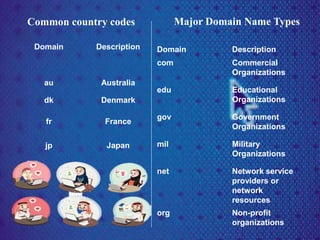
The document discusses the history and development of the Internet. It describes how ARPANET, developed by the US Department of Defense, connected various research institutions and eventually evolved into today's Internet. It also explains some key Internet technologies like TCP/IP protocols, URLs, HTML, and popular applications such as the World Wide Web, email, file transfers, chat, and e-commerce. Issues like security threats, firewalls, and spam are also briefly mentioned.