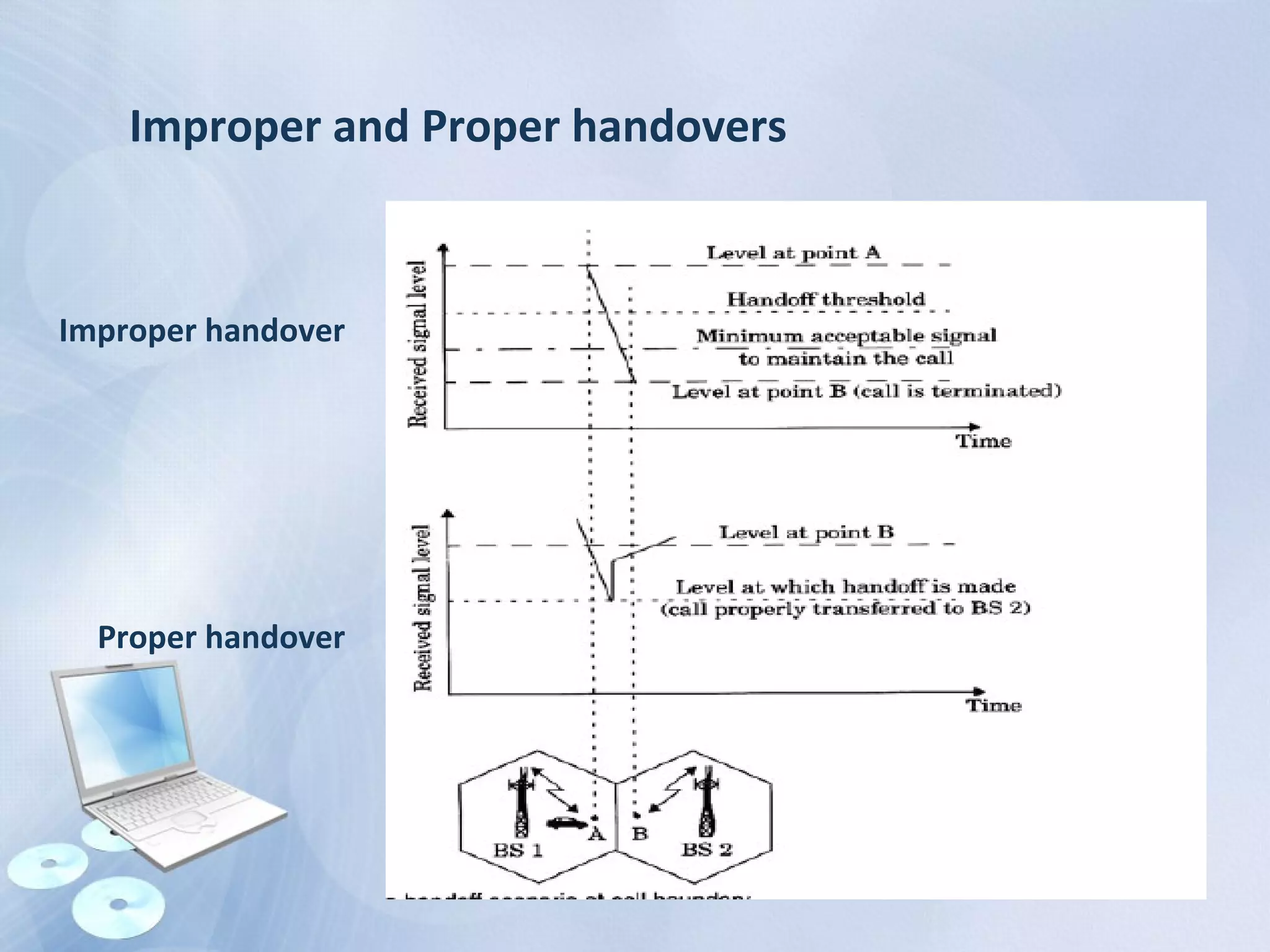
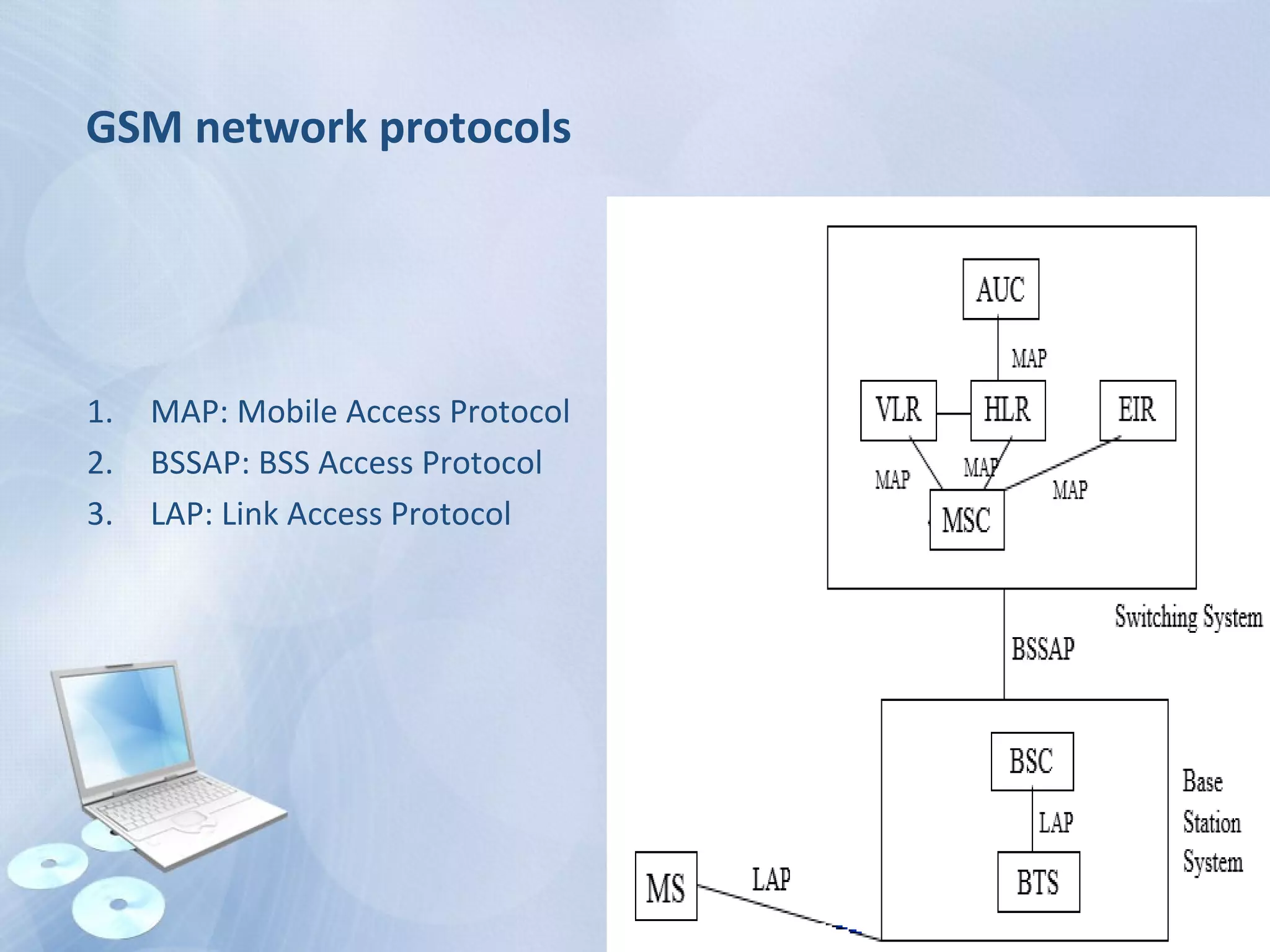
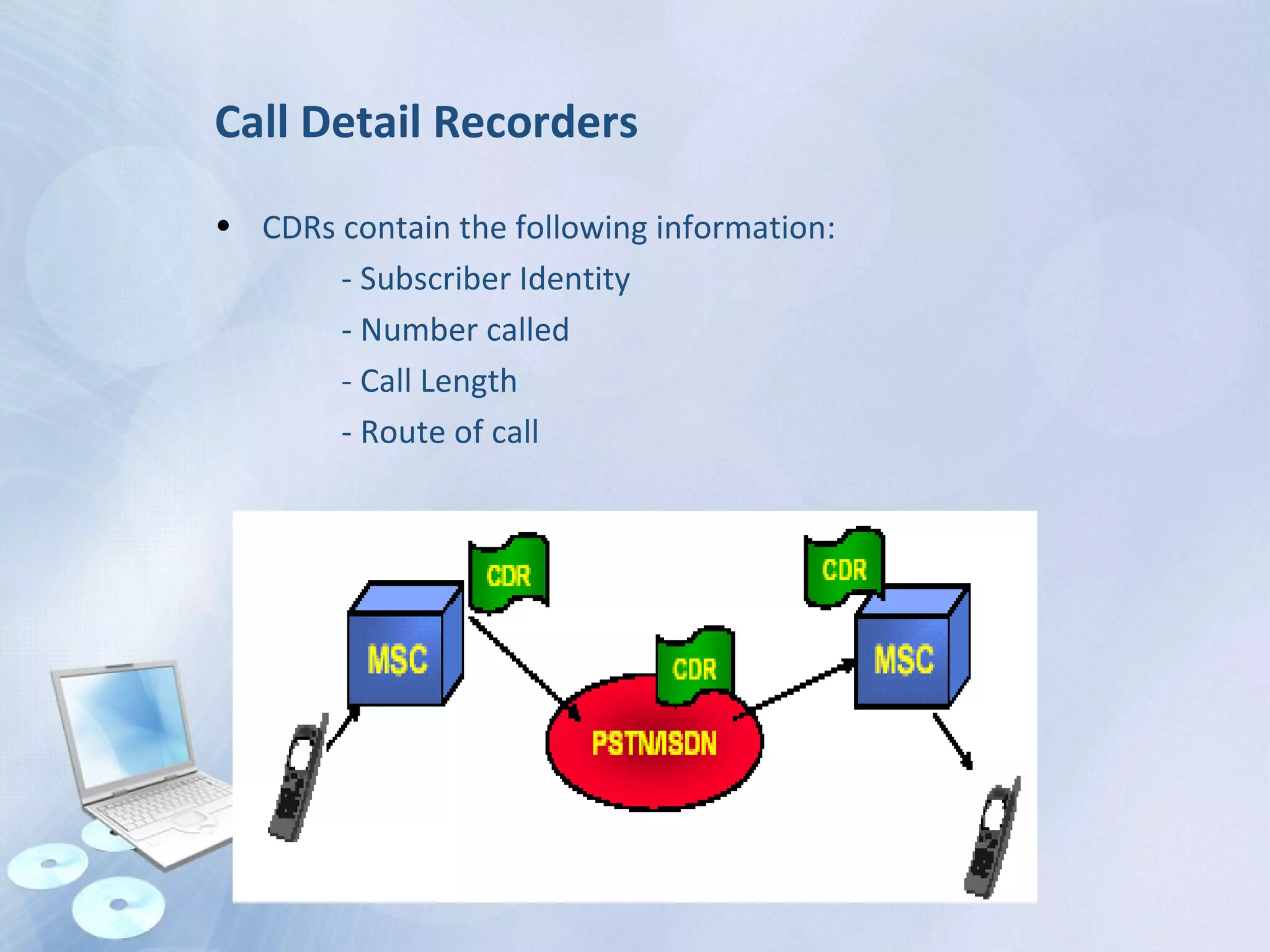
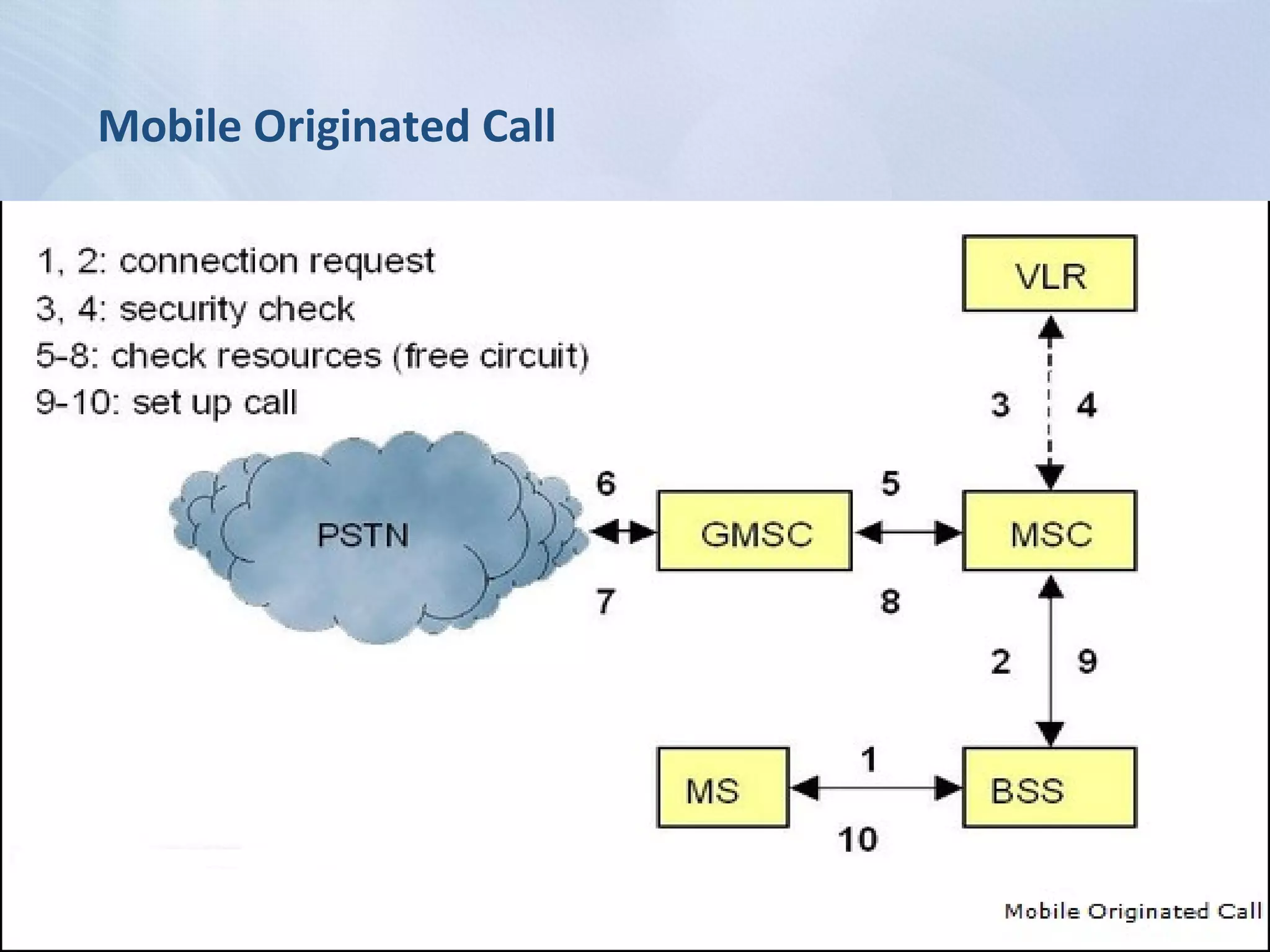
The document provides an overview of the Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), detailing its architecture, which includes the Mobile Station Subsystem, Base Station Subsystem, and Network Switching Subsystem, along with their components and functions. It describes the GSM specifications, such as frequency bands, as well as key elements like the Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI), Subscriber Identity Module (SIM), handovers, and databases like the Home Location Register (HLR) and Visitor Location Register (VLR). The document also touches on GSM network protocols and the operation of the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN).